* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Heart Anatomy
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
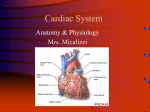
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Heart Anatomy General Closed System - Blood Remains in Blood Vessels & Heart Double System - Four Chambers (Separation of Oxygenated & Deoxygenated Blood) - Heart is Double Organ: * Pulmonary Circuit (Heart Lungs Heart) * Systemic Circuit (Heart Body Tissues Heart) Heart – Size & Location Size: Adult Clenched Fist Position: Mediastinum, 2/3 to Left of Midline Relationships to Other Organs: - Medial to Lungs - Superior to Diaphragm - Anterior to Esophagus, Descending Aorta Heart - Chambers Atria (2) - Superior Receiving Chambers (From Veins) - Auricles (ear-like flaps) - Right Atrium: * O2 Poor Blood From Venae Cavae & Coronary Sinus (Systemic Circ.) - Left Atrium: * O2 Rich Blood From Pulmonary Veins of Lungs Heart – Chambers continued Ventricles (2) - Inferior Pumping Chambers (to Arteries) - Receive from Atria - Right Ventricle: * O2 Poor Blood from Rt Atrium to Pulmonary Arteries (Pulmonary Circ.) - Left Ventricle: * O2 Rich Blood from Left Atrium to Aorta (Systemic Circ.) Heart - Valves One-Way, Direct Blood Flow Passive; blood pushes them closed 2 Pairs: - Atrioventricular (Cuspid) Valves *Between Atria & Ventricles Tricuspid (Right) Bicuspid (left) Atrioventricular Valves cont. * AV Valves are anchored to structures in the ventricles: Chordae Tendineae Strong, Fibrous Strings Prevent Cusp Eversion Papillary Muscle Conical Extensions of Myocardium in Ventricles Contract & pull on chordae tendinae AV (MITRAL) VALVES Cusps OPEN CLOSED Heart - Valves - Semilunar Valves *Between Ventricles & Arteries *Prevent blood from back flow into ventricles Pulmonary Semilunar Valve (Right) Aortic Semilunar Valve (Left) SEMILUNAR VALVES Cusps OPEN CLOSED Heart - Wall 3 Layers: - Endocardium (Inner) * Endothelium * Lines Chambers, Valves, Septa, Blood Vessels - Myocardium (Middle) * Thickest Layer (Esp. in Left Ventricle!) * Cardiac Muscle Tissue * Inherent Rhythmicity * Trabeculae Carnae – Ridges, Folds & Bridges of Ventricular Myocardium Heart – Wall continued - Epicardium (Outer) *Visceral Pericardium *Serous Membrane *Thin, Fibrous, Transparent Heart - Septa Internal Walls Separate Chambers 2 Septa: - Interatrial Septum (Between the Atria) - Interventricular Septum (Between the Ventricles) Heart – Pericardial Sac Parietal Pericardium - Encloses Heart & Bases of Great Vessels - Composed of : * Inner Serous Coat/Serous Pericardium Parietal & Visceral Pericardium Both Secrete Lubricating Pericardial Fluid into Pericardial Cavity (Space Between Serous Layers) Heart – Pericardial Sac continued * Outer Fibrous Coat Tough, Protective Reinforces Serous Coat