* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Magnetism
Magnetosphere of Saturn wikipedia , lookup
Van Allen radiation belt wikipedia , lookup
Geomagnetic storm wikipedia , lookup
Friction-plate electromagnetic couplings wikipedia , lookup
Edward Sabine wikipedia , lookup
Mathematical descriptions of the electromagnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic stripe card wikipedia , lookup
Neutron magnetic moment wikipedia , lookup
Magnetometer wikipedia , lookup
Electromotive force wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic monopole wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Magnetotactic bacteria wikipedia , lookup
Earth's magnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Giant magnetoresistance wikipedia , lookup
Magnetoreception wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Magnetohydrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Magnetotellurics wikipedia , lookup
Multiferroics wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnet wikipedia , lookup
Eddy current wikipedia , lookup
Superconducting magnet wikipedia , lookup
Force between magnets wikipedia , lookup
Magnetochemistry wikipedia , lookup
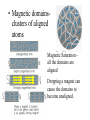
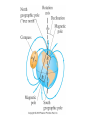
Magnetic field – Region where a magnetic influence (force) can be felt. Lines are drawn to represent the strength and direction of the field. Field is represented from N to S. Magnetic Forces • Magnetic forces, like electrical forces, are forces that act at a distance. (Objects do not have to be in contact.) • Like poles repel each other; opposite poles attract. Magnetic Poles • North–seeking poles- point northward. • South-seeking poles – point southward. Important difference between electric charges and magnetic poles is that electric charges can be isolated, but magnetic poles cannot. Domain Theory • All magnetism is due to the motion of electrons. • Electrons spin, like the earth, setting up magnetic poles. (paramagnetism) • Electrons revolve around the nucleus, like the earth around the sun. (diamagnetism) • Electrons are paired in orbitals. Paired electrons spin opposite directionscreating opposite magnets. The magnetic poles therefore cancel each other. Unpaired electrons create stronger magnets. (ferromagnetism) • Magnetic domainsclusters of aligned atoms Magnetic Saturation – all the domains are aligned Dropping a magnet can cause the domains to become unaligned. Select your answer a or b and explain why. DO NOT COPY the questions. Answer each with an illustration (drawing.) 1. What is the advantage of using a horseshoe magnet over a bar magnet –assuming the two are identical as bar magnets? 2. You are required to build a model of the Earth and its magnetic field using a ball of clay and a bar magnet. You will be forming the clay Earth around the magnet. What is the orientation (direction) of the magnet? Concept check 1: 1. Must every magnet have a north and south pole? Explain. 2. How can a magnet attract a piece of iron that is not magnetized? 3. Why will a magnet not pick up a penny or a piece of wood? 4. If you break a magnet have you destroyed it? 1. An iron nail is strongly attracted to the north end, the south end or both ends of a magnet equally strong. 2. Magnetism is due to the motion of the electron as they __________ and ______________. 3. Several nails dangle from the north pole of a magnet. The induced pole on the top of the first nail is______. The induced pole on the bottom of the lowestmost nail is _______. 4. A moving electron has a ___________ field and an ___________field around it. 5. Magnetic field lines show the ________ and the __________ of the field. 6. A magnetic field goes from _____ to ____. 7. Paramagnetism is due to _________. Diamagnetism is due to ____________. Ferromagnetism is due to _____________. Magnetism and Current • What causes all magnetism? • What is current? • Will current cause magnetism? Electromagnets Materials list: wire power supply (current) core (anything from air to metal) The strength of an electromagnet can be increased by •increasing the current in the wire, •increasing the number of turns of wire, or •by using a metal core. Lenz’s Law The current induced in a wire is such as to oppose the force that induced it. Generator Mechanical energy electrical energy Motor Electrical energy Mechanical energy Magnetism vs. electricity Both due to electrons Both force at a distance Both like repel unlike attract BUT magnetic poles cannot be separated Magnetism Domain Theory Paramagnetism- weak attraction – due to spin of electrons Diamagnetism – weak repulsiondue to revolving electrons Ferromagnetism – strong-due to unpaired electrons