* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
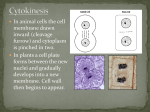
Download The diagrams below show a plant cell in four stages of cell division
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
3.11 B: Mitosis Quiz 1. The diagrams below show a plant cell in four stages of cell division. A student observing plant cells under a microscope notices a cell that has two nuclei. Which defect in the cell division process depicted above is most likely to result in a cell with two nuclei that are each identical to the parent nucleus? (A) Spindle fibers do not form in stage 1. (B) A mutation prevents sister chromatids from lining up at the equator in stage 2. (C) A chromatid breaks loose from the spindle during stage 3 and is segregated with its sister chromatid. (D) No cell plate is formed during stage 4. Page 1 of 4 3.11 B: Mitosis Quiz 2. A compound that blocks the attachment of chromosomes to spindle fibers is added to a cell during mitosis, as shown below. Which explanation describes how the process of mitosis is most likely affected by the compound? (A) The cell does not divide to produce two daughter cells because DNA replication is blocked. (B) The cell forms one daughter cell that has two nuclei because the cell is unable to undergo cytokinesis after mitosis. (C) The cell does not divide to produce two daughter cells because sister chromatids are not moved to opposite poles of the cell. (D) The cell forms one daughter cell that has a diploid (2n) nucleus because sister chromatids remain together in the nucleus of the new cell. Page 2 of 4 3.11 B: Mitosis Quiz 3. Research has shown that many cancer cells contain mutations that allow cells to grow and divide uncontrollably. Scientists are interested in finding a compound that will slow the spread of cancerous cells to other parts of the body. In an experiment, cancerous cells are removed from a tumor and treated with four different compounds. The data table below shows the percent of time that cancerous cells spent in each phase of the cell cycle for the four samples. Based on the data, which compound might be most effective as a drug to slow cell division in cancerous cells? (A) compound K, because it has the highest combined percentage of treated cells in the G0 and G1 phases, which shows that the cells are not dividing rapidly (B) compound L, because it has the lowest percentage of treated cells in the S phase, which shows that the cells are not actively replicating their DNA (C) compound M, because it has the highest combined percentage of treated cells in the G2 and S phases, which shows that the cells are not actively growing or dividing (D) compound N, because it has the lowest percentage of cells in the G1 phase, which shows that cell growth has slowed Page 3 of 4 3.11 B: Mitosis Quiz 4. A biology lab conducts an experiment to study the effect of the molecule lectin on the cell cycle in onion plants. In the experiment, onion plants are grown in containers filled with only water or a water/lectin solution. After a week, cells from the tips of the roots from both containers are extracted, and the stage of the cell cycle for each cell in the roots is determined and recorded in the table below. Which statement is the best description of how lectin is likely to affect the ability of onion plants to pass heritable information from parent cell to daughter cell? (A) Lectin interferes with the passage of heritable information because replication of DNA during the S phase is stunted, as supported by the fact that more of the lectin-treated cells remain in a mitotic state, compared to the cells grown only in water. (B) Lectin interferes with the passage of heritable information because lectin slows down the rate of cell growth in G1, as supported by the fact that fewer of the lectin-treated cells are in interphase, compared to the cells grown only in water. (C) Lectin accelerates the passage of heritable information because lectin induces mitosis, as supported by the fact that a greater percentage of the lectin-treated cells are undergoing mitosis, compared to the cells grown only in water. (D) Lectin accelerates the passage of heritable information because lectin speeds up the rate of cell growth in G1, as supported by the fact that fewer of the lectin-treated cells are still in interphase, compared to the cells grown only in water. Page 4 of 4