* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Genetics revision for learners
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
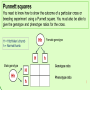
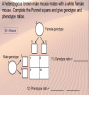
Starter: DNA This is a chromosome and a gene. Describe how an allele and DNA fit into this picture Do you have this?? Cells and mitosis Dalmations In Dalmations black spots are dominant over brown spots. Jordan picks up a black spotted one from the Silverdale shelter. He thinks the coat colour is perfect and decides he could make some money breeding her. Most people prefer black spots. How would he figure out if the dog was homozygous or heterozygous for its black spots? This is a test cross. Any time you get a problem like this the answer is ALWAYS the same. Breed it with a homozygous recessive one What is variation? Independent Assortment Revision Crossing Over Explain how independent assortment and crossing over lead to an increase in variation The answer to most variation questions Meiosis produces gametes with half the number of chromosomes. This means that pairs of alleles are separated at meiosis. During meiosis matching chromosomes cross over (swap sections of the chromosome) which adds variation. Independent assortment also increases variation as the chromosome pairs randomly line up and then separate At fertilisation, which sperm fertilise which egg is due to chance and this results in new combinations of alleles. The advantage of variation to a species is that it may enable some individuals to survive if some threatening event occurs. For example, if a new disease arrives, not all individuals will be wiped out