* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Photosynthesis
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical cascade wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Cyanobacteria wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Biosequestration wikipedia , lookup
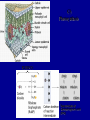
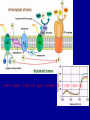
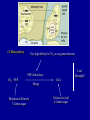
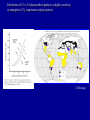
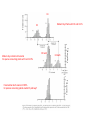
Photosynthesis Photosynthesis: CO2 + H2O + Energy CH2O + O2 + H2O Photosynthesis is a balance between competing processes C3 Photosynthesis RUBISCO CH20 CH20 | | HO-C-H HO-C-H | | COOH COOH Two molecules of 3-phosphoglyceric acid (3PG) C3 photosynthesis is dominant pathway …photosynthesis converts light energy to chemical energy chloroplast From Chapin et al. (2003) 2 H2O + 2 NADP+ + 3 ADP + 3 Pi + light → 2 NADPH + 2 H+ + 3 ATP + 3 H2O + O2 Photosynthesis C3 Photosynthesis: dominant photosynthetic pathway for land plants CO2 + RuBP RUBP Carboxylase Oxygenase Energy (ATP, NADPH) 2 PGA (3C sugar) Ribulose Bisphosphate 5 Carbon sugar Calvin-Benson Cycle: -- PGA forms sugars and starches -- RuBP, NADP and ADP are regenerated Photosynthesis Rubisco binds CO2 and O2; if binds O2 then no C fixation High CO2 favors C3 photosynthesis High Temperature / Dry environments C3 becomes inefficient Photorespiration…inefficiency in the Ps process 1. Stomata relatively closed to conserve water 2. CO2 diffusion into leaf and leaf [CO2] 3. photorespiration [O2 “fixation”] C4 Photosynthesis has evolved in warm & dry 3 Major differences w.r.t. C3 Ps -- Spatially segregated -- CO2 fixed into a 4-C sugar -- new enzymes & substrates C4 photosynthesis can dominate in grasslands C4 Photosynthesis Very high affinity for CO2, no oxygenase function Leaf Mesophyll PEP Carboxylase CO2 + PEP Phosphoenol Pyruvate 3 Carbon sugar OAA Energy Oxaloacetic Acid 4 Carbon sugar OAA Returned to mesophyll cells Pyruvate + CO2 Bundle Sheath Cells C3 Photosynthetic Pathway Now, RuBP and carboxylase are present under high [CO2] Photosynthesis 3 Distinct Ecological Features of C4 Photosynthesis (relative to C3): 1. C4 acid (OAA) transferred to BS where decarboxylated thereby ↑ [CO2] relative to [O2], ↑ rubisco efficiency 2. PEP carboxlase efficiently draws down internal leaf [CO2], ↑ concentration gradient with atmosphere, absorb CO2 w/more tighly closed stomata 3. PEP regeneration ↑ energy requirement by 30% relative to C3 Distribution of C3 vs C4 photosynthetic pathways is highly sensitivity to atmospheric CO2, temperature and precipitation J. Ehleringer Photosynthesis CAM Photosynthesis (Crassulacean Acid Metabolism) Based on C4 photosynthetic pathway Desert Species: Extremely hot and dry At night: Stomates open CO2 mesophyll cells CO2 + PEP OAA, stored in vaculoes During Day: Stomates closed OAA + enzymes CO2 (enters Calvin Cycle) + Pyruvate Photosynthesis Favored Ps Pathway C3 Ecosystem Type forests, arctic, tundra Temperature cold-warm Precipitation wet C4 warm – hot dry semi-aridgrasslands, tropical savanna CAM cold - hot extremely dry desserts Stable Isotopes of Carbon: 13C ~ 1.1% of total C 12C is ~98.9% of total C Two classes of C-isotope ratios in plants: δ 13C approximately –12‰ = C4 Ps pathway δ 13C approximately –28‰ = C3 Ps pathway Plants are ‘depleted’ in 13C 2 sources of isotope discrimination: A. Physical: 13CO2 diffusion slower than 12CO2 B. Enzymatic: Biology ‘favors’ light isotopes 12CO2 b/c of greater enzyme conformity C3 Isotope Discrimination (greater) -- Stomata more open, internal CO2 concentrations higher -- Rubisco has a ‘choice’ C4 Isotope Discrimination (less) -- Stomata more closed, internal CO2 concentrations lower -- PEP carboxylase has very high affinity for CO2 Stable Isotopes of Carbon: 13C ~ 1.1% of total C 12C is ~98.9% of total C Stable Isotopes are measured by mass spectrometry Isotope composition is expressed as a ratio (R) = 13C/12C In practice, measure R in a sample relative to that in a standard Rstd= fossil carbonates, Pee Dee Formation, southeastern US -standard abbreviated PDB - abundant fossils of Belemnita americana Carbon isotope ratios are expressed in parts per mil (‰) = parts per thousand according to: δ 13C = (Rsx/Rstd – 1) • 1000 The role of terrestrial plants in limiting atmospheric CO2 decline over the past 24 million years Pagani et al. (2009) Nature 460, 85-88 Equus Cerling, Ehleringer & Harris (1998) What are the implications of a drop in atmospheric CO2??? Major change in fauna spp. composition attributed to changes in climate East African Mammals Dorcatherium …reduced CO2 --> colder and drier & changes in vegetation composition Dryopithecus # Observations C4 Modern Day Plants with C3 and C4 Ps C3 Modern day animal tooth enamel for species consuming plants w/C3 and C4 Ps # Observations Fossil animal tooth enamel >8 MYA for species consuming plants w/what Ps pathway? C4 teeth # Observations C3 teeth Web Figure 9.5.A Transition in isotope composition in fossil soil and fossil animal teeth, indicating an expansion of C4 plants in the late Miocene. Isotope values are shown for carbonates (black circles) extracted from fossil soil from Pakistan, for fossil mammalian tooth enamel from Pakistan (light green squares), and for fossil horse tooth enamel from North America (green circles). The change in isotope composition 5 to 7 million years ago suggests a shift from a flora dominated by C3 plants to a flora dominated by C4 plants. (After Cerling et al. 1993.) Fossil Soil carbonates, Pakistan Mammalian tooth enamel, Pakistan Horse tooth enamel, North America