* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download X-Ray imaging Used in many different ways in medical diagnosis. A
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neurogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Functional magnetic resonance imaging wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
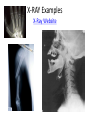
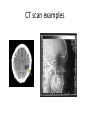
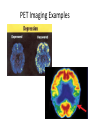
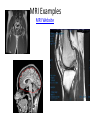
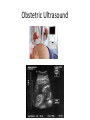
Medical Imaging • • • • • X-rays CT scans MRIs Ultrasounds PET scans X-Ray Imaging * Radiation passes through the body part & strikes a sheet of sensitive film * X-rays penetrate tissues varyingly, according to the tissue’s composition Example: * Calcium rich bone restricts radiation Resulting in white images on the X-ray film * Air filled lungs allow nearly all X-rays to strike the film, resulting in a black film image X-RAY Examples X-Ray Website CT or CAT scan: CT (CAT) (Computerized Axial Tomography) scanner * Special kind of X-ray machine * Instead of sending out a single X-ray through your body, as with ordinary X-rays, beams of rays are sent simultaneously from different angles How does a CT scanner work? Beams that have passed through less dense tissue (lungs) will be stronger, whereas, beams that have passed through denser tissue (bone) will be weaker A computer then uses this information to work out the relative density of the tissues examined. Each set of measurements made by the scanner is, in effect, a cross-section through the body CT Website CT scan examples PET Scan Imaging • PET = Positron Emission Tomography (PET) scan – Illustrates how the organs/tissues inside your body are actually functioning – Radioactive chemical (radiotracer) is injected into an arm vein • Tracer travels through the body and is absorbed by the organ/tissues – PET machine detects and records the energy given off by the tracer and a computer converts this energy into 3D pictures – A physician can then look at cross-sectional images of the body organ from any angle in order to detect any functional problems PET Scans Detect • How effective a patient’s treatment plan is, allowing the course of care to be adjusted, if necessary • Cancer • Heart problems – Coronary artery disease – Damage to the heart following a heart attack • Brain disorders – Brain tumors, memory disorders, seizures • Other central nervous system disorders as well as blood flow, oxygen use, and glucose metabolism • Cellular level metabolic changes occurring in an organ or tissue – Unlike a CT or MRI which only detects the changes later, as the disease begins to cause changes in the structure of organs or tissues PET Scan Website PET Imaging Examples MRI Scans • MRI = Magnetic Resonance Imaging • Use magnetic and radio waves • Meaning, there is no exposure to X-rays or any other damaging forms of radiation • Radio waves, 10,000-30,000x stronger than the magnetic field of the earth, are sent through the body, forcing the body's atoms’ nuclei (hydrogen atoms from water) into a different position, and send out radio waves of their own. The scanner picks up these signals and a computer turns them into a picture. MRIs Provide • Pictures of almost all the different types of tissues in the body • Tissues – Least number of hydrogen atoms, (bones), turn out dark – Many hydrogen atoms, (fatty tissue), look much brighter • Clear pictures of the brain & spinal cord (even when surrounded by bone) • The best technique for – Finding tumors in the brain, or abnormal tissue that occurs if someone has MS, bleeding in the brain, or find out if the brain tissue has suffered lack of oxygen, after a stroke • Pictures/information in regards to – Heart defects, as well as, changes in the thickness of the heart muscle following a heart attack – Joints, spine and sometimes the soft parts of your body, such as the liver, kidneys and spleen MRI Examples MRI Website Ultrasounds • Use high-frequency sound waves • Reflected sound wave echoes are recorded and displayed as a real-time visual image. No ionizing radiation (X-ray) is involved • Obstetric ultrasound – Refers to the specialized use of sound waves to visualize and thus determine the condition of a pregnant woman and her embryo or fetus • Useful way of examining many of the body's internal organs, including but not limited to the heart, liver, gallbladder, spleen, pancreas, kidneys and bladder • Ultrasound images are captured in real time, thus they can show movement of internal tissues and organs and enable physicians to see blood flow and heart valve functions. This can help to diagnose a variety of heart conditions and to assess damage after a heart attack or other illness Ultrasound Website Obstetric Ultrasound