* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 6 - learning
Abnormal psychology wikipedia , lookup
Thin-slicing wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Learning theory (education) wikipedia , lookup
Theory of planned behavior wikipedia , lookup
Insufficient justification wikipedia , lookup
Theory of reasoned action wikipedia , lookup
Attribution (psychology) wikipedia , lookup
Observational methods in psychology wikipedia , lookup
Applied behavior analysis wikipedia , lookup
Descriptive psychology wikipedia , lookup
Verbal Behavior wikipedia , lookup
Adherence management coaching wikipedia , lookup
Psychophysics wikipedia , lookup
Behavior analysis of child development wikipedia , lookup
Social cognitive theory wikipedia , lookup
Psychological behaviorism wikipedia , lookup
Behaviorism wikipedia , lookup
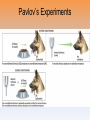
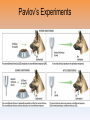
Chapter 6 - Learning Our next chapter is on learning... As high school seniors, if you could write to your past self as a freshman entering high school, what advice would you give yourself? Consider your experiences thus far, the lessons you have learned, and the situations you wish you had handled better or would have preferred not to have experienced at all. This entry MUST be at least ONE full page. Think about it... How did you learn...to learn? What study skill strategies work for you? True or False Becoming sick from eating a certain food can be a genuine learning experience. If you are afraid of snakes, it may help to surround yourself with them. Negative reinforcement is the same thing as punishment. People who watch a lot of violence on television are more likely to be violent themselves than people who watch less violence on television. http://www.learner.org/series/discoveringpsychology/08/e08expand.html http://watchdocumentary.com/watch/discovering-psychology-episode-08learning-video_1f745f1c9.html Why are A's better than B's? Why do certain old songs evoke a rush of sensations that you used to feel back when the song was popular? Classical conditioning Conditioning --> learning Stimulus --> something that produces a response Response --> a reaction Learning that takes place when an originally neutral stimulus comes to produce a conditioned response because of its association with an unconditioned stimulus Wait, what???? Ivan Pavlov Pavlov and the salivating dogs... Can dogs "learn" to salivate to ANY stimulus that signaled meat or food? Pavlov’s Experiments Pavlov’s Experiments Pavlov’s Experiments Pavlov’s Experiments Important concepts Unconditioned stimulus (UCS) - a stimulus that causes a response that is automatic Unconditioned response (UCR) - the automatic response Conditioned response (CR) - a learned response to a stimulus that was previously neutral, or meaningless Conditioned stimulus (CS) - a stimulus that has come to elicit a CR because it has been associated with the UCS Everyday applications of Classical Conditions Can openers Car alarms Scents Adapting to the environment Taste aversions - a learned avoidance of a particular food Extinction - when a conditioned stimulus is no longer followed by the unconditioned stimulus, it will eventually lose its ability to evoke the CR Spontaneous recovery - occurs when a previously extinguished CR suddenly reappears after a period of time Continued... Generalization - the act of responding in the same ways to stimuli that seem to be similar Discrimination - the act of responding differently to stimuli that are not similar to each other Classical conditioning and fears/habits Flooding Systematic desensitization Counterconditioning Bell-and-pad method for bed-wetting Little Albert!!! Section 1 Review Answer in your notebooks… Describe Pavlov's experiment with dogs using the following terms: UCS, UCR, CS, and CR. Explain what is meant by extinction, spontaneous recovery, generalization, and discrimination in classical conditioning. Define flooding, systematic desensitization, counterconditioning in your notebooks! In your own words, define classical conditioning. 1. Develop a fear of teddy bears by using the principles of classical conditioning. Identify the UCS, UCR, CS, CR 2. What could be done to extinguish this fear? Identify the UCS, UCR, CS, CR 1. Every time someone flushes a toilet in the apartment building, the shower becomes very hot and causes the person to jump back. Over time, the person begins to jump back automatically after hearing the flush, before the water temperature changes. 2. You eat a new food and then get sick because of the flu. However, you develop a dislike for the food and feel nauseated whenever you smell it. 3. An individual receives frequent injections of drugs, which are administered in a small examination room at a clinic. The drug itself causes increased heart rate but after several trips to the clinic, simply being in a small room causes an increased heart rate. 4. John Watson conducted an experiment with a boy named Albert in which he paired a white rat with a loud, startling noise. Albert now becomes startled at the sight of the white rat. CC Review 1. Ivan Pavlov’s experiments with the salivating dogs yielded information about … 2. What’s spontaneous recovery again??? 3. In Ivan Pavlov’s experiment, what was the conditioned stimulus? 4. A person’s mouth watering at the thought of a meal is a(n) … 5. In Watson’s experiment with “Little Albert,” Albert was conditioned to fear not only white rats, but anything white and furry. What is this an example of? Answer in your notebooks... How can we influence people's behaviors? How do we increase/decrease the occurrence of various behaviors? Provide 2 examples Operant Conditioning Actions have consequences that can either increase or decrease the likelihood that the behavior will reoccur. Reinforcement The process by which a stimulus increases the chances that the preceding behavior will occur again Primary reinforcers - food, water Secondary reinforcers - grades, money, attention, social approval B.F. Skinner http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qy_mIEnnlF4 Skinner’s Experiments • Edward Thorndike’s Law of Effect • B.F. Skinner –Behavioral technology –Behavior control Law of Effect = Thorndike’s principle that behaviors followed by favorable consequences become more likely, and that behaviors followed by unfavorable consequences become less likely. Skinner’s Experiments • Operant Chamber (Skinner Box) Operant Chamber = in operant conditioning research, a chamber (also known as a Skinner Box) containing a bar or key that an animal can manipulate to obtain a food or water reinforcer; attached devices record the animal’s rate of bar pressing or key pecking. Is negative reinforcement and punishment the same thing??? + vs. Positive reinforcement - increases the frequency of the behavior (most effective for elementary-age children) Negative reinforcement - increases the frequency of the behavior by taking away something bad Punishment Unwanted events that decrease the frequency of a behavior - does not teach alternate acceptable behavior - tends to only work when guaranteed - may try to leave situation than change behavior - can create anger and hostility - may be imitated as a way of solving problems - sometimes accompanied by unseen benefits that make the behavior more likely to be repeated Schedules of Reinforcement Continuous reinforcement - reinforcement of a behavior every time the behavior occurs Partial reinforcement – behavior that is not reinforced every time; behaviors tend to last longer if no longer reinforced Schedules... Fixed interval - the first target response after a fixed amount of time has passed is rewarded Variable interval - varying amounts of time go by between reinforcements (pop quizzes) Fixed ratio - a fixed number of target responses must be made before a reward is given Variable ratio - the number of target responses required for a reward changes (lottery tickets) * extinction also occurs in operant conditioning Answer on a separate sheet of paper... 1. Explain the difference between classical conditioning and operant conditioning. 2. Name four types of reinforcers. 3. How are fixed schedules of reinforcement different from variable schedules? 4. How do parents and teachers use rewards and punishments to influence behavior? Give an example of each. Contrasting Classical and Operant Conditioning Applications of Operant Conditioning Shaping - a technique in which successive approximations of a behavior are reinforced They see me rollin’… Latent Learning Learning that is hidden until it is needed Cognitive maps Learning may not be evident until reinforcement is given (Tolman’s rats) DEBATE!!! Do video games increase violent behavior in teens???? Remember: If you are on the PRO or CON side…be ready to present your side with supporting evidence Jury Members – 2 sources must be summarized relating to either side of the debate. Include source. Observational Learning "Do what I say not what I do?" Albert Bandura Bandura’s Experiments Dependent On… Attention Retention Ability to reproduce Motivation Who are your role models??? By the time you graduate…you have spent more time watching TV than sitting in school. The average US student has witnessed about 8000 murders and well over 100,000 violent acts by the end of elementary school. Aggression can be learned through observation. There is a correlation... It is NOT a cause- effect relationship. Section 3 Review How might studying a cookbook for fun be a form of latent learning? Provide an example of observational learning that takes place in school. Has observation of violence through the media affected YOUR behavior?