* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Bio Notes Plant Anatomy Stem Transport
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
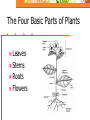
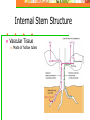
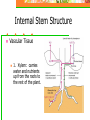
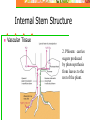
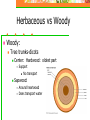
The Four Basic Parts of Plants Leaves Stems Roots Flowers Stems: Transport Plant Structure: Organs: Roots, Stems (trunks) and leaves Tissues: a group of cells working together to perform a certain task Stems Mostly above ground Except: Potatoes and ginger are underground stems Stems Functions Support flowers & leaves Movement of materials: Vascular System Stores food and water Internal Stem Structure Vascular Tissue Made of hollow tubes Internal Stem Structure Vascular Tissue 1. Xylem: carries water and nutrients up from the roots to the rest of the plant. Internal Stem Structure Vascular Tissue 2. Phloem: carries sugars produced by photosynthesis from leaves to the rest of the plant. Internal Stem Structure Xylem Water and dissolved minerals move up from the roots to the rest of the plant. Cohesion and Adhesion: physical properties of water (Hydrogen bonding) allows water to rise through the plant Transport Cohesion (“co”-together, “haerere”-to cling): strong attraction between water molecules to each other. Adhesion: attraction of water molecules for other surfaces (such as water molecules for the wall of the xylem tissue) Transport Capillary Action: tendency of water to move upward in a hollow tube. Caused by tension created by cohesion and adhesion Transport Transpiration: Loss of water, “evaporation” from leaves (high to low concentration) Outward flow of water (out of plant) causing a vacuum, pulling water upward. Internal Stem Structure Phloem Example: sap (fluid): products of photosynthesis move from leaves to stems and roots. Minerals traveling up can also move here. Internal Stem Structure Phloem Sugar source: high concentration of sugar (leaves, can be roots) Sugar sink: uses or stores sugar Growing shoots and stems, fruits, storage roots Herbaceous vs Woody Herbaceous: soft, low growing, green and conduct photosynthesis Monocot or Dicot Herbaceous vs Woody Woody: Tree trunks-dicots Center: Hardwood: oldest part Support No transport Sapwood: Around heartwood Does transport water Tree Rings Each Annual Ring: Includes both a light and dark ring: represents one year of growth Evidence of the age of tree: count the number of rings Tree Rings Tells us how much tree grew each season Good supply of water in spring: Cells are wide and have thin walls light in color Water limited: Cells smaller and thicker walls darker in color