* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download (1.5) Square Roots. Compare and Order Real Numbers. Math 8
Vincent's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Georg Cantor's first set theory article wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics of radio engineering wikipedia , lookup
Infinitesimal wikipedia , lookup
Large numbers wikipedia , lookup
Positional notation wikipedia , lookup
Real number wikipedia , lookup
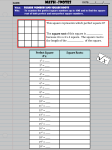
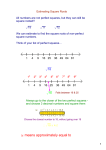
(1.5) Square Roots. Compare and Order Real Numbers. Math 8 Numbers such as 1, 4, 9, 16, and 25 are called _________________, because they are squares of __________. A ______________ of a number is one of its two equal factors. 4 · 4 = 16, so 4 is the _____________ of 16. The symbol √ , called a __________________ , is used to show a __________________ square root. Every positive number has TWO square roots: positive and negative. Positive: √ Negative: Since (5)² = 25, then √ √ Both roots: √ (–5)² = 25, then √ =5 √ = –5 = 5 = 5 and –5 What if it is not a perfect square? The square root of a number that is not a perfect square falls between two _______________ whole numbers. Step 1 Determine whether a number is a perfect square. 1. Is the number 29 a perfect square? Is there a whole number which can be squared to equal 29? _____ Step 2 Find the two consecutive whole numbers between which the √ lies. 2. The number 25 is the closest perfect square _________ than 29. What is √ 3. The number 36 is closest perfect square greater than 29. What is √ 4. √ lies between √ _____________ and √ ? _____ ? _____ . What are the two consecutive whole numbers between which √ lies? Find the two consecutive whole numbers between which the square root of a given number lies. Then circle the nearest integer. √ √ _______ _______ Numbers like √ ,√ ,√ _______ _______ √ _______ _______ , … are called ______________________ ___________ . They have infinite amount of digits after the decimal point without any obvious pattern of repeating digits. Graph and order real numbers Order numbers from least to greatest: , √ , √ , –2.5, √ Begin by graphing the numbers on the number line. Use a calculator to approximate irrational numbers. -3 -2 -1 0 Read the numbers from left to right: 1 2 3 4