* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Biology Chapter 1 Study Questions
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
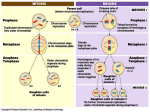
Unit 4 Study Questions Please note these are practice questions!!!! Do not simply answer these questions and feel that you are prepared for the exam. Use these questions as a guide to locate areas where you need more study. The transmission of traits from one generation to the next is known as _____________. The study of heredity and hereditary information is the scope of the field of __________. There are three levels at which geneticists work; list them: A unit of heredity is the _____________. A ____________ refers to the physical location of a gene on a chromosome. Organisms produced by asexual reproduction are __________; genetically identical to the parent. Name the type of reproduction which involves the fusion of gametes._______________ ________ is the diploid number of a human somatic cell. A pair of homologous chromosomes consists of a _______________ chromosome and a ______________ chromosome. __________________ are tests performed to observe cells ploidy levels. These are often used to test for ___________ _____________ such as _____________ ____________. In humans, the 23rd pair of chromosomes is known as the ______________. Males and females differ with respect to this pair how? In the space below draw a synapsed tetrad and label the centromeres, sister chromatids, non-sister chromatids, and chiasmata. 1 The fusion of _______ and egg produce a single cell known as a __________________. What stage of mitosis are the cells arrested to produce a karyotype? In animals, meiosis results in the production of __________; fertilization results in the production of a __________. Name the two processes which occur during meiosis that promote genetic diversity: Name the phases of meiosis in order in the space below: What is a recombinant chromosome? In what phase(s) of meiosis does the process of crossing over occur? In what phase(s) of meiosis does independent assortment occur? Phase of meiosis where each of the following occur: Tetrads lined up at equator of cell______________________________ Synapsis occurs and tetrads form_______________________________ DNA replication occurs______________________________ Period of rest between Meiosis I & II_______________________________ Sister chromatids separate__________________________ Tetrads separate ___________________________________ When a single diploid cell divides by mitosis what is the result? When a single diploid cell divides by meiosis, what is the result? Are the nuclei present following meiosis I haploid or diploid? Assume that a cell (2n=6) divides by meiosis. How many chromatids are present in each daughter nuclei following Meiosis I?________ How many chromosomes are present in each nuclei following Meiosis II? ___________ 2 Meiosis I is said to be a ___________ division while Meiosis II is said to be a ___________ division. For a species with a diploid number of ten, how many different combinations of maternal and paternal chromosomes are possible for gametes? What are punnett squares used for? If you cross a homozygous recessive with a heterozygous individual, what is the chance (percentage) of producing an offspring with the recessive phenotype? ____________ are alternative genes that code for the same character and occupy corresponding positions on homologous chromosomes. Mendel began his experiments with pea varieties that were _________________; meaning that self pollination always resulted in offspring of the same variety as the parent. A _________________ is a genetic cross between an individual exhibiting the dominant phenotype (but of unknown genotype) and an individual with the recessive phenotype. Two purple flowered pea plants were crossed. There were 100 peas produced as offspring. Of these offspring 67, later produced plants with purple flowers and 33 produced plants with white flowers. This suggests that the original parents were _______________. homozygous recessive homozygous dominant heterozygous List three reasons Mendel chose pea plants for his experiments. In the space below, diagram a cross of pea plants with purple and white flowers which begins with a P generation which is true breeding. List the ratios for genotype and phenotype of the F1 generation and the F2 generation. 3 List and define the two genetic principles that Mendel derived using his genetic studies of pea plants. Assume a couple has three children; all three children have brown eyes and blond hair. Both parents are homozygous for brown eyes (BB), but mother is blonde (rr) and the father is a red head (Rr). What is the probability that their next child will be: Brown-eyed and have red hair? Green-eyed and blonde? Compare and contrast incomplete and complete dominance? A phenotypic ratio of 1:2:1 in the F2 generation of a monohybrid cross suggests ___________ dominance Type of inheritance pattern seen with a 9:3:4 phenotypic ratio in the F2 generation _______________. List an example of codominance in humans. In the space below work a dihybrid cross for true breeding pea plants that are: Yellow seeds with green pods X green seeds with yellow pods 4 Name an example of multiple alleles found in humans. If a man with type O blood and a woman with type O blood have a child, what is the percent chance that their child will have : Type A blood_____ Type B blood_____ Type AB blood______ Type O blood______ Cystic fibrosis is a genetic disorder that exhibits an inheritance pattern known as ____________. Cystic fibrosis is common in Americans of ____________ descent. Heterozygotes are phenotypically _________ and are called ____________. What segment of the American population is most susceptible to sickle cell disease? ___________________ Sickle cell disease exhibits _________ dominance and it is a __________ inherited disorder. Name two sex-linked recessive disorders. ________________________ & _______________________ The twisting of a unicorn’s horn is an inherited character. The right-hand twist (R) is dominant to the left hand twist (r). A second gene determines if a horn will be present (H). Unicorns that are homozygous recessive (hh) for the second gene will not have a horn at all. What type of inheritance pattern is exhibited here?_____________________ If a male unicorn named Rambo and female unicorn named Leia are each heterozygous for both genes produce a foal unicorn, what is the probability that the foal will have the following phenotypes: a right handed twist horn_______ no horn__________ a left handed twist horn________ What is the phenotype for Rambo?___________ What is the phenotype for Leia?____________ 5 Name the type of inheritance patter each of the following illustrates: Skin pigmentation in humans_________________________ Achondroplasia ________________________ Sickle cell disease_______________________________ Huntington’s disease __________________________ Hair color in mice____________________________ Pea flower color_________________________________ ABO blood groups____________________________ MN blood groups__________________________________ Cystic fibrosis_____________________________ What is CVS sampling and amniocentesis tests useful for? Which test involves the insertion of a large needle into the amniotic fluid to obtain fetal cells? Which test involves the removal of placental tissue to obtain fetal cells? How many genes are there thought to be in the human genome? Describe the loci of linked genes. Do sex-linked genes follow Mendel’s patterns of inheritance? Name the pattern of inheritance seen in color-blindness. ________________________ Which sex is more likely to exhibit the color blind phenotype?___________________ Bill and Jan have a color blind son, Bob. Both Bill and Jan have normal vision. If they choose to have another child, what are the probabilities for each of the following: Normal vision daughter____________ Normal vision son__________ Color blind daughter ______________ Color blind son ___________ 6 What is a Barr-body? Why are tortoise shell and calico cats always female? _________ is defined as an abnormal number of chromosomes. ___________ is the condition where a cell has an extra chromosome and ____________ is the condition where a cell has a chromosome missing. These are usually the result of _______________ which occurs during meiosis. Name a disorder which is caused by a cell that is (2n+1) ________________________ The likelihood of a child with this disorder increases after the ______________ reaches the age of _________________. Describe the sex chromosomes and phenotype for an individual with Turner syndrome: Describe the sex chromosomes and phenotype for an individual with Klinefelter syndrome: A man who carries an X linked allele will pass it on to: all of his daughters all of his sons half of his sons half of his daughters all of his children 7