* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download day 7 how the heart works
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Aortic stenosis wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
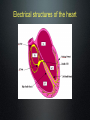
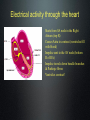
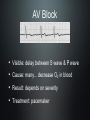
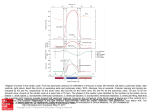
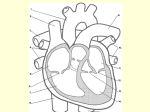
How the Heart Works. Electrical activity in the heart. Blood flow through the heart http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Ww2OAsAUIT0 Heat Beats Step 1: Enter Atrium • Right Side - Deoxygenated blood enters the right atrium through 2 large veins - Superior vena cava: upper half of the body - Inferior vena cava: below the diaphragm Left Side - Oxygenated blood (from the lungs) enters the left atrium through the pulmonary vein Heat Beats Step 2: Contract Atrium • Blood flows from the atrium into the ventricle • The atrioventricular (AV) valve allows for a one-directional flow • The AV valve closes once the ventricle is full Heat Beats Step 3: Contract Ventricle Right Side •Right ventricle contracts •Blood flows through the pulmonary valve into the pulmonary arteries •Blood flows towards the lungs Left Side •Left ventricle contracts •Blood flows through the aortic valve into the aorta (largest artery) •Blood flows out towards the body 2 parts of the heart beat • Two parts of Heart Beat – LUB: closure of the AV valves (beginning of ventricular contraction - systole) – DUB: closure of the pulmonary & cardiac valves (end of ventricular systole – diastole) Electrical structures of the heart Electrical activity through the heart Starts from SA node in the Right Atrium (top R) Causes Atria to contract (ventricles fill with blood) Impulse sent to the AV node (bottom R of RA) Impulse travels down bundle branches & Purkinje fibres Ventricles contract! Electrocardiogram - ECG • P wave: SA node fires and the • • atria contract QRS complex: AV node stimulates the ventricles to contract (AV valves close) T wave: ventricles relax (the pulmonary valve and aortic valve close) Normal sinus rhythm ECG is used to measure: - heart rate & regularity of heartbeats - the size and position of the chambers - any damage to the heart - the effects of drugs or devices used to regulate the heart Atrial Fibrillation • Visible: lack of P wave • Cause: hypertension • Result: chest pain, heart palpitations, fainting, heart failure, higher risk of stroke • Treatment: blood thinners, medication to slow heart rate Ventricular Fibrillation • Visible: no clear rhythm • Cause: heart attack • Result: chest pain, NO heart beat • Treatment: defibrillation (Shock) AV Block • Visible: delay between S wave & P wave • Cause: many... decrease O2 in blood • Result: depends on severity • Treatment: pacemaker Asystole • Visible: no waves • Cause: lack of electrical activity • Result: no blood flow, no contractions • Treatment: none