* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 5 Lipid and Protein Metabolism
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
15-Hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid wikipedia , lookup
Specialized pro-resolving mediators wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Glyceroneogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
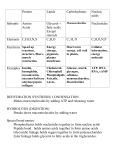
Physiology Unit1 METABOLISMOFLIPIDSANDPROTEINS InPhysiologyToday AlternateFuelSources • Whenglucoselevelsarelow • Storedproteinsandlipids willbemetabolized • Changesinprimaryfuel sourcesbetweenresting andexerciseandfasting conditions • Proteinmetabolismwill happenunderfastingor starvationconditions AminoAcids Essential Non-Essential 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 1. Alanine 2. Arginine 3. Asparagine 4. Asparticacid 5. Cysteine 6. Glutamicacid 7. Glutamine 8. Glycine 9. Proline 10. Selenocysteine 11. Serine 12. Tyrosine Histadine Isoleucine Leucine Lysine Methionine Phenylalanine Threonine Tryptophan Valine PeptideBondFormation DehydrationSynthesis Transamination • Makeanothertypeof aminoacidby transferringanamine (NH2) fromanexisting aminoacidtoaketo acid • Anaminegroupis transferedfromL-alanineto α-ketoglutaratetomake pyruvateandL-glutamate Amine group is BLUE AminoAcidsasFuel • Aminoacidscanbeclassifiedinto2groupsas afuelsource – GlucogenicAminoAcids • Aminoacidsfromproteinsconvertedtopyruvicacid • Thentoglucosebygluconeogenesisintheliver – KetogenicAminoAcids • Aminoacidsfromproteinsaredeaminatedtoproduce acetyl-CoAandacetoaceticacid • thentomakefattyacidsorketonebodiesorATP • Cannotbeconvertedtoglucose(WHY?) OxidativeDeamination • Theaminegroupfrom anaminoacidis removedandgivesrise toNH3 • Oxygenreplacesthe nitrogen • Oxygencomesfrom splittingH2O • Givesrisetoaketo acid orketonebody • Occursinalltissues ESPECIALLY theliver KetoAcids • Typesofketoacids – α ketoacid• pyruvicacid • oxaloaceticacid • α-ketoglutarate – βketoacid– • acetoaceticacid Pyruvic acidisan αketo acid! KetoneBodies • 3watersolublemoleculesmadebytheliverfrom fattyacidmetabolismduringfastingorcarbohydrate restrictiontouseasenergyinsteadofglucose • 2ofthe3areusedbytheheart andbrain and muscle forATPsynthesis – Pickedupbycellsandusedtomakeacetyl-CoA – Inthebrain • • UsedtomakelongchainfattyacidsthatcannotpasstheBBB Essentialduringfastingandstrenuousexercise – Intheliver • Ketonebodiesusedingluconeogenesisduringstarvation KetoneBodies • ProducedifKreb’scannotkeepupwiththeamountofAcetylCoA thatisbeingproduced • Formedbyjoiningtogether2acetates • Thereare2ketonebodiesusedbythebody 1. Acetoaceticacid(4C) • Convertedtoacetyl-CoA – Acetone(3C) • Wasteproduct • Fasting • Ketogenicdiet 2. β-hydroxybutyricacid(4C) • Convertedtoacetyl-CoA LipidsasFuel • Triglyceridemetabolism – Digeststriglyceridesintoglyceroland3fattyacids • Fateofglycerol – Gluconeogenesis,Glycogenesis • Inliver – Glycolysis – GlycerolentersglycolysisasPGAL • Fateoffattyacids – β-oxidationisthebreakdownoffattyacidchain – ProducesAcetyl-CoA – Manyfates – Dependentontheneedsofthecell β-Oxidation • Occursinthematrixof mitochondria • Enzymesremove2carbon(acetate) moleculesfromthe carboxylendoffatty acidchain • FormsAcetylCoA TriglycerideStructure TriglycerideStructure Palmitic Acid (C16H32O2) Carbonyl Group C=O Found in chocolate!! HowMuchATPisFormedfrom PalmiticAcid? • 7bonds – 1NADH+H+ +1FADH2 perbond CC CC CC CC CC CC CC • 8acetylCoA – eachacetylCoA----->Krebscycle • 1ATP • 3NADH+H+ • 1FADH2 X8 X8 = = X8 8ATP 24NADH+H+ = 8FADH2 CC ATPFromβOxidationof1FattyAcidChain • ATP = • NADH+H+ 8ATP – 7+24=31NADH+H+ – 31X3= 93ATP • FADH2 – 7+8=15FADH2 – 15X2= 30ATP Costofinitiatingβ-oxidation 8ATP 93ATP +30ATP 131ATP -1ATP 130ATP HowMuchATPfortheEntireTriglyceride? • Glycerol – convertedbacktoPGAL – Yields20ATP • Three16-Cfattyacidchains – 3x130ATP =390ATP • Grandtotal – 390+20= 410ATP