* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 9 Vocab
Vasopressin wikipedia , lookup
Gynecomastia wikipedia , lookup
Hypothyroidism wikipedia , lookup
Neuroendocrine tumor wikipedia , lookup
Sex reassignment therapy wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (female-to-male) wikipedia , lookup
Graves' disease wikipedia , lookup
Hyperthyroidism wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (menopause) wikipedia , lookup
Bioidentical hormone replacement therapy wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (male-to-female) wikipedia , lookup
Hyperandrogenism wikipedia , lookup
Hypothalamus wikipedia , lookup
Pituitary apoplexy wikipedia , lookup
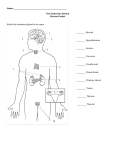
Chapter 9 Vocabulary 1. Acromegaly – results when hypersecretion continues to occur even after long bone growth has ceased; body proportions are not normal 2. Androgens – male sex hormones 3. Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) – causes kidneys to reabsorb more water from the forming urine, thus decreasing urine volume and increasing blood volume and blood pressure 4. Cretinism – iodine deficiency in children that results in dwarfism (abnormal proportions) and mental retardation 5. Endocrinology – the study of hormones 6. Endocrine – gland that secretes hormones that are distributed by blood to be used within the body 7. Epinephrine – adrenal hormone that increases rate of metabolism and constricts blood vessels 8. Erythropoietin – kidney hormone that stimulates the production of red blood cells 9. Exocrine – gland that secretes products to the outside of the body via ducts 10. Follicle-‐stimulating hormone (FSH) – pituitary hormone that stimulates the development of the ovaries and sperm development in the testes 11. Gastrin – stomach hormone that stimulates the release of stomach acid 12. Gigantism – hypersecretion of growth hormone which causes a person to be extremely tall, reaching 8 to 9 feet in height; body proportions are normal 13. Glucagon – pancreas hormone that raises blood sugar levels 14. Goiter – an enlargement of the thyroid gland that results when the diet is deficient in iodine 15. Growth hormone (GH) – hormone that directs growth of skeletal muscles and long bones of the body 16. Hormonal stimuli – when endocrine glands are forced into action by other hormones 17. Hormones – chemical substances that are secreted by endocrine cells into the extracellular fluids and regulate the metabolic activity of other cells 18. Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) – hormone produced by the developing embryo that stimulates estrogen production so that the lining of the uterus is not sloughed off in menses 19. Humoral stimuli – when changing blood levels of certain ions and nutrients stimulate hormone release 20. Insulin – pancreas hormone that reduces blood sugar levels 21. Luteinizing hormone (LH) – pituitary hormone that triggers ovulation in females and testosterone production in men 22. Masculinization – condition resulting from overproduction of sex hormones 23. Melatonin – hormone produced by the pineal gland that plays a large role in the sleep-‐wake cycle. 24. Menopause – a decline in the efficiency of the ovaries in old age, resulting in the loss of the ability to bear children 25. Negative feedback – mechanism in which hormone secretion is triggered by an internal stimulus and secretion of this hormone stops when this stimulus no longer exists 26. Neural stimuli – when nerve fibers stimulate hormone release 27. Oxytocin – pituitary hormone that stimulates powerful uterine contractions during labor and sexual intercourse 28. Pituitary dwarfism – hyposecretion of growth hormone which causes a person to develop to a size much smaller than the average human (max height of 4 ft), even though body proportions are normal 29. Placenta – temporary organ formed in the uterus of pregnant women that produce several hormones that maintain pregnancy 30. Polydipsia – excessive thirst resulting from water loss; a symptom of diabetes 31. Polyphagia – hunger due to inability to use sugars and the loss of fat and proteins from the body; a symptom of diabetes 32. Polyuria – excessive urination to flush out glucose; a symptom of diabetes 33. Prolactin – pituitary hormone that stimulates the production of milk by the mother’s breasts 34. Relaxin – placental hormone that relaxes the pelvis, thus easing the birth passage 35. Steroids – hormones made from cholesterol 36. Target cells – the specific target of a specific hormone 37. Testosterone – male sex hormone that produces growth and maturity of the reproductive system and development of secondary sexual characteristics 38. Tetany – uncontrollable spasms of the muscles 39. Thyroid hormone – controls the rate at which glucose is burned 40. Tropic hormones – hormones that stimulate their target organs to secrete their own hormones which effect the body