* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download What`s Rational and What`s Irrational ? Finding Square Roots of
Infinitesimal wikipedia , lookup
Georg Cantor's first set theory article wikipedia , lookup
Vincent's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Law of large numbers wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics of radio engineering wikipedia , lookup
Large numbers wikipedia , lookup
Positional notation wikipedia , lookup
Fundamental theorem of algebra wikipedia , lookup
Location arithmetic wikipedia , lookup
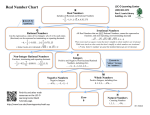
What’s Rational and What’s Irrational ? Rational #s - numbers that can be placed in an a (fraction) where b cannot equal zero b o Repeating Decimals – never end / has a pattern 0.33 -4.62.63 o Terminating Decimals – decimals that END 6.25 3.14 -0.56 Irrational #s – numbers that can not be placed in o No repeating Decimals, no patterns 6.756890… symbol is irrational 2 a form b ** Remember ** Every number is real number Real numbers are both sets of Rational and Irrational numbers Finding Square Roots of Numbers that aren’t Perfect Squares Estimate - first, get as close as you can by finding two perfect square roots your number is between. 2. Divide - divide your number by one of those square roots. 3. Average - take the average of the result of step 2 and the root. 4. Use the result of step 3 to repeat steps 2 and 3 until you have a number that is accurate enough for you. Example: Find the square root of 10 ( ) to 2 decimal places. 1. Find the two perfect square numbers it lies between. 32 = 9 and 42 = 16, so lies between 3 and 4. 2. Divide 10 by 3. 10/3 = 3.33 (you can round off your answer) 3. Average 3.33 and 3.