* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Functional Anatomy of the Shoulder
Sex reassignment therapy wikipedia , lookup
Gynecomastia wikipedia , lookup
Hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (female-to-male) wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (menopause) wikipedia , lookup
Hypothyroidism wikipedia , lookup
Neuroendocrine tumor wikipedia , lookup
Bioidentical hormone replacement therapy wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (male-to-female) wikipedia , lookup
Graves' disease wikipedia , lookup
Hypothalamus wikipedia , lookup
Hyperthyroidism wikipedia , lookup
Growth hormone therapy wikipedia , lookup
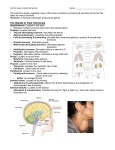
Endocrine and Metabolic Systems Chapter 6 Objectives Identify and discuss the organs of the endocrine and metabolic systems and their function(s) Discuss common illnesses involving the endocrine and metabolic systems signs & symptoms management Glands of the Endocrine System Pituitary-hypothalamus Pituitary Thyroid Parathyroid Adrenal Pancreas Testes Ovaries Endocrine System The endocrine glands secrete hormones regulate the organ systems within the body inhibit or stimulate the release of additional hormones Collectively these hormones work to maintain homeostasis Endocrine System Once a hormone is secreted, it travels through the blood to the target cells designed to receive its message Along the way, hormones bind to specific proteins, which act as carriers The carriers regulate the amount of hormone available to the target cells Endocrine System The target cells have receptors that will only communicate with specific hormones When the hormones reach the target cells, they latch onto the receptors The hormone-receptor connection transmits chemical instructions to the inner working of the cell Pituitary Secretes thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) Works to regulate thyroid function Secretes luteinizing hormone Stimulates ovulation Stimulates release of testosterone Pituitary (cont.) Secretes follicle-stimulating hormone Increases estrogen release in females Increases sperm production in males Secretes Stimulates the kidneys to absorb water Secretes antidiuretic hormone adrenocorticotropic hormone Stimulates the adrenal glands to release cortisol Thyroid Secretes thyroid hormone (T4 and T3) Designed to increase metabolism Adrenal Glands One on top of each kidney Each made up of an inner & outer portion Adrenal Glands Outer portion (adrenal cortex) Secretes corticosteroids aldosterone Cortisol Influences or regulates Fluid balance Immune system Response to stress Sexual development & function Adrenal Glands Inner portion (adrenal medulla) Secretes catecholamines Epinephrine Norepinephrine Increases blood pressure and heart rate when the body responds to stress Glands of the Endocrine System Pancreas Secretes Insulin Glucagon Works to maintain steady levels of glucose in the blood Maintain stores of energy Keeps the body supplied with fuel Glands of the Endocrine System Ovaries Secretes estrogen progesterone Regulates menstrual cycle Produces secondary female sex characteristics Glands of the Endocrine System Testes Secretes testosterone Produces secondary male sex characteristics Regulates sperm production characteristics Involved in protein synthesis General Signs & Symptoms Changes in skin color, texture, or appearance Hyperhydrosis/diaphoresis Body/breath odor Polydipsia/polyuria Arthralgia/myalgia Amenorrhea/impotence General Signs & Symptoms (cont.) Confusion or change in mental function Paresthesia Edema/pitting edema Polyphagia Postural (orthostatic) hypertension Lethargy & fatigue Common Pathology of the Endocrine System Diabetes Type I Type II Hyperthyroidism Hypothyroidism Adrenal insufficiency Growth hormone problems Questions?