* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download MMP 3 Test Review: Complete the following review sheet to prepare
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in stem-cell differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
DNA damage theory of aging wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
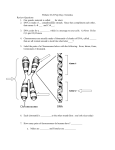
MMP 3 Test Review: Complete the following review sheet to prepare for the MMP 3 Test on May 13th. In addition to this review sheet you should review the material on my website. DNA Structure and Function: 1. How to the nucleotides pair up in the structure of DNA? AT CG 2. What shape does DNA make? Double helix 3. A mismatch in the base pairing of DNA is called a _Mutation___. 4. Why is DNA considered “life’s blueprint”? DNA holds the instructions for all things you. More specifically, it codes for proteins which play a role in nearly every cell function and control things like eye color and hair color. Protein Synthesis: 5. The monomer of proteins are amino acids. 6. Transcription occurs in the nucleus. 7. Transcription can be summarized as DNA→ mRNA. 8. The ribosome is the structure where mRNA is translated. 9. Translation can be summarized as mRNA → tRNA → amino acid. 10. Transcribe and Translate the following DNA sequence. Use a codon wheel to determine the amino acid. Cell Cycle: 11. What part of the cell cycle does the cell spend most of its time? Interphase 12. When is DNA duplicated during the cell cycle? S phase. 13. At what point of the cell cycle does the cytoplasm split into two? cytokinesis Mitosis & Meiosis: 14. Which part of mitosis do the chromosomes align in the Middle of the cell? metaphase 15. When does chromatin condense into chromosomes? prophase 16.How does mitosis differ from meiosis (provide at least three differences)? mitosis 2 new cells, meiosis 4 new cells mitosis new cells w/ 46 chromosomes, meiosis new cells w/ 23 chromosomes mitosis not sex cells, meiosis sex cells Karyotyping: 17. What is a karyotype? visual and ordered display of chromosomes 18. What is the gender of the individual whose chromosomes are displayed in the karyotype? XX female 19. Does this individual have a genetic disorder? If so, what is it? Yes, an extra chromosome 21 Down syndrome Inheritance: 20. crossing over explains why you are genetically different from your parents? 21. What is an allele? A form of a trait. Ex hair color is a trait. There are alleles for brown hair and alleles for blonde hair. 22. One allele masks another, what form of inheritance is this called? Complete dominance. 23. Identify the following genotypes as either homozygous (HO) or heterozygous (HE). Gg HE GG HO Yy HE yy HO 24. In dogs, wirehair (S) is dominant to smooth (s). In a cross of a homozygous wirehaired dog with a smoothhaired dog, what will be the phenotype of the F1 generation? What would the genotype be? F1 phenotype: Wirehair F1 genotype: Ss 25. What would be the ratio of wirehaired to smoothhaired dogs in the F2 generation? 3 wired: 1 smooth 26. Whisker length in wild boars is either long (LL), short (SS), or medium (SL). In a small litter of new baby boars there were 25% with long whiskers, 50% with medium whiskers, and 25% with short whiskers. What are the genotype and phenotype of the parents? Mothers genotype WL Fathers genotype WL Mothers phenotype Medium whiskers Fathers phenotype Medium whiskers 27. What kind of inheritance is described above? Incomplete dominance 28. In some species of frogs, being spotted in controlled by codomiance. Frogs can either be blue (BB), yellow (YY), or spotted blue and yellow (BY). A blue frog met a yellow frog. What is the genotype of the offspring? Offspring genotype: BY 29. A woman with redgreen colorblindness has a mother with normal vision. Knowing that colorblindness is a sexlinked recessive gene, can you determine what her father's phenotype is? If so, what is it? Yes 30. The woman marries a man with normal vision. What is the probability they will have sons who are redgreen colorblind?