* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download red blood cell (rbc) membrane and enzyme disorders
Survey
Document related concepts
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Paracrine signalling wikipedia , lookup
Lipid signaling wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
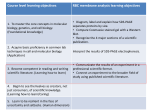
RED BLOOD CELL (RBC) MEMBRANE AND ENZYME DISORDERS Joan Lluis Vives Corrons Joan-Lluis Red Cell Pathology Unit Hospital Clinic i Provincial Universty of Barcelona 1 HEREDITARY HAEMOLYTIC ANAEMIA - GENERAL FEATURES Anemia, reticulocytosis, Anemia reticulocytosis elevated bilirubin and LD levels, decreased haptoglobin levels, direct antiglobulin test (Coombs) negative Chronic hemolysis vs periodic hemolytic episodes Palor,icterus,gall stones,splenomegaly,dark urines HAEMOLYTIC ANAEMIA - SIMPLIFIED FLOWCHART - 2 Red blood cell membrane disorders DISORDERS RBC MEMBRANE/CYTOSKELETON - Morphological abnormalities- Red blood cell membrane and enzyme RBC MEMBRANE AND ENZYME DISORDERS disorders – why discriminate? -WHY DISCRIMINATE ?Diagnosis Therapy - prevention of certain food & medications - splenectomy (Genetic) counseling - membrane disorders: autosomal dominant - enzyme disorders: autosomal recessive recessive, some X X-linked linked To better understand pathophysiology - future (gene) therapies 3 thethe red cell Multiprotein complexes complexesin in RBC membrane Plasma membrane & Integral proteins Anchoring proteins Cytoskeletal proteins Salomao M et al. PNAS 2008;105:8026-8031 A deficiency or dysfunction in any one of these membrane proteins can weaken or destabilize the cytoskeleton, resulting in membrane surface area loss and a reduced life span: hemolysis Horizontal the RBC membrane Red bloodInteractions cell membrane in disorders Spectrin-Actin-Protein 4.1 junctional complex 4 Horizontal the RBC membrane Red bloodInteractions cell membrane in disorders HEREDITARY ELLIPTOCYTOSIS Hereditary elliptocytosis (normal osmotic fragility) 5 Hereditary pyropoikilocytosis HEREDITARY PYROPOIKILOCYTOSIS (decrased membrane heat stability) Severe form of elliptocytosis Presentation usually in neonatal period (severe anemia) Homozygous/compound heterozygous for spectrin mutations Vertical Interactions in disorders the RBC membrane Red blood cell membrane 6 Hereditary spherocytosis HEREDITARY SPHEROCYTOSIS Vesiculation of unsupported surface components cause a progressive reduction in membrane surface area Red cell shape changes from a flexible, deformable biconcave disc to a spherical, poorly deformable (fragile) red cell – the spherocyte Hereditary spherocytosis HEREDITARY SPHEROCYTOSIS Most common cause of inherited chronic hemolysis in Northern Europe and North America Prevalence EU: 1:3000 America. Inheritance:Dominant: 75%, recessive: 25% Ankyrin (50-60%), spectrin (20%), and Band 3 (15-20%),Protein 4,2 defects Severity of hemolysis depends on the extent of decrease in membrane surface area (contents of spectrin) 20% mild, 60% moderate HS, 10% moderate severe, 3-5% severe HS Excellent response to splenectomy 7 Laboratorydiagnosis diagnosisofofRBC red cell membrane Laboratory membrane disorders disorders 1. Screening tests RBC Morphology RBC Osmotic fragility test Increased RBC OF HERDITARY SPHEROCYTOSIS OSMOTIC FRAGILITY TEST ↑ NaCl Water NORMAL CONTROL HEREDITARY SPHEROCYTOSIS HYPOTONIC LYSIS OF RBCs 8 Laboratorydiagnosis diagnosisofofRBC red cell membrane Laboratory membrane disorders disorders 2. Special diagnostic tests - Spectrin (RIA) - EMA (Eosine-5-maleimide) (binds Lys430 of Band 3, Rh(AG), CD47) - SDS-PAGE - Laser-assisted Optical Rotational Cell Analyzer (LORCA)- Viscometry- Example: Spectrin: 100% (ref: 85-115%) EMA: 40% relative fluorescence (ref:> 80%) Red blood cell membrane disorder due to band 3 deficiency Laboratory of RBC membrane disorders Hereditarydiagnosis pyropoikilocytosis 3. Molecular studies Example: SLC4A1 analysis (Anion exchanger 1 or Band 3 gene) 9 Southeast Asian Ovalocytosis (SAO) SOUTHEAST ASIAN OVALOCYTOSIS (SAO) Dominant inheritance Very common in malaria-endemic areas in Asia Asia, 5-25% SAO SLC4A1 gene is due to a 27 bp deletion (amino acids 400-408) in Band 3, at the boundary of the cytoplasmic and membrane domains in cis with the Lys56Glu substitution SAO cells are rigid and hyperstable Hemolysis is mild or absent Child, 2 months of age (Molukkan) Hb 5.1 mmol/L, MCV 81, Retics N Hereditary Stomatocytosis HEREDITARY STOMATOCYTOSIS A group of very rare, dominantly inherited hemolytic anemias with abnormal membrane permeability to univalent cations - Hydrocytosis - Xerocytosis - Cryohydrocytosis - Familial pseudohyperkaliemia p yp Splenectomy is contra-indicated because of increased risk of trombotic complications ! 10 Hereditary red blood cell ENZYME enzyme disorders HEREDITARY RBC DISORDERS A red blood cell enzyme disorder should be assumed in cases of persistent normocytic hemolytic anemia in which hemoglobin abnormalities and antiglobulin reactions have been cluded,spherocytes are absent, and osmotic fragility is normal Red blood cell enzymopathies cause hereditary nonspherocytic hemolytic anemia (HNSHA) METABOLIC PATHWAYS OF THE ERYTHROCYTE Glycolytic pathway GLUCOSE Enzymes Lactate ATP Haemoglobin 11 Hereditary pyropoikilocytosis RED BLOOD CELL ENZYMES Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase* Gluthathione peroxidase Gluthathione reductase Glutathione synthetase y Glutathione-S-transferase Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase Glyoxalase I Hexokinase * Hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyl transferase ITPase Lactate dehydrogenase NADPH di diaphorase h Phosphofructokinase Phosphoglucomutase Phosphoglycerate kinase Pyrimidine-5’-nucleotidase * Pyruvate kinase * Triosephosphate isomerase 6-Phosphogluconate dehydrogenase 6-Phosphogluconolactonase Acetylcholinesterase Adenine phophoribosyl transferase Adenosine deaminase Adenylate kinase Aldolase AMP deaminase Bisphosphoglycerate mutase Carbonic anhydrase I Carbonic anhydrase II Catalase Cytochrome b5 reductase δ ALA d δ-ALA dehydrase h d Enolase Galactokinase Galactose-1-P-uridyltransferase γ-Glutamylcysteine synthetase Glucose phosphate isomerase * Enzymatic activity strongly age-dependent ENZYMOPATHIES WITH CLEAR CAUSE Hereditary pyropoikilocytosis EFFECT RELATIONSHIP Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase * Gluthathione peroxidase Gluthathione reductase Glutathione synthetase Glutathione-S-transferase Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase Glyoxalase I Hexokinase * Hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyl transferase ITPase Lactate dehydrogenase NADPH diaphorase Phosphofructokinase Phosphoglucomutase Phosphoglycerate kinase Pyrimidine-5’-nucleotidase * Pyruvate kinase * Triosephosphate isomerase 6-Phosphogluconate dehydrogenase 6-Phosphogluconolactonase Acetylcholinesterase Adenine phophoribosyl transferase Adenosine deaminase (hyperactivity) Adenylate kinase Aldolase AMP deaminase Bisphosphoglycerate mutase Carbonic anhydrase I Carbonic anhydrase II Catalase Cytochrome b5 reductase δ-ALA dehydrase Enolase Galactokinase Galactose-1-P-uridyltransferase γ-Glutamylcysteine synthetase Glucose phosphate isomerase 12 HEREDITARY RBC Hereditary red blood cellENZYMOPATHIES enzymopathies In general: two groups Enzyme deficiencies of glycolysis and nucleotide metabolism I I. continuously impaired ATP generation: → lack of sufficient energy ATP is required for maintenance of: - glycolysis - electrolyte red cell/plasma gradient - glutathione synthesis phospholipid p p asymmetry y y - membrane p - purine/pyrimidine metabolism → chronic haemolytic anaemia Most common cause: pyruvate kinase (PK) deficiency HEREDITARY RBC Hereditary red blood cellENZYMOPATHIES enzymopathies II. Enzyme deficiencies of the hexose monophosphate shunt and glutathione metabolism IInadequate d t levels l l off reduced d d glutathione l t thi (GSH) (GSH): inability to withstand oxidative stress GSH is required for: - maintenance of hemoglobinʼs iron in itʼs functional (ferrous) state - protection of metabolic enzymes and membrane b proteins t i ffrom oxidative id ti d denaturation t ti → acute hemolytic crisis induced by oxidant drugs, food (favism), infection, physiologic stress Most common cause: glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency 13 Hereditary red blood cellENZYMOPATHIES enzymopathies HEREDITARY RBC Metabolic dysfunction depends on: - Importance of the affected enzyme (rate-limiting enzymes) - Functional abnormalities (kinetic properties) of the mutant enzyme - Stability of the mutant enzyme (RBC lacks biosynthesis) - Possibility of compensation for the deficiency by isoenzyme overexpression or use of alternative pathways Most enzymopathies are associated with extravascular hemolysis Hereditary red blood cellENZYMOPATHIES enzymopathies HEREDITARY RBC Clinically highly heterogeneous! Fully compensated hemolysis (without anemia) to severe hemolytic anemia requiring regular transfusions Presentation at later age vs neonatal death (hydrops fetalis) No correlation between residual enzyme activity and clinical severity Exacerbation of hemolysis during infection In some cases also non-hematological symptoms: e.g. myopathy in phosphofructokinase (PFK) deficiency, severe neuropathy in triosephosphate isomerase (TPI) deficiency 14 PYRUVATE KINASE DEFICIENCY Pyruvate kinase (PK) Key enzyme of glycolysis: sole source of energy for the red blood cell Catalyses the irreversible phosphoryl group transfer from phosphoenolpyruvate to ADP, yielding pyruvate + ATP Mammals: 2 genes – 4 isozymes PKM PK-M1 (muscle, heart, brain) PK-M2 (leukocytes, platelets, erythroblasts) PKLR PK-L (liver) PK-R (red blood cell) Clinical symptoms confined to the red blood cell PYRUVATE KINASE DEFICIENCY Most common cause of hereditary chronic non-spherocytic hemolytic anemia Rare, but most frequently occuring abnormality of glycolysis Autosomal recessive disorder Estimated prevalence: 1:20,000 (white population) Worldwide distribution Highly variable phenotypic expression severe: mild diagnosed at birth (hydrops fetalis) fully compensated hemolytic anemia diagnosed later in life 15 EFFECTS PYRUVATE Effects ofOF pyruvate kinase KINASE deficiencyDEFICIENCY Biochemical features of the PK-R deficient red blood cell: - PK enzymatic activity usually decreased ATP levels usually decreased 2,3-DPG levels increased due to metabolic block at PK step ??? Red cell destruction - Precise mechanism of red cell destruction is unknown - ATP depletion initiates a series of events leading to premature destruction of (young!) PK-deficient PK deficient red cells in the spleen Premature destruction as well as apoptosis of RBC progenitors may contribute to the pathogenesis of PK- R deficiency GLUCOSE 6 PHOSPHATE DEHYDROGENASE (G6PD) DEFICIENCY 1‐ X CHROMOSOME LINKED HEREDITARY TRANSMISSION Women (heterozygous o homozygous) Men (hemicygotes) 2‐ PREVALENCE 1/10.000 3‐ NO CLINICAS MANIFESTATIONS 4‐ HAEMOLYTIC ANAEMIA Acute (crisis) in case of oxidative effect Chronic (sporadic forms) 5‐ PROTECTION AGAINST THE MALARIA PARASITE 6‐ HIGH GENETIC POLYMORPHISM 16 G6PD DEFICIENCY ↓ GSH SKISTOCYTES “BITTED” CELLS EXCCENTROCYTES G6PD DEFICIENCY AND MALARIA Geographical areas with endemic Malaria (present or past) 17 G6PD DEFICIENCY: HAEMOLYTIC TRIGGERS 1. Drug ingestion • Antimalarial A ti l i l d drugs • Sulphonamides • Phenacetin • Vitamin K g (favism) ( ) 2. Fava beans ingestion 3. Infections 4. Metabolic acidosis ENZYMOPATHIES: DIAGNOSIS AND PITFALS Diagnostics and pitfalls Diagnosis Demonstration of the specific enzyme defect by measuring red blood cell enzyme activities Molecular characterization Pitfalls Blood transfusions Reticulocytosis: some red cell enzymes are red cell age dependent (HK, PK, G6PD, aldolase, P5N) → density gradient separation Leucocyte and platelet contamination Enzyme deficiencies may be less pronounced under optimized in vitro conditions → low [S] assays Storage and shipment conditions 18 Hereditary pyropoikilocytosis FAMILY SCREENING COINHERITANCE OF TWO DIFFERENT RBC MTATIONS AKNOWLEDGEMENTS To all the members of the Biological Haematology Department and Red Cell Pathology Unit Hospital Clinic i Provincial.University of Barcelona Assumpciò Pujades Josep-Lluis Aguilar Dolors Colomer Montserrat Corbella Mar Mañu Pereira Nuria Radó 19