* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download How Life Began 2014.notebook
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
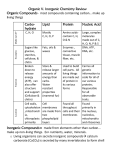
How Life Began 2014.notebook November 29, 2016 Origins How Life Began Chapter 18 You have to know: How do we know? >Big Bang 13.7BYA >Math of expansion of the Universe >Radio telescopes detecting radio waves from that time >From basic elements H, other elements formed Sun was Born: 5 BYA Earth was born: 4.6 BYA Atmosphere of ancient earth: CO2, NO2, H2 O, H2 S, CH4 No Oxygen in the atmosphere (Is this important?) Why were the seas an olive green? STEPS to the formation of a life evidences for each Inorganic compounds > Organic compounds > Single cell containing the most organic compounds > cell needs to survive and reproduce > More cells > multicellular organisms 1 How Life Began 2014.notebook November 29, 2016 Abiotic Synthesis of Organic Compounds Most imp Organic Compounds needed _____ and ________ From inorganic compounds by synthesis and rearrangement of the elements ___ ____ ____ _____ using energy from ____ _____ ____ But how?? Hypothesis One organic compounds formed on earth from earthly compounds Evidence: StanleyMiller experiment Hypothesis Two: Hydrothermal vents oxygen poor and can make organic compounds with the heat and inorganic materials 2 How Life Began 2014.notebook November 29, 2016 Hypothesis three organic compounds came from outer space Evidence • Airplane experiment • Meteorites from space have amino acids (Australia) • Capsule Experiment Hypothesis four Clay Hypothesis by Carl Woose organic compounds formed from clay like particles 3 How Life Began 2014.notebook November 29, 2016 Inorganic compounds > Organic compounds > Single cell containing the most organic compounds > cell needs to survive and reproduce > More cells > multicellular organisms How did the first cell form? By chance! The ancient seas were filled with organic compounds. Some accidentally enclosed with a lipid membrane like structure and was capable of surviving, using energy from outside and able to reproduce YooHoo! Evidence: Lab experiments 4 How Life Began 2014.notebook November 29, 2016 When did this happen? ~3.5 BYA What was the first cell like? A heterotroph Heterotroph Hypothesis Oparin and Haldane Cell was a heterotroph which obtained energy from the environment full of organic compounds and other heterotrophs Evidence: • Oldest fossil 3.5 BYO was a heterotroph • Chlorophyll necessary for photosynthesis is a more complex organic compound and may not have evolved so soon. • Photosynthesis results in a) the buildup of oxygen in the atmosphere and b) formation of the ozone layer (allowed life to evolve on land) • No evidence of oxygen in rocks till about 3.2 BYA 5 How Life Began 2014.notebook November 29, 2016 First cell was an anaerobic heterotroph and a prokaryote (simplest cell still exists today) What does a prokaryote look like? Then simple autotrophs evolved with the formation of chlorophyll Evidence: Fossils. stromatolites, rust on rocks After that some bacteria evolved a method to use oxygen from atmosphere to get more energy from carbs. Anaerobic respiration produces _____ ATP per glucose Aerobic produces _________ ATP per glucose 6 How Life Began 2014.notebook November 29, 2016 What are the different type of prokaryotes in the world? How and when did the prokaryote evolve to form an eukaryotic cell Endosymbiotic theory Lynn Margulis http://bugs.bio.usyd.edu.au/learning/resources/CAL/Microconcepts/moviePages/ incorporation.html Evidence? 1. DNA present in all chloroplasts and mitochondria 2. All organelles have double membranes 3. DNA in chloroplasts and mitochondria are circular (just like bacterial DNA today) The Seven Daughters of Eve (2001, ISBN 0393020185) by Bryan Sykes presents the theory of Human mitochondrial genetics for a general audience. Sykes explains the principles of genetics and human evolution, mitochondrial genetics, and his analyses of ancient DNA to genetically link modern humans to their prehistoric ancestors 7 How Life Began 2014.notebook November 29, 2016 8 How Life Began 2014.notebook November 29, 2016 9