* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Proteins and Mutations – Revision Pack (B3)
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
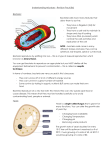
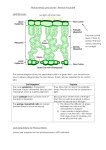
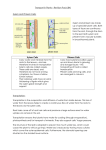
Proteins and Mutations – Revision Pack (B3) Types of Proteins: Proteins are made of long chains of amino acids. Each protein has its own number and sequence and number of amino acids, which results in differently shaped molecules, which have different functions. The function of proteins includes: - Structural – used to build cells and tissues (limited to collagen) Hormones – carry messages to control a reaction (limited to insulin) Carrier Molecules – self explanatory (limited to haemoglobin which carries oxygen) Enzymes Enzymes: Describe enzymes as: - Biological catalysts (speed up reactions in the body) Catalysing chemical reactions occurring in living cells: respiration, photosynthesis, protein synthesis Having a high specificity for their substrate. The substrate molecule fits into the active site like a key into a lock: - This is why enzymes are described as working in a ‘lock and key mechanism’ It also explains why each enzyme can only work with a certain substrate. This is called specificity and happens because the substrate must be the right shape to fit into the active site Page 1 of 10 Proteins and Mutations – Revision Pack (B3) Enzymes work best at a particular temperature and pH. This is called optimum and any change away from either optimum will slow the reaction down. When explaining how enzyme activity is affected by pH and temperature, include: - lower collision rates at low temperatures denaturing at extremes of pH and high temperatures denaturing as an irreversible change inhibiting enzyme function denaturing changing the shape of the active site It’s possible to work out how temperature affects the rate of reaction by calculating the temperature coefficient, called Q 10 . This is done for a 10oC change in temperature using: Q 10 = rate at higher temperature Rate at lower temperature Mutations: Gene mutations may lead to the production of different proteins. Mutation may occur spontaneously but can be made to occur more often by radiation or chemicals. Mutations are often harmful but may be beneficial or have no effect. Only some of the full set of genes is used in any one cell; some genes are switched off. The genes switched on determine the functions of a cell. Changes to genes alter, or prevent the production of the protein which is normally made, this is because they change to base code of DNA, and so change the order of amino acids in the protein. Page 2 of 10 Proteins and Mutations – Revision Pack (B3) PPQ(1): OCR Gateway B1 B2 B3 January 2012 Page 3 of 10 Proteins and Mutations – Revision Pack (B3) PPQ(2): OCR Gateway B1 B2 B3 January 2013 Page 4 of 10 Proteins and Mutations – Revision Pack (B3) PPQ(3): OCR Gateway B1 B2 B3 June 2012 PPQ(4): OCR Gateway B1 B2 B3 June 2013 Page 5 of 10 Proteins and Mutations – Revision Pack (B3) PPQ(5): OCR Gateway B3 C3 P3 January 2013 PPQ(6): OCR Gateway B3 C3 P3 June 2013 Page 6 of 10 Proteins and Mutations – Revision Pack (B3) PPQ(7): OCR Gateway B3 C3 P3 June 2012 Page 7 of 10 Proteins and Mutations – Revision Pack (B3) Mark Schemes: PPQ(1): PPQ(2): PPQ(3): Page 8 of 10 Proteins and Mutations – Revision Pack (B3) PPQ(4): PPQ(5): PPQ(6): Page 9 of 10 Proteins and Mutations – Revision Pack (B3) PPQ(7): Page 10 of 10