* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Human Genome Analysis Variable Number Tandem Repeats
DNA sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Comparative genomic hybridization wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Promoter (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Exome sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Community fingerprinting wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Whole genome sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
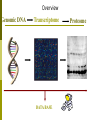
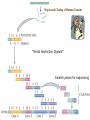
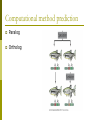
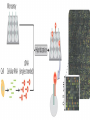
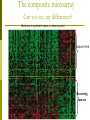
Genomics Analysis Chapter 20 Overview of topics to be discussed The Human Genome Analysis Variable Number Tandem Repeats Short Tandem Repeats Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms and Haplotypes Expressed sequence tags (ESTs) Predicting Protein Function BLAST searches (in lab) Homlogous genes Orthologs versus paralogs Microarray Analysis and an example of its application Overview Genomic DNA Transcriptome DATA BASE Proteome The Human Genome Project June 2002 Methods to used include: The two strategies used: Bac-to-Bac Sequencing (Map Based Sequencing) Shot-Gun Method http://www.sciencemag.org/content/291/5507/1304.full Map-based Cloning of Human Genome “Partial Restriction Digests” Smaller pieces for sequencing Time Consuming Process whereby: Areas of overlap between identifies the sequence of DNA http://www.hhmi.org/biointeractive/dna/DNAi_human_genome_seq.html Shot-Gun Sequencing of the human genome http://bcs.whfreeman.com/thelifewire/conte nt/chp17/1702002.html Human Genome approximated: 3.4 billion base pairs 32,000 genes Average gene 27,000 bases Chromosome 17, 19, 22 high density May encode 96,000 proteins Ongoing data bases from human genome project: Variable Number Tandem Repeats (VNTRs) Short Tandem Repeats (STRs) Single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) SNP Maps and haplotypes http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11029002 http://www.fruitfly.org/SNP/ Expressed-sequence tags (ESTs) Oops! Need to understand cDNA Haplotype:A set of SNPs and other varians on the same chromosome http://hapmap.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ Variable number tandem repeats (VNTRs) in multiple loci Short stretches of DNA base pairs that are repeated at multiple loci in the chromosomes. GAGGAG GAGGAGGAG GAGGAGGAG GAGGAGGAGGAGGAG GAGGAGGAGGAG GAG GAGGAGGAG GAGGAGGAGGAG GAGGAGGAGGAGGAGGAG GAGGAGGAGGAGGAGGAG Forensic Analysis: STRs FBI: Combined DNA Index System 13 loci STRs (4-5 nucleotide repeats) Example of D1S80 STR Distance migrated on gel electrophoresis corresponds to size of repeating nucleotide sequence. cDNA mRNA Reverse transcriptase cDNA Predicting Function from Homology Search Phylogenetic Profile Computational method prediction Paralog Ortholog Microarray Analysis http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VNsThMNjKhM Microarray Protocol DNA or cDNA is added robotically to chip Chips exposed to labeled cDNA Label monitored by laser Microarrays from breast tumors cDNA from breast tumors breast cancer patients EACH patient has a chip and microarray containing “candidate” genes Time passes and some women remain “cancer-free” while other women have recurring cancer. Now return to the original microarrays and compare these two groups of women (disease-free and recurring cancer). Is gene expression different? The composite microarray Can you see any differences? (Each row is a patient’s tumor, a column a gene) Cancer free Recurring cancers Expression patterns varies between patients Those “genes” that are green from “normal” tissue genes Those “genes” that are red are associated with cancer! BLAST searches Unknowns and examples of how to search database provided tomorrow in lab. Mouse: Mus musculus 2.6 billion bp 99% in common with human genome