* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ap Biology Discussion Notes
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Saethre–Chotzen syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
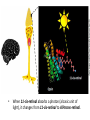
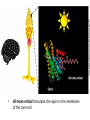
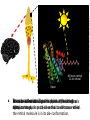
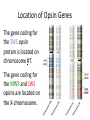
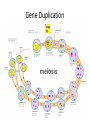
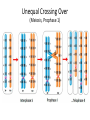
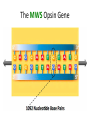
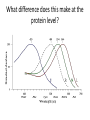
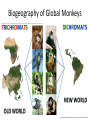
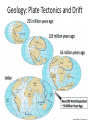
Ap Biology Discussion Notes Monday 5/2 Goals for the Day • Be able to tie together multiple disciplines in biology • Be prepared for the AP test Question of the Day 5/2 • Is it possible that things that are advantageous in one environment are “maladaptive” or disadvantageous in others? Give an example to explain your answer. Dichromatic Vision Trichromatic Vision Day 3 The Cell Biology of Color Vision in Monkeys How Does Color Vision Work? Cell Biology • The retina has two types of cells: rod cells and cone cells. There are more rod cells than cone cells. Cone cells are responsible for color vision. How Does Color Vision Work? Cell Biology How Does Color Vision Work? How Does Color Vision Work? There are three types of cone cells. More accurately, any given cone cell may be using only one of three types of transmembrane opsin proteins. Three types of Cone Cell • Different kinds of opsin proteins embedded in the membrane of cone cells make each kind able to receive different information from the others. • Central Dogma of Molecular Biology: DNA RNA Protein Genes code for…. Proteins which lead to function!. Chromatic Vision: Cone Cells Cone cells in the retina of the eye allow light of different wavelengths to be interpreted as color in the brain. The following slides describe how this pathway works. The Brain Light Waves Color The Cone cell • To produce the signal for color vision, retinal must stimulate the opsin protein but this cannot occur while the retinal molecule is in its cis- conformation. • When 11-cis-retinal absorbs a photon (a basic unit of light), it changes from 11-cis-retinal to All-trans-retinal. • All-trans-retinal stimulates the opsin in the membrane of the cone cell. • The cone cell sends a signal to the brain, resulting in vision. Opsin Image modified from Scientific American, April 09 All-trans-retinal 11-cis-retinal Opsin • To produce the signal for color vision, retinal must All-trans-retinal stimulates the opsin in membrane The cone cell sends aabsorbs signal toa the brain, resulting When 11-cis-retinal photon (athe basic unitinof stimulate the opsin protein but this cannot occur while of the it cone cell. vision. light), changes from 11-cis-retinal to All-trans-retinal. the retinal molecule is in its cis- conformation. The Cell Biology of Color Vision in Monkeys • A retinal chromophore opsin molecule is activated by a photon of light. This in turn stimulates the opsin protein that tells the cone cell to send a signal to the brain. The Role of Opsins There are three types of opsins: Short Wave Sensitive (SWS) Medium Wave Sensitive (MWS) Long Wave Sensitive (LWS) An individual possessing only SWS and MWS opsins will have dichromatic vision. An individual possessing SWS, MWS and LWS opsins will have trichromatic vision. How Does Color Vision Work? How Does Color Vision Work? - When cone cells with the MWS opsin protein are stimulated, green color is perceived by the brain. - When cone cells with the LWS opsin protein are stimulated, red color is perceived by the brain. - When cone cells with the SWS opsin protein are stimulated, blue color is perceived by the brain. - When cone cells with the MWS opsin protein are stimulated AND cone cells with the LWS opsin are stimulated, yellow color is perceived by the brain. How Does Color Vision Work? - When cone cells with the MWS opsin protein are stimulated AND cone cells with the SWS opsin are stimulated, violet color is perceived by the brain. - When cone cells with the SWS opsin protein are stimulated AND cone cells with the LWS opsin are stimulated, cyan color is perceived by the brain. - When all cone cells are stimulated in equal proportions, white light is perceived by the brain. - We perceive different shades of light when our different types of cone cells are stimulated in different proportions. Chromatic Vision: Opsins What is the building block ( ________mer) of an opsin protein? 3D Visualization Chromatic Vision: Opsins 3D Visualization 2D Visualization The opsin protein is composed of a string of amino acids. Each green dot in the 2D visualization represents one amino acid. Opsin Structure MWS opsin LWS opsin The LWS opsin differs from the MWS opsin in three significant places in the amino acid sequence: Position 180: alanine to serine Position 277: phenylalanine to tyrosine Position 285: alanine to threonine Opsin Structure The LWS opsin differs from the MWS opsin in three significant places in the amino acid sequence: Position 180: alanine to serine Position 277: phenylalanine to tyrosine Position 285: alanine to threonine MWS opsin LWS opsin Opsin Response to Light The responses to light of each opsin protein (S, M and L) in trichromats are shown to the right. Note how similar the curves look for M and L. The L curve is shifted by about 30 nm response maximum to the right (longer wavelength). Opsin Response to Light A third opsin provides another channel for sending color signals to the brain. Three opsin proteins allow the eye to detect a richer variety of light wavelengths resulting in the ability to distinguish more colors. The Genetics of Color Vision in Monkeys The Genetics of Color Vision • The section of DNA on a chromosome that codes for an opsin protein is called an opsin gene. Location of Opsin Genes The gene coding for the SWS opsin protein is located on chromosome #7. The gene coding for the MWS and LWS opsins are located on the X-chromosome. Evolution of LWS Opsin Gene The LWS gene arose through gene duplication and gene mutation of the MWS gene on the Xchromosome. Origin of the LWS Opsin Gene The LWS gene arose through gene duplication and gene mutation of the MWS gene on the Xchromosome. Gene Duplication Unequal Crossing Over (Meiosis, Prophase 1) Origin of the LWS Opsin Gene The LWS gene arose through gene duplication and gene mutation of the MWS gene on the Xchromosome. Origin of the LWS Opsin Gene The LWS gene arose through gene duplication and gene mutation of the MWS gene on the Xchromosome. The MWS Opsin Gene The MWS Opsin Gene 1092 Nucleotides The MWS Opsin Gene GTCGTTAGATAG 1092 Nucleotides MWS Opsin Gene vs. LWS Opsin Gene Each opsin gene is exactly the same length (1092 nucleotides) MWS Opsin Protein vs. LWS Opsin Protein These 1092 nucleotides undergo transcription and translation and result in a protein that is 364 amino acids in length. MWS Opsin Gene vs. LWS Opsin Gene (mutations at the nucleotide level that result in protein functional changes) GT TA GA • Three simple substitution mutations change the properties of the opsin protein. • Now, rather than being maximally stimulated at ~534nm, the resulting opsin protein is maximally stimulated at ~564nm. What difference does this make at the protein level? Evolution of LWS Opsin Gene The LWS gene arose through gene duplication and gene mutation of the MWS gene on the Xchromosome. Fact or Fiction? A monkey researcher in South America discovered that some monkey females are trichromatic. 1. 2. 3. 4. Definitely Fact Possibly Fact Possibly Fiction Definitely Fiction The Case of Trichromatic Females Genes code for opsin proteins; the opsin proteins facilitate color vision. Genes code for opsin proteins; the opsin proteins facilitate color vision. • Some new world monkey species have two different MWS alleles. If a female is heterozygous for these alleles she can produce three different types of opsin protein. This means that SOME females in SOME new world species are trichromatic. Females that are homozygous for the MWS gene on the xchromosome are dichromatic. The Phylogenetics of Color Vision in Monkeys Biogeography of Global Monkeys Photo: Frans de Waal, M Arunprasaad, D Wright, P Gonnet, L DeVoldor, W Endo Monkeys of the World Phylogenetics – Exploring Relationships Among Species Geology: Plate Tectonics and Drift Wooly Monkey Spider Monkey Sakis Marmoset Owl Monkey Squirrel Monkey Capuchin Colobus Langur Mona Mangabey Baboon Rhesus Gibbon Orangutan Gorilla Chimpanzee Human Continents Split 50 Million Years Ago Color Vision Evolves! Gene Duplication and Mutation Primates In New/Old World 55 Million Years Ago Rise of Primates 75 Million Years Ago Ancestral Characteristic • An Ancestral Characteristic is a characteristic shared through common ancestry. A characteristic that is thought to have also been present in the common ancestor. • In primates for example DICHROMATIC vision would be considered an “ancestral characteristic” while trichromatic vision would be considered a derived characteristic (one not present in the common ancestor of 2 groups) Wooly Monkey Spider Monkey Sakis Marmoset Owl Monkey Squirrel Monkey Capuchin Colobus Langur Mona Mangabey Baboon Rhesus Gibbon Orangutan Gorilla Chimpanzee Human Continents Split 50 Million Years Ago Color Vision Evolves! Gene Duplication and Mutation Primates In New/Old World 55 Million Years Ago Rise of Primates 75 Million Years Ago Day 3 Questions