* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Case study I: DNA copy number changes
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
SNP genotyping wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
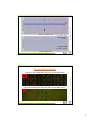
Array-CGH and SNP-analysis Helle Lybæk Introduction to Microarray technology September 2009 microarray.no DNA copy number changes Background • The underlying cause of the developmental delay remains unidentified in approx. 50% of these individuals microarray.no • Children and adults with mental retardation (IQ<70) represent a large group of the general population, approx. 1–3% • Chromosomal abnormalities are a known cause of mental retardation 1 Chromosomal analysis by G-banding microarray.no Chromosomal analysis by G-banding microarray.no 2 Chromosomal analysis by G-banding microarray.no Resolution: 5-10 Mb Chromosomal analysis by G-banding microarray.no ? Detection rate in MR-patients: 10-16%; The majority have normal findings 3 Background • Need of more knowledge about which chromosomal abnormalities -and disrupted genes- that cause developmental impairment microarray.no • Need of development -and application- of improved chromosomal screening methods for better detection of chromosomal abnormalities in MR-patients From chromosomes to arrays 2x microarray.no 2x NMC-produced array with BAC-DNA from 3500 clones; Resolution: ~1 Mb 4 Chromosomal analysis by array-CGH Patient DNA Normal DNA Cot-1 DNA microarray.no Normal DNA-spots Duplication Normal Deletion 1 Mb array-CGH analysis microarray.no 5 1 Mb array-CGH analysis microarray.no 1 Mb array-CGH analysis del: 41,2Mb – 45,3Mb microarray.no del(3)(p21.3p22.1) The MR-patient had normal findings on G-banding 6 dup(7)(q35q36.1) microarray.no dup: 144Mb – 152Mb del(7)(q36.2qter) del: 154Mb – 158,5Mb Array-CGH analysis 1 Mb array-CGH (NMC BAC-array with 18.000 DNA spots) microarray.no 6 Kb array-CGH (Agilent oligo-array with 244.000 DNA spots) 7 Array-CGH analysis -4 -2 -1 0 +1 +2 +4 6 Kb oligo array-CGH microarray.no -0.6 -0.4 0.0 0.4 0.6 1 Mb BAC array-CGH Lybæk et al., Eur J Hum Genet 2009, 904-10 Genotype-phenotype mapping microarray.no Disease genes can be identified by overlapping phenotypes 8 Array-CGH mapping of MR-patients microarray.no Mapping of 96 MR-patients for improved genotype-phenotype information Lybæk et al., Eur J Hum Genet 2008, 1318-28 Array-CGH mapping of MR-patients microarray.no Detection rate: 27% in MR-patients with normal findings on G-banding Lybæk et al., Eur J Hum Genet 2008, 1318-28 9 SNP-based DNA copy number analysis • Normal occurring single base variants • More than 6 millions SNP´s in the human genome • Approx 1 SNP per 1.000 bp microarray.no SNP: Single Nucleotide Polymorphism • 90% of the genes are covered by at least one SNP SNP-based DNA copy number analysis • Resolution: ~1,4 kb microarray.no • 900.000 SNPs • 900.000 oligos Affymetrix SNP-array 6.0 Comparison of the DNA copy number of the detected SNPs and oligos in the patient sample versus in a control group (database) 10 SNP-based DNA copy number analysis microarray.no Detection of a 17,4 kb sized deletion; Easier to pinpoint candidate genes Result from the microarray-group at Center for Medical Genetics and Molecular Medicine, HUH Copy number variations (CNVs) Approx. 12% of the human genome consists of copy number variations microarray.no i.e. DNA-variants in the genome which are frequent occurring in the normal population and that does not (themselves) give rise to a phenotype/disease even though genes are localised in these areas! 11 SNP-based DNA copy number analysis microarray.no The higher analysis resolution the more detection of CNVs Result from the microarray-group at Center for Medical Genetics and Molecular Medicine, HUH DNA copy number analysis – New possibilities and challenges - Before the time-consuming challenge was to find the areas with chromosome- or gene abnormalities microarray.no The microarray-technology has given us new possibilities and new challenges: - Today the time-consuming challenge is to interpret the findings you surely will make! 12