* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Structure of Seed Plants
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Venus flytrap wikipedia , lookup
Historia Plantarum (Theophrastus) wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Verbascum thapsus wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
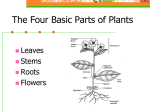
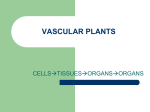
Structure of Seed Plants Vascular Tissues What is a Vascular Tissue? Specialized tissues that conduct nutrients and water from one part of the plant to another. 2 Types of Vascular Tissues 1) Xylem 2) Phloem Xylem Xylem type of tissue that provides support and conducts water and nutrients from the roots. Phloem Phloem The tissue that conducts food in vascular plants. The Roots! Root Functions 1) Supply plants with water and minerals. 2) Hold plants securely in soil. 3) Help store surplus food in some plants. Ex: Carrots, potatoes, onions. Root Structure Root cap release a substance that helps the root grow through soil. Root Systems 2 type of root systems 1) Taproot, one main root that grows downward. 2) Fibrous, several roots that spread out from the base of a plant’s stem. What type of roots do these plants have? Stem (Shoot) Stem Functions 1) Stems support the plant’s body (flowers/leaves). 2) Stems support materials (via xylem and phloem) between the roots and leaves. 3) Some stems store water/materials Ex: Cactus have adapted to store water in their stems. 2 Types of Stems Herbacious Stems that are soft, thin, and flexible. Woody Rigid stems made of wood and bark. Leaves The main function of leaves is to make food for the plant. 1. Chloroplast in leaves capture sunlight. Leaves absorb CO2 2.