* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plant tissues
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
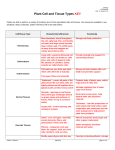
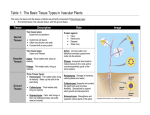
Plant tissues Asmaa alfarajeen Heba Al-Tamimi Plant tissues • A tissue :is a group of cells that perform a common function Plant tissues Meristematic tissues Apical meristems Lateral meristems Permanent tissue Simple Permanent tissues Complex permanent tissues Protective tissue Epidermis Cork (phellem) TYPES OF PLANT TISSUE Meristematic tissue Apical meristems Lateral meristems Permanent tissue 1. Simple permanent tissue Parenchyma chlorenchyma Collenchyma Sclerenchyma 2. Complex permanent tissue Xylem Phloem Protective tissue Epidermis Cork (phellem) /Periderm Meristematic tissue Meristematic tissues are composed of embryonic, undifferentiated cells that play a critical role in plant growth Have distinguish feature : without any intercellular spaces thin cell wall large nucleus small or no vacuoles Meristematic tissues occur in two regions Apical meristem growing points of stem and root give rise to primary permanent tissue (primary growth) Lateral meristem in cambium producing secondary permanent tissues (secondary growth) Meristematic tissues – localized regions of cell division Apical Meristems Primary or Transitional Meristem Primary growth Protoderm gives rise to epidermis Ground meristem gives rise to ground tissue o Procambium gives rise to 1 vascular tissue Lateral Meristems o Vascular cambium 2 vascular tissue Cork cambium or phellogen periderm Permanent tissue Simple permanent tissue Parenchyma chlorenchyma Collenchyma Sclerenchyma Complex permanent tissue Xylem Phloem Monocot Monocots stem C.S Dicot Dicots Monocots Dicot Epidermis Structure: One cell thick covers the whole of the primary plant body Secrete a waxy substance to form a layer of cuticle Function: protection Root hair Parenchyma Distribution in cortex, pith & packing tissue of vascular tissues ( xylem and phloem) Shape usually spherical unspecialised cells thin cell wall Function store food ( starch) Photosynthesis intercellular space around parenchyma cells allow exchange of gases respiration Parenchyma thin walled & alive at maturity. Parenchyma Chlorenchyma parenchyma with numerous chloroplasts (common in leaves). Collencyma Distribution outer region of cortex in young stems Shape shape similar to parenchyma but thickened cell wall at he corners of cell elongated Collencyma thick-walled but flexible and strong, usually right below the epidermis of a leaf or stem, used for support in stems and leaves of non-woody or young plants. Collenchyma thick walled & alive at maturity Collenchyma Sclerenchyma Structure heavily thickened with deposits of lignin (a complex substances with great strength in the cell wall), even thickening of cell wall. mature sclerenchyma cells are dead (stained red under microscope) Function provide support Sclerenchyma 2. Permanent Tissues B. Complex/Conducting Permanent Tissues made of more than type of cell. include the xylem (vascular tissue), phloem (vascular tissue) Sieve Tube Element Companion Cell Xylem Vessel Air Space Compound plant tissue Plant tissues consists of more than one types of cell e.g. Xylem consist of parenchyma cells fibres(elongated sclerenchyma cells) vessels tracheids Xylem : Function provide mechanical strength give support to plant conduct water and mineral salts Xylem tissues transports water and dissolved substances This tissue is composed of parenchyma, fibers, vessels and/or tracheids, and ray cells. Phloem (Compound plant tissue ) Consist of: Parenchyma Fibers sieve tube element companion cells Function translocation of food no mechanical function Periderm Woody Stems WOODY DICOT STEM Summer Spring Wood Wood Phloem Phloem Fibers Xylem Ray Cortex or Phloem Ray Pith Cork Cambium Cork Annual Ring Primary Xylem Secondary Xylem Vascular Cambium Go To Work ……..