* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 2 Ecosystems
Biological Dynamics of Forest Fragments Project wikipedia , lookup
Latitudinal gradients in species diversity wikipedia , lookup
Introduced species wikipedia , lookup
Storage effect wikipedia , lookup
Molecular ecology wikipedia , lookup
Island restoration wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity action plan wikipedia , lookup
Biogeography wikipedia , lookup
Reconciliation ecology wikipedia , lookup
Natural environment wikipedia , lookup
Coevolution wikipedia , lookup
Habitat conservation wikipedia , lookup
Ecological fitting wikipedia , lookup
Occupancy–abundance relationship wikipedia , lookup
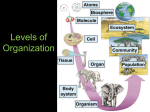
Chapter 2 Ecosystems “When We Try to Pick Out Anything by Itself, We Find It Hitched to Everything Else in the Universe.” John Muir Ecosystems • All the organisms living in a certain area, and their physical environment. • Often described as isolated units, but usually do not have clear boundaries. • Consist of biotic and abiotic factors. • Biotic factors – all the living parts. • Abiotic factors – all the nonliving parts. Abiotic Factors • Include temperature, sunlight, humidity, water supply, soil type, and mineral nutrients. • In an ecosystem, everything is interconnected. Change a biotic or abiotic factor and the whole system can be disrupted. Biotic Disruption • DDT sprayed to kill mosquitoes that carry malaria. • Thatch-eating caterpillars multiply, destroying thatch roofs. • DDT covered cockroaches eaten by geckos. Geckos suffer nerve damage, move slower and are caught and eaten by cats. Biotic Disruption (Cont.) • Cats suffer from high concentrations of DDT and die. • Rat populations increase bringing plague infected fleas. • Incidence of the plague increase. • All because we sprayed DDT to kill mosquitoes. Abiotic Disruption • Farmer over fertilizes his fields (increase in nitrogen and phosphorus). • Extra fertilizer runs off fields into adjacent stream and eventually to a nearby lake. • Extra nutrients in the lake cause phytoplankton populations to expand dramatically. Lake becomes green. Abiotic Disruption (Cont.) • Increase in phytoplankton causes increases in zooplankton. • Increases in plankton cause dissolved oxygen (DO) levels to fall rapidly. • Low DO levels cause massive fish and plankton die-off. • Resulting dead material falls to lake bottom and decomposes (slowly). • Lake starts to fill in rapidly. Ecosystem Structure • The biotic elements of a ecosystem are organized in a specific manner. – Organisms – individual living things. – Species – a group of organisms that can reproduce together and share common genes. – Population – a group of individuals of the same species living in a particular place. – Community–- a group of interacting populations. Niche and Habitat • Niche – an organisms way of life. Includes all the relationships with its environment. • Habitat – where in the environment an organism lives. • Niche includes habitat, as well as other relationships. Species Relationships 1. Predation – when one organism kills & eats another. • Prey – animal being eaten. • Predator – animal doing the eating. • Predator-prey relationships can be simple or complex. • Sometimes predators can limit a prey population size, other times they can have no affect on prey population size. Species Relationships (Cont.) 1. Competition – a relationship between species where they attempt to use the same limited resource. – – Sometimes species can compete w/o coming into contact w/ each other. Ex: 2 flowers competing for pollinators. Competition almost always results in 1 winner and 1 loser. Species Relationships (Cont.) 3. Parasitism – the relationship between a parasite and its host. – Host – the organism that the parasite gets its nutrition from. – Parasite – organisms that live in or on another organism w/o killing it. – Parasites usually weaken their host making them susceptible to other things. Species Relationships (Cont.) 4. Mutualism – a cooperative partnership between 2 species. – Both parties have to benefit. 5. Commensalism – relationship where 1 species benefits & the other is not harmed nor helped.