* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download SPECIATION
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Genetics and archaeogenetics of South Asia wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
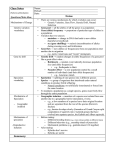
How Do We Get A New Species? SPECIATION Is It This Easy? NO! The gene pools of two populations must separate. 1 • Because members of a population interbreed, they share a common group of genes called a GENE POOL ___________. • A gene pool consists of ____________ ALL the genes present in a population, including all the alleles different _________. The ____________________ relative frequency is the number of times that an allele occurs in the gene pool compared to the occurrence of other alleles in the gene pool. Sample Population 48% heterozygous black Frequency of Alleles allele for brown fur allele for black fur 16% homozygous black 36% homozygous brown RELATIVE FREQUENCY is often expressed as a __________________. percentage EX: In this population Dominant B allele (black) = 40% Recessive b allele (brown) = 60% 2 NOTHING RELATIVE FREQUENCY has _________ to do with whether an allele is DOMINANT or _____________ RECESSIVE ______________ In this population, the recessive allele is more frequent. _______________________IS THE SEXUAL REPRODUCTION MAJOR SOURCE OF VARIATION IN NOT POPULATIONS, but it does _______ change the __________________ of relative frequency alleles in population! Shuffling a deck of cards can shuffle to produce many different hands, but doesn’t change the number of kings or queens in the deck. Interbreeding Fertile Offspring = Reproductive Isolation 3 Reproductive Isolation • Behavioral Isolation • Geographical Isolation • Temporal Isolation Behavioral Isolation Two populations can mate, but mating rituals differ. Geographic Isolation Populations are separated by geographic barriers. 4 Temporal Isolation When two or more species reproduce at different times. 5