* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Mutations Practice Sheet
Heritability of autism wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Saethre–Chotzen syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genetic testing wikipedia , lookup
BRCA mutation wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
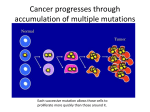
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Advanced Biology II Mutations Practice Sheet Mutations 1. Examine the following genetic codes closely. What type of mutation are you seeing in the second code? Why will this be a problem? ATCCCGAGCTTAC ATCGAGCTTAC 2. Examine the following genetic codes closely. What type of mutation are you seeing in the second code? How many amino acids will be produced incorrectly? Will this be a problem? GACTACGCATG GACTACGCAGT 3. Examine the following genetic codes closely. What type of mutation are you seeing in the second code? How many amino acids will be produced incorrectly? Will this be a problem? ATCCCGAGCTTAC ATCCTCGAGCTTAC 4. Examine the following genetic codes, the second of which has a mutation. What type of mutation are you seeing (be specific, and be careful!)? How many proteins will be produced incorrectly? CGGGCTAGCTAG CGGGCCTAG 5. Which is worse: an insertion of an extra base, or a substitution of the wrong base? Why? 6. Which do you think would be more damaging: an error in DNA, RNA, or protein? Why? Rate of Mutation 7. Current estimates say that DNA in a human consists of about 3 billion bases arranged into 25,000 genes. If this is true, is every person likely to have a mutation in their genetic code? 8. 1 in how many humans are likely to have a mutation? (Think about the basic rate of mutation). Impacts of Mutations 9. List the three results a mutation can have. 10. Which of the three results of a mutation is most common? Why? 11. Explain why neutral mutations will only be acted on by genetic drift, and not natural selection. Mutations and Evolution 12. Why are mutations referred to as the fundamental source of evolution? 13. Explain how mutations and natural selection work together to create new traits in populations. 14. Describe how a mutation might lead to two species diverging from a common ancestor, as might have occurred between apes and humans, or fish and amphibians.