* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Electrocardiogram
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
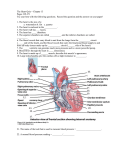
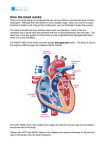
The Heart Chapter The Heart Is a Double Pump Delivers Oxygen and nutrients to the tissues Removes carbon dioxide and waste from the tissues Location and Design Hollow muscular organ located within the center of the chest in the mediastinum. 60% is located to the left of midline 5”X3.5” approximately the size of a clenched fist. Shape Oval type shape Base - is the top of the heart Apex - is the bottom of the heart •Organ Layers The heart moves freely and can change its stroke volume (SV) and twist to eject blood friction free. Pericardium Surrounds: • Heart • Great vessels •3 Layers of the Heart Muscle Epicardium The outer most layer. Is contiguous with the visceral pericardium Myocardium The actual muscle of the heart. It is the thickest. Responsible for contraction (more later) Endocardium The inner lining of the heart, made of epithelial cells In contact with the blood in the chambers. Myocardial Muscle Specialized found only in the heart Striated like skeletal Electrical properties like smooth muscle Chambers Double pump. Right and left sides. 4 chambers. 2 atria - upper chambers deliver blood to ventricles. 2 ventricles- lower chambers pump blood out of the heart. Valves of the heart Designed to promote forward flow Valves close to prevent backflow Made of fibrous tissue that has grown out of the walls of the heart 2 types: Atrioventricular (AV) (separate chambers) Semilunar (separate chamber/vessel) AV Valves The two valves that separate the atrial chambers are called AV or atrioventricular valves. The Bicuspid or Mitral valve is between the left atrium and ventricle Tricuspid is between the right atrium and ventricle Semilunar valves (half moon) Both arteries that leave the heart have these valves separating them from the ventricles Pulmonary Aortic Are between the two ventricular chambers and the large arteries that carry blood away from the heart. They each have 3 leaflets