* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Indicate whether the statement is true or false. If false
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Selective breeding wikipedia , lookup
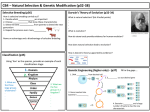
Final Review Modified True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make the statement true. ____ 1. A trait is a specific characteristic that varies from one individual to another. _________________________ ____ 2. An organism with a dominant allele for a particular form of a trait will sometimes exhibit that trait. _________________________ ____ 3. Mitosis results in two cells, whereas meiosis results in one cell. _________________________ ____ 4. The replication of a DNA molecule results in four copies of the same gene. _________________________ ____ 5. If a nucleic acid contains uracil, it is DNA. _________________________ ____ 6. A codon consists of four nucleotides. _________________________ ____ 7. The anticodon AGA is complementary to the mRNA codon TCT. ___________________ ____ 8. People have used selective breeding to produce many different dog breeds. _________________________ ____ 9. In a human karyotype, 44 of the chromosomes are autosomes. _________________________ ____ 10. In a human karyotype, 23 chromosome pairs are similar in size and shape. _________________________ ____ 11. A dominant X-linked trait would be more common in males than in females. _________________________ ____ 12. If a cat has both orange and black spots, it is homozygous for the alleles on the X chromosome that code for spot color. _________________________ ____ 13. In natural selection, human breeders, rather than the environment, select the variations of traits to be passed to offspring. ______________________________ ____ 14. According to Darwin, the word selection would indicate organisms’ ability to survive and reproduce in their particular environments. _________________________ ____ 15. The fact that species today look different from their ancestors can be described as descent with modification. _________________________ ____ 16. According to Charles Darwin, members of a species must share limited resources. _________________________ ____ 17. A polygenic trait is controlled by one gene. _________________________ ____ 18. In a population of snakes with a range of body lengths, if the longest individuals have the highest fitness, disruptive selection is likely to occur. _________________________ ____ 19. In small populations, an allele can become more or less common simply by chance. _________________________ ____ 20. In a lysogenic infection, host cells can make copies of virus DNA for many generations. _________________________ ____ 21. A disinfectant is a chemical solution that kills bacteria. _________________________ ____ 22. An antibiotic is a preparation of weakened or killed virus or viral proteins. _________________________ Completion Complete each statement. 23. The different forms of a gene are called ____________________. 24. In regards to plant height, the possible genotypes of a pea plant are TT, ____________________, or tt. 25. When two heterozygous tall pea plants are crossed, the expected genotype ratio of the offspring is _________________________. Figure 12–1 26. The structure labeled X in Figure 12–1 is a(an) ____________________. Figure 12–3 27. In Figure 12–3, A, B, and C are three types of ____________________. 28. The order of nitrogenous bases in DNA determines the order of ____________________ in proteins. 29. The tRNA bases called the ____________________ are complementary to three consecutive nucleotides on one mRNA molecule. 30. Humans use selective breeding to pass desired _________________________ on to the next generation of organisms. 31. To produce a fruit that has some characteristics of an orange and some of a grapefruit, you would use the selective breeding technique of _________________________. 32. Genetic defects caused by excessive inbreeding can be eliminated through the process of _________________________. 33. Scientists use radiation and chemicals to induce ____________________. 34. Darwin proposed that natural selection took place as individuals best suited to the ____________________ survived and reproduced. 35. Crossing-over can occur during the meiotic divisions that produce cells called ____________________. 36. For new species to evolve, populations must be ____________________ isolated from each other. Figure 19–2 37. The organism labeled A in Figure 19–2 is an example of a(an) ____________________. 38. The process of converting nitrogen to a form plants can use is called _________________________. 39. By breaking down the nutrients from dead organisms in an ecosystem, bacteria act as ____________________. 40. Although viruses come in many different shapes, the core of every virus contains ____________________.