* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Structure of the Heart
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
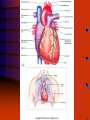
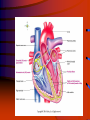
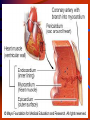
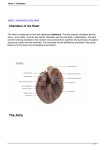
Cardiac System Anatomy & Physiology Mrs. Micalizzi Functions of the circulatory system • Heart pumps and circulates blood to all parts of the body. • Blood vessels circulate blood between heart and cells • Blood carries oxygen and nutrients to cells and carries away waste. • Lymph system returns excess fluids from tissues and makes lymphocytes. Heart • • • • The heart is a hollow, muscular, double pump. The heart is the shape and size of a closed fist Located in the thoracic cavity. The organ is located in the mediastinum with two thirds of mass to the left of midline and one third to the right. • Apex of heart lies on diaphragm Four Chambers of the Heart • • • • Right atrium Left atrium Right ventricle Left ventricle Heart Chambers • Two upper chambers are called atria (receiving chambers)-right and left atria • Two lower chambers are called ventricles (discharging chambers) -right and left ventricles. • Septum-Muscular wall separating heart into two halves. Heart Valves • Four valves permit blood flow in only one direction • Tricuspid-at the opening of the right atrium into the right ventricle • Bicuspid (mitral) valve- at the opening of the left atrium into the left ventricles • Pulmonary semilunar valve –at the beginning of the pulmonary artery • Aortic semilunar valve- at the beginning of the aorta Sinoartial (SA) or Pacemaker • Sinoatrial (SA) node or pacemaker sends out an electrical impulse that regulates the heart. The impulse spreads out over the atria, making them contract or depolarize. This causes blood to flow downward from the upper atrial chambers • At the same time, the ventricles are relaxed, allowing them to fill with blood Atrioventriclular (AV) Node • The AV node stimulates the contraction of both ventricles • From the AV node, the electrical pulse is carried to the conducting fibers in the septum, called bundle of HIS or atrioventricle bundle. • Then the electrical impulse shoots along the Purkinje fibers to the ventricles causing them to contract. Layers of the Heart • Pericardium-fibrous, double outer layer that has pericardial fluid between layers. • Inner layer is called visceral pericardium or epicardium. Outer layer called parietal pericardium. • Myocardium-cardiac muscle tissue: the wall of the heart. • Endocardium-Smooth inner lining of the heart. Structures leading to and from heart • Superior and inferior vena cava are blood vessels that brings deoxygenated blood to the right atrium from all parts of the body. • Pulmonary artery takes deoxygenated blood from the right ventricle to the lungs for oxygen. • Pulmonary vein brings oxygenated blood from lungs to left atrium. • Aorta takes blood from left ventricle to the body Blood Vessels • Arteries- carry blood away from the heart to the arterioles. • Veins- carry blood toward the heart from the venules. • Capillaries-caries blood from the arterioles to the venules Structure of The Heart The End Questions?