* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Final Exam Review Study the following terms and concepts to
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Frameshift mutation wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Mir-92 microRNA precursor family wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
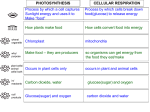
Final Exam Review Study the following terms and concepts to prepare for the final Chapter 1-What is science? • Designing an experimento Hypothesiso Theoryo Controlled experiment• Tools of Biology o Light Microscopeo TEMo SEMo Metric system Unit for Temperature Length Mass VolumeChapter 2 Section 2-3- Macromolecule • What is the function of each Macromolecule? o Carbohydrateo Lipido Proteino Nucleic AcidChapter 7-The cell 7.2--Know the structures and functions of a cell • Prokaryote vs. Eukaryote• Cell membrane• Ribosome• Mitochondria• Chloroplast• Nucleus• Vacuole- 7.3--Cell transport • Diffusion• Osmosis• HomeostasisChapter 8 8.2—Photosynthesis • What is the purpose of it? • Equation for Photosynthesis= • What are the products? • What are the reactants? • What would happen if you removed any of the reactants? Chapter 9 9.1- Cellular Respiration • What is the purpose of it? • Equation for Respiration= • What are the products? • What are the reactants? • What would happen if you removed any of the reactants? • Why cellular respiration is considered an opposite process of Photosynthesis? Who do they relate? • Aerobic – • Anaerobic• Lactic acid fermentation• Alcoholic fermentationChapter 10 10.2—Cell division • Cell regulation• What controls cell regulation? • Cancer• Cell cycle• Events of cell cycleo Interphaseo Mitosis Prophase Anaphase- • Metaphase Telophase CytokinesisWhat is the end result of mitosis? Chapter 11 11.2-Probability and Punnett Squares • • • • • • • Know how to do a genetic cross Know how to predict the probabilities of both phenotypes and genotypes GameteGenotypeHomozygousHeterozygousPhenotype- 11.3 – Exploring Mendelian Genetics • • • • • Incomplete dominanceCo dominanceBlood Types crossesSex-linked TraitsWhy do more males get these (example colorblindness) than females? 11.4-Meiosis • Diploid• Haploid• Gamete• Meiosis• What is the end result of meiosis? Chapter 12 12.1-DNA • Bacteriophage• Transformation• Base-pair rules- • • StructureParts of a nucleotide- 12.2-DNA replication • What is replication? 12.3-RNA and Protein synthesis • What is the structure of RNA? • Types of RNAo mRNAo tRNAo rRNA• Transcription• Translationo Codon o Exono Introno What are the building blocks of protein? o Who do you determine which amino acid comes next in the genetic code? 12.4-Mutations • What is a mutation? • Gene mutation• Chromosomal mutationChapter 13 • • • • • • • Selective breedingHybridizationInbreedingTransgenic organismsWhy are they useful? What is a clone? What are the two main sources of genetic variation? 1. Mutations 2. Gene shuffling3. Crossing over Chapter 15-Evolution • What did Lamarck propose? • Evolution• Theory• Fossil• What did Darwin observe? • Where did he go to make these observations? • Artificial selection• Natural selectiono struggle for existenceo survival of the fittesto fitnesso adaptation• • Descent with modificationEvidence of evolutiono Fossil recordo Geographical distribution o Homologous body structureso Similarities in Embryology-