* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download KINGDOMS OF ORGANISMS
Magnesium in biology wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Venus flytrap wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
Verbascum thapsus wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
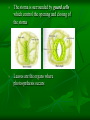
KINGDOM PLANTAE Tissues, Structures, Classification and Tropisms Plant Tissues Dermal: outermost layer on leaves and stems; covered with a waxy layer called the cuticle to prevent water loss Vascular: used for transport Ground: photosynthetic cells, support cells, and all other cells that are not dermal or vascular Xylem and Phloem Xylem: Made up of dead cells Carries water and minerals Transport is unidirectional from root to stems to leaves Phloem: Made up of living cells Carries sugar Transport is bidirectional (leaves to stems, stems to leaves, roots to stems, stems to roots) Plant Structures—NonReproductive 1. Roots: 2 types—taproot and fibrous root Taproots anchor tall plants and are important when water is not abundant Protected by the root cap Usually the part of the plant that grows below the surface of the soil and anchors the plant Can store food Absorb water and minerals Root Cap 2. Stems: Support leaves and flowers Can function to store food (ex: potato is an underground stem) Transport water and nutrients within the plant Node: place where leaves attach to stems 3. Leaves: Common features of leaves include: Blade: flat, broad section of the leaf Petiole: short stalk that connects the blade to the stem Veins: carry water, minerals and sugar Dermal tissue of leaves contain stomata, openings that allow carbon dioxide to enter and oxygen & water to leave The stoma is surrounded by guard cells which control the opening and closing of the stoma Leaves are the organs where photosynthesis occurs 4. Structures Found in Multiple Locations: Cambium: found between the xylem and the phloem it is responsible for making vascular tissue Chloroplast: structure where photosynthesis takes place Plant Structures—Reproductive 1. Male Reproductive Parts: Called the stamen Made up of the anther (produces pollen) and the filament (supports the anther) 2. Female Reproductive Parts Called the pistil Made up of the stigma (the pollen lands here) the style (connects the stigma and the ovary) and the ovary (makes ovules) 3. Sterile Parts Petals: brightly colored parts of the flower Sepals: green, leaf-like structures that support the flower and protect the bud before the flower blooms Plant Classification Botanists divide the plant kingdom into four groups based on three key features: The presence of vascular tissue The presence of seeds The location of seeds The four groups are: Nonvascular plants--mosses Vascular seedless plants--ferns Gymnosperms (seeds in cones)--pines Angiosperms (flowering plants) Tropisms Tropisms are responses by plants to environmental stimuli Examples: Thigmotropism: a plant’s response to touch (i.e. vines wrap around a trellis or Venus fly trap captures an insect) Phototropism: a plant’s response to light (i.e. plant’s grow towards a window) Tropisms (cont.) Gravitropism: a plant’s response to gravity stem’s show negative gravitropism since they grow against the force of gravity root’s show positive gravitropism since they grow with the force of gravity