* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Darwin`s Theory: Natural Selection
Sexual selection wikipedia , lookup
Evolving digital ecological networks wikipedia , lookup
Vestigiality wikipedia , lookup
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
Catholic Church and evolution wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Saltation (biology) wikipedia , lookup
The Descent of Man, and Selection in Relation to Sex wikipedia , lookup
Theistic evolution wikipedia , lookup
Genetics and the Origin of Species wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
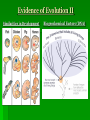
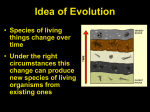
Darwin’s Theory: Natural Selection (14.1-14.3) The basics… Evolution: process by which modern organisms have descended from ancient organisms (change over time) Scientific Theory: a well-supported, testable explanation of phenomena that have occurred in the natural world Voyage of the Beagle 1831: Darwin set sail from England aboard the H.M.S. Beagle as a Naturalist Throughout the voyage he went ashore and collected plant and animal specimens He also read scientific literature and kept journals The Galapagos Characteristics of plants and animals varied noticeably among the different islands. Darwin’s Observations Summary of Observations Many plants and animals are especially well-suited to the environments they inhabit Organisms tend to have many more offspring than are able to survive. Influences on Darwin Hutton & Lyell: Geologic forces that shape the earth occur very slowly, so earth must be more than a few thousand years old; Geologic forces continue to act on the earth Malthus: Population growth exceeds food supply growth leading to struggle for existence ** If the Earth has changed, life probably has too. If people experience struggle for existence, other organisms probably do as well. Lamarck: Tendency for Perfection Use and Disuse Acquired Traits Lamarck believed changes acquired in a lifetime could be passed on leading to a change in a species. Applying Lamarck’s Hypothesis: Evaluating Lamarck Strength’s • Species weren’t static and changed over time • Species were related through common ancestry • Helped paved way for Darwin by bringing evolution to the forefront of scientific debate Weakness’s • Lamarck didn’t know about genes and how traits were inherited • An organism’s behavior has no effect on its heritable characteristics On the Origin of Species Proposed a mechanism for evolution called natural selection Presented evidence that evolution has been taking place for millions of years and continues today 1858, Darwin received a manuscript from Alfred Russell Wallace proposing similar ideas, he finally decided to publish. Book was released in 1859 Artificial Selection • Selection by humans for breeding of useful traits from natural variation among different organisms • Natural selection works essentially the same way, but the environment, not humans determines the desirable traits. Process of Natural Selection (S.N.A.S.D.) Struggle for Existence: Organisms generally have more offspring than resources can support Natural Variation: Even within a species there will be distinct differences between individual organisms Adaptation: Some variations provide individuals with an advantage that increases their chances of survival. Survival of the Fittest: Those with the adaptations are more likely to survive and reproduce Descent with Modification: Genes for the beneficial adaptations are passed on and the trait becomes increasingly more common in each new generation of the species Evidence of Evolution I The Fossil Record Geographic Species Distribution Homologous Structures Vestigial Structures: organs that are so reduced that they are just traces (vestiges) of homolgous structures in other species Evidence of Evolution II Similarities in Development Biogeochemical Factors (DNA)