* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plant Cells and Tissues
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Venus flytrap wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
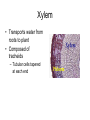
Plant Cells and Tissues Chapter 23.1 • Plants are composed of cells which contain: – Cell wall – Central vacuole – Chloroplasts Plant Tissues • There are four types of tissues in plants: – – – – Dermal tissue Vascular tissue Ground tissue Meristematic tissue Dermal Tissue • • • • Also called the epidermis Composed of flattened cells Protects and covers the body of the plant Produces the cuticle Located in the Epidermal Layer… • Stomata: – Opening in leaf tissue – Help control water loss from plant • Guard Cells: – Controls the opening/closing of stomata • Trichomes: – Hairlike projections on stem and leaf – Reduces evaporation of water from plant Vascular Tissue • Main function is to transport water, food throughout plant • Two types of vascular tissue – Xylem – Phloem Xylem • Transports water from roots to plant • Composed of tracheids – Tubular cells tapered at each end Phloem • Transports sugars to all parts of the plant • Made up of tubular cells joined end to end Ground Tissue • In charge of photosynthesis, storage, and secretion • Found throughout plant Meristematic Tissue • Produces most of a plant’s new cells • Located in regions of actively dividing cells Roots, Stems, and Leaves Chapter 23.2 Roots • Anchor, absorb nutrients, contain vascular tissue to transport materials • Can be short or long, thick or thin • Have root hairs – Tiny extensions – Increase surface area of root Stems • Support leaves and flowers, contains vascular tissue to transport materials • Arrangement of vascular tissue: – Monocots: Xylem and phloem scattered throughout stem – Dicots: Xylem and phloem in a circle that form a ring Growth of Stem • Primary growth – Increase in length • Secondary growth – Increase in diameter Ex: Woody Stem: Leaves • Primary function: Photosynthesis • Some leaves joined directly to stem – Example: grass blade • In some leaves, a stalk called a petiole joins the leaf blade to the stem • Simple leaf – Blade that is not divided • Compound leaf – Blade divided into leaflets • Transpiration: – Loss of water through the stomata • Leaf venation: – Patterns of veins in the leaves • Parallel • Pinnate • Palmate Plant Responses Chapter 23.3 Plant Hormones • Plants have hormones that regulate growth and development • Auxins and Gibberellins (2 hormones) that promote growth in plants Plant Responses • Why do stems grow up and roots grow down? • Tropism – Plant’s response to an external stimulus • Phototropism – Plant growth toward light • Gravitropism – Plant growth in response to gravity