* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cellular Respiration
Gaseous signaling molecules wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Radical (chemistry) wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
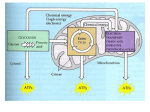
Cellular Respiration http://www.biology.clc.uc.edu/courses/bio104/atp.htm Vocabulary • Anaerobic- without oxygen • Aerobic- with oxygen Cellular Respiration • The process by which living things release the energy (ATP) stored in organic molecules Equation • C6H12O6 + 6O2 -----> 6CO2 + 6H20 + energy (heat and ATP) Cell Respiration Glycolysis aka: Step 1 • A series of 10 reactions • The process breaks down glucose into 2 pyruvate molecules and 2 ATP • Occurs in cytosol/cytoplasm Glycolylsis • Glucose (6 carbon sugar) is broken down into 2 Pyruvate acids (3 carbon sugars) Glycolysis Fermentation aka: Step 1.5 • The process by which pyruvate is converted in the absence of oxygen into either alcohol or lactic acid Alcohol Fermentation Lactic Acid Fermentation Fermentation Plant Vs. Animal • Alcohol Fermentation • Creates CO2 • EX= Root beer and ethanol • Lactic Acid Fermentation • No CO2 • EX= Muscle Aches and cheese Availability of Oxygen AKA: Aerobic Respiration • If no oxygen is available- the process stops. • If oxygen becomes available, the process moves onto oxidative reduction & the kreb’s cycle. • Possible for 36 ATP to be made. Oxidative Reaction • The process by which pyruvate is broken down in the presence of oxygen into a two-carbon molecule (acytl COA) which enters the Krebs cycle. Oxidative Reduction Continued • Carbs are broken down into water and CO2. • Removal of H+ = Oxidation • Addition of H+= Reduction • OIL RIG Krebs cycle aka: Step 2 • H+ is added to NAD+ • NADH is produced to supply the electron transport system • Occurs in mitochondrial matrix Krebs cycle cont. • The two-carbon fragment joins with a four-carbon sugar. Eight additional reactions occur releasing carbon dioxide and 2 ATP Krebs cycle • The NADH transports hydrogen atoms and electrons to the electron transport chain • ATP is generated and the hydrogen joins oxygen • 2 H+ + O H2O(water) Simple Krebs Cycle Products of Krebs Cycle • 1 glucose= 2 turns on the cycle • Plus- 6NADH, 2FADH, 2ATP and acetyl co A. Electron Transport Chain Electron Transport Chain aka: Step 3 • NADH2 releases H+ and eare transferred to eacceptors. • E- get passed along in redox reactions. (hot potato) • Most (34) ATP is made here E.T.C. cont. • When e- run out of energy, oxygen binds with H+ to form water. E.T.C. Drawing ATP • In the presence of oxygen, up to 36 additional ATP are produced ATP Yield • Glycolysis= 2 ATP • Kreb Cycle = 2 ATP • E.T.C. = 34 ATP • ____________________ • Total Possible = 38 ATP http://www.biology.clc.uc.edu/courses/bio104/atp.htm • Add animation http://www.phschool.com/science/biology_place/labbench/lab5/c ellular.html • Recipes- http://biology.clc.uc.edu/Courses/bio104/cellresp.htm • animation http://www.life.uiuc.edu/plantbio/cell/images/ATPSynthesis.gif