* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Protists
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
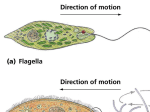
Protist Kingdom What is a Protist? ~ Diverse group of Eukaryotic organisms that exist as independent cells or as a colony of cells. ~ Do not fall into the category of animals, plants, or fungi. ~ They are more complex than bacteria because they have a nucleus. ~ They are bigger than bacteria. What the following Clip http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UOfY26qd bU0 Animal-like Protists Known as Protozoans: There are 4 types named based on the way they live and move Amoeba eating paramecia Pseudopod: An amoeba uses pseudopods to move and feed. Pseudopods form when th cell membrane bulges and cytoplasm flows into the bulge. Cytoplasm Nucleus: The nucleus controls the cell’s functions and is involved in reproduction. Amoebas usually reproduce by binary fission Food Vacuole: When the ends of two pseudopods fuse, they form a food vacuole. Food is broken down inside the food vacuole in the cytoplasm Contractile Vacuole: The contractile vacuole collects excess water from the cytoplasm and expels it from the cell Group 1: Protozoans with Pseudopods Amoeba ~ Belong to group called Sarcodines ~ Sarcodines move and feed by forming pseudopods ~ pseudopod: means false foot ~ Amoeba: temporary bulge of the cell membrane that fills with cytoplasm forming the false foot, allowing it to push outward in one location. Cytoplasm fills the foot and the rest of the organism follows. ~ Amoeba’s have a slight problem. They allow water to pass through their cell membrane. If they allow too much through the cell will explode. They have a contractile vacuole that collects the extra water and expels it from the cell. ~ Amoebas eat algae, bacteria, plant cells, and microscopic protozoa and metazoa. ~Amoebas live in fresh water (like puddles and ponds), in salt water, in wet soil, and in animals (including people). ~ Reproduce by binary fission (asexual) Ameba eating using pseudopod Food Vacuole: Forms and pinches off from the oral groove. It moves into the cytoplasm inside the vacuol, the food is broken down and then distriubted Oral Groove: Funnel-like indentation lined with cilia. The cilia move water containing food into the vacuole that forms at the end of the oral groove. Cilia: Thousands of cilia project through the pellicle. The beating cilia enable a paramecium to move smoothly in one direction Large Nucleus Group 2 Protozoan with Cilia Paramecium ~ Group called ciliates ~ this group has cilia, hair like projections from cells that move with a wavelike pattern. ~ Cilia used to move, obtain food, and sense the environment. ~ More complex cell than Amoeba, as they have a Nucleus and a Nucleolus. ~ Reproduce asexually – binary fission; some occasions may reproduce sexually through conjugation ~ Found in freshwater environments such as lakes, ponds and puddles. ~ Paramecium eat algae, bacteria, other protozoans, dead plant and animal matter, and other tiny animals. Paramecium Expelling Excess Water Group 3: Protozoan with Flagella Zooflagellates ~ Animal like protists that use flagella to move ~ Have one to eight long whip-like flagella that help them move. Symbiotic relationship : mutualism in which both species benefits Zooflagettates digest wood that the termite eats, producing sugars for themselves and for the termite Giardia: zooflagellate is a parasite in humans. Wild animals such as beaver, deposit Giardia into freshwater When humans drink the water the Giardia attach to intestinal walls feeding and reproducing Group 4: Other Protozoans ~ Sporozoans classified by the way they live instead of the way they move. ~ Parasictic feeding on the cells and body fluids of their hosts. ~ They may move by flagella, catching a ride on a host, or even through slime that it produces. Plasmodium: sporozoan that causes malaria Plasmodium: must be in the human taken in by blood by the mosquito into another human Fungus-like Protist ~ Like fungi, fungus like protists are heterotrophs, have cell walls, and use spores to reproduce. ~ Unlike fungus all fungus-like protists are able to move at some point in their lives. 3 Types Water molds, downy mildews, slime molds Water Molds & Downy Mildews ~ Live in water or moist places ~ Parasite that grows on living organisms ~ Grow as tiny threads that look like a fuzzy covering ~ Attack life within water ~ Attack food crops like potatoes, cabbages, corn and grapes. Fish attacked by water mold Water mold destroyed the Irish potato crops in 1845-1846 Los of these crops led to a famine that resulted in the deaths of over one million Irish people Slime Mold ~ Live in moist soil and on decaying plants and trees. ~ Beautifully colored (many bright yellow) ~ Glistening bodies creep over fallen logs and dead leaves on shady, moist forest floors. ~ Move in an amebalike way by forming pseudopods and oozing along the surfaces of decaying materials. ~ Feed on bacteria and other microorganisms Yellow Slime Mold on Dead Wood