* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Individual behavior in Organization
Social tuning wikipedia , lookup
Personal identity wikipedia , lookup
Mnemic neglect wikipedia , lookup
False consensus effect wikipedia , lookup
Zero-acquaintance personality judgments wikipedia , lookup
Attitude (psychology) wikipedia , lookup
Attribution bias wikipedia , lookup
Personality psychology wikipedia , lookup
Team composition wikipedia , lookup
Attitude change wikipedia , lookup
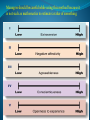
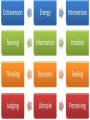
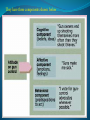
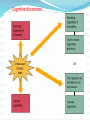
Amel Adilović Individual behavior refers to how individual behaves at work place, as a result of his personality and conditions in which he works. This relationship is a proof that you are a part of company or organization called a psychological contract. Contributions Inducements Effort Pay Ability Job security Loyalty Benefits Skills Career oppurtunities Time Promotion oppurunities This is happening when one side (individual or organization) thinks that contract is not fair, then this side can initiate a change of contract to make a new agreement. This means a right person for a certain kind of job. There are some techiques or steps which can show is an individual a right person for a some kind of job. Individual differences are personal properties which are different from person to person. They can be physical, psychological or emotional. Set of this differences creates a specific personality which is unique. Personality is a relative stable set of psychological attributes that make a difference between each person. People identified five fundamental personality traits which are extremely important for organizations. Managers should be careful while using this method because it is not such as mathematics to estimate a value of something. The Myers-Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI) is a way of examining the personality of an individual. It is one of today's most widely used personality assessment tools. There are 16 personality types in the Myers-Briggs taxonomy. Types are not right or wrong: they are simply different from one another. The main difference between extroverts and introverts is that introverts gain their energy by being alone and extroverts gain their energy by being with others. The main difference between sensing and intuition is that sensors take in information via their five senses and through facts, and intuitives take in information via patterns, impressions ands possibilities. The main difference between thinking and feeling is that thinkers make decisions based on facts, and feelers make decisions based on values. The main difference between perceivers and judgers is that judgers prefer their world to be structured and planned, while perceivers prefer their world to be open ended and find that having plans is stifling. Other personalitiy traits at works Locus of control Other personalitiy traits at works Self-efficacy Measure of one's own ability to complete tasks and reach goals. Other personalitiy traits at works Authoritarianism Other personalitiy traits at works Machiavellianism A person's tendency to deceive and manipulate others for personal gain. Machiavellianism is one of the three personality traits referred to as the dark triad, along with narcissism and lack of empathy. Narcissism Lack of empathy Other personalitiy traits at works Self-esteem It is a judgement of oneself as well as an attitude toward the self Other personalitiy traits at works Risk propensity Risk propensity is a degree to which an individual is willing to make a decision with defined chances with respect to risk of loss. Other personalitiy traits at works Risk propensity There are three kinds of risk propensity: A) Physical status: the domains of health and safety risk; B) Lifestyle: social and recreational risk; C) Livelihood : career and finance risk Emotional intelligence is ability to be aware of your emotions and the emotions of others and then to use that knowledge for making some decisions which are affecting you or other people. People who have high level of emotional intelligence are able to understand physical, mental and social impact that negative emotions have on their bodies, minds, relationship and ability to achieve goals. Attitudes are complexes of beliefs and feelings that people have about specific ideas, situation or other people. They are like systems through which most people express their feelings. They have three components shown below Cognitive dissonance Work-Related attitudes Job satisfaction or dissatisfaction This means positive or negative feelings and attitudes about one’s job. Does job satisfaction cause job performance? Or Does job performance cause job satisfaction? Factors which affect this attitude Organizational Commitment This means worker’s feelings and attitudes about the entire work organization. Affective Commitment: a person’s desire to work for an organization because he or she agrees with its goals and wants to do so Normative Commitment: a person’s desire to continue working for an organization because he or she feels obligations from other to remain Continuance Commitment: a person’s desire to continue working for an organization because he or she needs to and cannot afford to do otherwise Affect and mood can have effects on your work in company. Managers believed that emotion and feelings varied among the people from day to day, but after some time research show that there are underlying stable predisposition towards fairly constant and predictable moods and emotional states. Negative affectivity Positive affectivity An important element of an attitude is the individual's perception of the object about attitude is formed. Perception is the set of processes by which an individual becomes aware of and interprets information about the environment. The way we perceive our environment is what makes us different from each other. The process of screening out information that we are uncomfortable with or that contradicts our beliefs. It is the process by which individual selects, organizes and evaluates stimuli from the environment to provide meaningful experiences for him- or herself. Stereotyping The process of categorizing/labeling people on the basis of a single attribute. It is the process that organizes beliefs about one group of people and assigns them to everyone in that group. Perception and Attribution Attribution is the process of observing behaviour and attributing casues to it. How do we attach meaning to other's behavior, or our own? This is called attribution theory. For example, is someone angry because they are badtempered or because something bad happened? The basic frame work of attribution consists of: Consensus (the extent to which other people in the same situation behave the same way) Consistency (the extent to which the same person behaves in the same way in different times) Distinctiveness (the extent to which same persons behaves in the same way in other situations) Self bias The self-serving bias is people's tendency to attribute positive events to their own character but attribute negative events to external factors. It's a common type of cognitive bias that has been extensively studied in social psychology. Stress and Individual behavior Stress is a state of tension experienced by individuals facing extraordinary demands, constraints, or opportunities. Stressors are things that cause stress and have the potential to influence work attitudes, behavior, job performance, and health. There are three types of stressors: Work factors as potential stressors: Excessively high or low task demands Role conflicts or ambiguities Poor interpersonal relationships Too slow or too fast career progress Personal factors as potential stressors: Includes needs, capabilities, and personality Stressful behavior patterns of the Type A personality: Always moving, walking, and eating rapidly Acting impatient, hurrying others, disliking waiting Doing, or trying to do, several things at once Feeling guilty when relaxing Hurrying or interrupting the speech of others Nonwork factors as potential stressors: Family events Economics Personal affairs Constructive stress: Acts as a positive influence Can be energizing and performance enhancing Destructive stress: Acts as a negative influence Breaks down a person’s physical and mental systems Can lead to job burnout and/or workplace rage. Burnout is a feeling of exhaustion that may develop when someone experiences too much stress for an extended period of time. It results in constant fatigue, frustration and helplessness. How to manage stress Workplace behavior is a pattern of action by the members of an organization that directly or indirectly influences organizational effectiveness. They are: Performance behaviors: All of the total set of work-related behaviors that the organization expects the individual to display. Absenteeism: Absenteeism is the term generally used to refer to unscheduled employee absences from the workplace. Turnover: Occurs when people quit their jobs An organization usually incurs costs in repleacing individuals who have quit, but if turnover involves especially productive people, it is even more costly. Organizational citizenship: The extent to which a person’s behavior makes a positive overall contribution to the organization.