* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Old Test for Practice Only
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrial replacement therapy wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
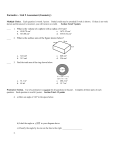
Old Test for Practice Only Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. ____ 1. The ATP made when fermentation happens is generated by which of the following? a. the electron transport chain b. substrate-level phosphorylation c. chemiosmosis d. oxidative phosphorylation e. aerobic respiration Figure 10.3 ____ 2. In which cell would you expect photorespiration (Rubisco to have a slight confirmational change)? a. Cell I b. Cell II c. Cell I at night d. Cell II at night e. neither Cell I nor Cell II 1 ____ 3. Assume a thylakoid is somehow punctured so that the interior of the thylakoid is no longer separated from the stroma. This damage will have the most direct effect on which of the following processes? a. the splitting of water b. the absorption of light energy by chlorophyll c. the flow of electrons from photosystem II to photosystem I d. the synthesis of ATP e. the reduction of NADP + ____ 4. In the thylakoid membranes, what is the main role of the antenna pigment molecules? a. split water and release oxygen to the reaction-center chlorophyll b. harvest photons and transfer light energy to the reaction-center chlorophyll c. synthesize ATP from ADP and Pi d. transfer electrons to ferredoxin and then NADPH e. concentrate photons within the stroma ____ 5. In any ecosystem, terrestrial or aquatic, what group(s) is (are) always necessary? a. autotrophs and heterotrophs b. producers and primary consumers c. photosynthesizers d. autotrophs e. green plants Use the following information to answer the next questions. In the presence of oxygen, the three-carbon compound pyruvate can be catabolized in the citric acid cycle. First, however, the pyruvate 1) loses a carbon, which is given off as a molecule of CO 2 , 2) is oxidized to form a two-carbon compound called acetate, and 3) is bonded to coenzyme A. ____ 6. Which of the following intermediary metabolites enters the citric acid cycle and is formed, in part, by the removal of a carbon (CO 2 ) from one molecule of pyruvate? a. b. c. d. e. ____ lactate glyceraldehydes-3-phosphate oxaloacetate acetyl CoA citrate 7. What are the products of the light reactions that are subsequently used by the Calvin cycle? a. oxygen and carbon dioxide b. carbon dioxide and RuBP c. water and carbon d. electrons and photons e. ATP and NADPH 2 ____ 8. If photosynthesizing green algae are provided with CO 2 synthesized with heavy oxygen ( 18 O), later analysis will show that all but one of the following compounds produced by the algae contain the 18 a. b. c. d. ____ O label. That one is G3P. O2. glucose. RuBP. 9. Which of the following statements describes the results of this reaction? C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6 O 2 → 6 CO 2 + 6 H 2 O + Energy a. C 6 H 12 O 6 is oxidized and O 2 is reduced. b. O 2 is oxidized and H 2 O is reduced. c. CO 2 is reduced and O 2 is oxidized. d. C 6 H 12 O 6 is reduced and CO 2 is oxidized. e. O 2 is reduced and CO 2 is oxidized. ____ 10. The direct energy source that drives ATP synthesis during respiratory oxidative phosphorylation is a. oxidation of glucose to CO 2 and water. b. c. d. e. the thermodynamically favorable flow of electrons from NADH to the mitochondrial electron transport carriers. the final transfer of electrons to oxygen. + the difference in H concentrations on opposite sides of the inner mitochondrial membrane. the thermodynamically favorable transfer of phosphate from glycolysis and the citric acid cycle intermediate molecules of ADP. ____ 11. Whenever energy is transformed, there is always an increase in the a. free energy of the system. b. free energy of the universe. c. entropy of the system. d. entropy of the universe. e. enthalpy of the universe. ____ 12. The ATP made during glycolysis is generated by a. substrate-level phosphorylation. b. electron transport. c. photophosphorylation. d. chemiosmosis. e. + oxidation of NADH to NAD . 3 ____ 13. One function of both alcohol fermentation and lactic acid fermentation is to + a. reduce NAD to NADH. b. reduce FAD to FADH 2 . c. oxidize NADH to NAD . d. oxidize FADH 2 to FAD . e. none of the above + + + ____ 14. During aerobic respiration, which of the following directly donates electrons to the electron transport chain at the lowest energy level? + a. b. c. d. NAD NADH ATP ADP + P i e. FADH 2 ____ 15. In a plant cell, where are the ATP synthase complexes located? a. thylakoid membrane b. plasma membrane c. inner mitochondrial membrane d. A and C e. A, B, and C ____ 16. Water passes quickly through cell membranes because a. the bilayer is hydrophilic. b. it moves through hydrophobic channels. c. water movement is tied to ATP hydrolysis. d. it is a small, polar, charged molecule. e. it moves through aquaporins in the membrane. ____ 17. Which of the following are important biotic factors that can affect the structure and organization of biological communities? a. precipitation, wind b. nutrient availability, soil pH c. predation, competition d. temperature, water e. light intensity, seasonality 4 Refer to Figure 9.2, showing the citric acid cycle, as a guide to answer the following questions. Figure 9.2 ____ 18. Starting with citrate, which of the following combinations of products would result from three turns of the citric acid cycle? a. 1 ATP, 2 CO 2 , 3 NADH, and 1 FADH 2 b. 2 ATP, 2 CO 2 , 1 NADH, and 3 FADH 2 c. 3 ATP, 3 CO 2 , 3 NADH, and 3 FADH 2 d. 3 ATP, 6 CO 2 , 9 NADH, and 3 FADH 2 e. 38 ATP, 6 CO 2 , 3 NADH, and 12 FADH 2 ____ 19. When chemical, transport, or mechanical work is done by an organism, what happens to the heat generated? a. It is used to power yet more cellular work. b. It is used to store energy as more ATP. c. It is used to generate ADP from nucleotide precursors. d. It is lost to the environment. e. It is transported to specific organs such as the brain. ____ 20. In glycolysis, for each molecule of glucose oxidized to pyruvate a. 2 molecules of ATP are used and 2 molecules of ATP are produced. b. 2 molecules of ATP are used and 4 molecules of ATP are produced. c. 4 molecules of ATP are used and 2 molecules of ATP are produced. d. 2 molecules of ATP are used and 6 molecules of ATP are produced. e. 6 molecules of ATP are used and 6 molecules of ATP are produced. 5 ____ 21. Evidence shows that some grasses benefit from being grazed. Which of the following terms would best describe this plant-herbivore interaction? a. mutualism b. commensalism c. parasitism d. competition e. predation Use the following diagram of a hypothetical food web to answer the following questions. The arrows represent the transfer of food energy between the various trophic levels. Figure 54.2 ____ 22. Which letter represents an organism that could be a producer? a. A b. B c. C d. D e. E ____ 23. Which letter represents an organism that could be a primary consumer? a. A b. B c. C d. D e. E ____ 24. Plants growing in a partially dark environment will grow toward light in a response called phototropism. Choose the incorrect statement regarding phototropism. a. It is caused by a chemical signal. b. One chemical involved is auxin. c. Auxin causes a growth increase on one side of the stem. d. phototropism is caused by gravity e. Removing the apical meristem prevents phototropism. 6 ____ 25. Where does glycolysis takes place? a. mitochondrial matrix b. mitochondrial outer membrane c. mitochondrial inner membrane d. mitochondrial intermembrane space e. cytosol ____ 26. For living organisms, which of the following is an important consequence of the first law of thermodynamics? a. The energy content of an organism is constant. b. The organism ultimately must obtain all of the necessary energy for life from its environment. c. The entropy of an organism decreases with time as the organism grows in complexity. d. Organisms are unable to transform energy. e. Life does not obey the first law of thermodynamics. ____ 27. CAM plants keep stomata closed in daytime, thus reducing loss of water. They can do this because they a. fix CO 2 into organic acids during the night. b. fix CO 2 into sugars in the bundle-sheath cells. c. fix CO 2 into pyruvate in the mesophyll cells. d. use the enzyme phosphofructokinase, which outcompetes rubisco for CO 2 . e. use photosystems I and II at night. ____ 28. Which of the following abiotic factors has the greatest influence on the metabolic rates of plants and animals? a. water b. wind c. temperature d. rocks and soil e. disturbances ____ 29. During cellular respiration, acetyl CoA accumulates in which location? a. cytosol b. mitochondrial outer membrane c. mitochondrial inner membrane d. mitochondrial intermembrane space e. mitochondrial matrix 7 ____ 30. Which of the following is considered an open system? a. an organism b. liquid in a corked bottle c. a sealed terrarium d. food cooking in a pressure cooker ____ 31. Which of the following statements is representative of the second law of thermodynamics? a. Conversion of energy from one form to another is always accompanied by some b. c. d. e. gain of free energy. Heat represents a form of energy that can be used by most organisms to do work. Without an input of energy, organisms would tend toward decreasing entropy. Cells require a constant input of energy to maintain their high level of organization. Every energy transformation by a cell decreases the entropy of the universe. ____ 32. Approximately how many kg of carnivore production can be supported by a field plot containing 2000 kg of plant material? a. 20,000 b. 2,000 c. 200 d. 20 e. 2 ____ 33. To recycle nutrients, the minimum an ecosystem must have is a. producers. b. producers and decomposers. c. producers, primary consumers, and decomposers. d. producers, primary consumers, secondary consumers, and decomposers. e. producers, primary consumers, secondary consumers, top carnivores, and decomposers. ____ 34. What term is used to describe the transfer of free energy from catabolic pathways to anabolic pathways? a. feedback regulation b. bioenergetics c. energy coupling d. entropy e. cooperativity 8 ____ 35. Which process in eukaryotic cells will proceed normally whether oxygen (O2) is present or absent? a. electron transport b. glycolysis c. the citric acid cycle d. oxidative phosphorylation e. chemiosmosis ____ 36. Where are the proteins of the electron transport chain located? a. cytosol b. mitochondrial outer membrane c. mitochondrial inner membrane d. mitochondrial intermembrane space e. mitochondrial matrix ____ 37. Where do the enzymatic reactions of the Calvin cycle take place? a. stroma of the chloroplast b. thylakoid membranes c. outer membrane of the chloroplast d. electron transport chain e. thylakoid space ____ 38. When hydrogen ions are pumped from the mitochondrial matrix across the inner membrane and into the intermembrane space, the result is the a. formation of ATP. + b. reduction of NAD . c. d. e. restoration of the Na /K balance across the membrane. creation of a proton gradient. lowering of pH in the mitochondrial matrix. + + ____ 39. In addition to ATP, what are the end products of glycolysis? a. CO 2 and H 2 O b. CO 2 and pyruvate c. d. NADH and pyruvate CO 2 and NADH e. H 2 O, FADH 2 , and citrate 9 ____ 40. Which of the following levels of organization is arranged in the correct sequence from most to least inclusive? a. community, ecosystem, individual, population b. ecosystem, community, population, individual c. population, ecosystem, individual, community d. individual, population, community, ecosystem e. individual, community, population, ecosystem 10 ____ 41. Identical heat lamps are arranged to shine on identical containers of water and methanol (wood alcohol), so that each liquid absorbs the same amount of energy minute by minute. The covalent bonds of methanol molecules are non-polar, so there are no hydrogen bonds among methanol molecules. Which of the following graphs correctly describes what will happen to the temperature of the water and the methanol? (Note: This is a good question for review, but properties of water will not be on the current unit exam for Energy and Ecology). a. b. c. d. e. 11 ____ 42. What is the primary function of the Calvin cycle? a. use ATP to release carbon dioxide b. use NADPH to release carbon dioxide c. split water and release oxygen d. transport RuBP out of the chloroplast e. synthesize simple sugars from carbon dioxide ____ 43. Ecosystems are a. processors of energy and transformers of matter. b. processors of matter and transformers of energy. c. processors of matter and energy. d. transformers of matter but not of energy. e. neither transformers or processors of matter nor energy. ____ 44. Which kind of metabolic poison would most directly interfere with glycolysis? a. an agent that reacts with oxygen and depletes its concentration in the cell b. an agent that binds to pyruvate and inactivates it c. an agent that closely mimics the structure of glucose but is not metabolized d. e. + an agent that reacts with NADH and oxidizes it to NAD an agent that blocks the passage of electrons along the electron transport chain ____ 45. Which of the following is an example of an ecosystem? a. b. c. d. e. 2 All of the brook trout in a 500 hectare river drainage system. The plants, animals, and decomposers that inhabit an alpine meadow. A pond and all of the plant and animal species that live in it. The intricate interactions of the various plant and animal species on a savanna during a drought. Interactions between all of the organisms and their physical environment in a tropical rain forest. ____ 46. Which of the following terms encompasses all of the others? a. heterotrophs b. herbivores c. carnivores d. primary consumers e. secondary consumers 12 ____ 47. The oxygen consumed during cellular respiration is involved directly in which process or event? a. glycolysis b. accepting electrons at the end of the electron transport chain c. the citric acid cycle d. the oxidation of pyruvate to acetyl CoA e. the phosphorylation of ADP to form ATP Short Answer Use the survivorship curves in Figure 53.1 to answer the following questions. Figure 53.1 48. Which curve best describes survivorship in humans who live in developed nations? (We didn’t cover this concept. However, use your knowledge of humans to attempt to answer this question.) 13 ID: A Old Test for Practice Only Answer Section MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. ANS: B PTS: 1 2. ANS: B PTS: 1 MSC: Application/Analysis 3. ANS: D PTS: 1 MSC: Application/Analysis 4. ANS: B PTS: 1 MSC: Knowledge/Comprehension 5. ANS: D PTS: 1 MSC: Synthesis/Evaluation 6. ANS: D PTS: 1 7. ANS: E PTS: 1 MSC: Knowledge/Comprehension 8. ANS: B PTS: 1 MSC: Application/Analysis 9. ANS: A PTS: 1 10. ANS: D PTS: 1 11. ANS: D PTS: 1 12. ANS: A PTS: 1 13. ANS: C PTS: 1 14. ANS: E PTS: 1 15. ANS: D PTS: 1 MSC: Knowledge/Comprehension 16. ANS: E PTS: 1 17. ANS: C PTS: 1 18. ANS: D PTS: 1 19. ANS: D PTS: 1 20. ANS: B PTS: 1 21. ANS: A PTS: 1 22. ANS: B PTS: 1 23. ANS: C PTS: 1 24. ANS: D PTS: 1 25. ANS: E PTS: 1 26. ANS: B PTS: 1 27. ANS: A PTS: 1 MSC: Knowledge/Comprehension 28. ANS: C PTS: 1 29. ANS: E PTS: 1 30. ANS: A PTS: 1 31. ANS: D PTS: 1 32. ANS: D PTS: 1 33. ANS: B PTS: 1 TOP: Concept 9.5 MSC: Knowledge/Comprehension TOP: Concept 10.4 TOP: Concept 10.2 TOP: Concept 10.2 TOP: Concept 10.1 TOP: Concept 9.3 MSC: Knowledge/Comprehension TOP: Concept 10.1 TOP: Concept 10.1 TOP: TOP: TOP: TOP: TOP: TOP: TOP: Concept Concept Concept Concept Concept Concept Concept 9.1 MSC: 9.4 MSC: 8.1 MSC: 9.1 MSC: 9.5 MSC: 9.4 MSC: 10.2 Knowledge/Comprehension Knowledge/Comprehension Knowledge/Comprehension Knowledge/Comprehension Application/Analysis Knowledge/Comprehension TOP: TOP: TOP: TOP: TOP: TOP: TOP: TOP: TOP: TOP: TOP: TOP: Concept Concept Concept Concept Concept Concept Concept Concept Concept Concept Concept Concept 7.2 MSC: 52.2 9.3 MSC: 8.3 MSC: 9.2 MSC: 54.1 54.2 54.2 39.2 9.1 MSC: 8.1 MSC: 10.4 Knowledge/Comprehension TOP: TOP: TOP: TOP: TOP: TOP: Concept Concept Concept Concept Concept Concept 52.2 9.3 MSC: Knowledge/Comprehension 8.1 MSC: Knowledge/Comprehension 8.1 MSC: Knowledge/Comprehension 54.2 55.1 1 Application/Analysis Knowledge/Comprehension Knowledge/Comprehension Knowledge/Comprehension Synthesis/Evaluation ID: A 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. 39. 40. 41. 42. 43. 44. 45. 46. 47. ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: MSC: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: MSC: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: C PTS: 1 B PTS: 1 C PTS: 1 A PTS: 1 Knowledge/Comprehension D PTS: 1 C PTS: 1 B PTS: 1 B PTS: 1 E PTS: 1 Knowledge/Comprehension B PTS: 1 C PTS: 1 E PTS: 1 A PTS: 1 B PTS: 1 TOP: TOP: TOP: TOP: Concept Concept Concept Concept 8.3 MSC: Knowledge/Comprehension 9.1 MSC: Knowledge/Comprehension 9.4 MSC: Knowledge/Comprehension 10.3 TOP: TOP: TOP: TOP: TOP: Concept Concept Concept Concept Concept 9.4 MSC: Knowledge/Comprehension 9.2 MSC: Knowledge/Comprehension 52.1 3.2 MSC: Synthesis/Evaluation 10.3 TOP: TOP: TOP: TOP: TOP: Concept Concept Concept Concept Concept 55.1 9.2 MSC: Application/Analysis 55.1 55.1 9.1 MSC: Knowledge/Comprehension SHORT ANSWER 48. ANS: A PTS: 1 TOP: Concept 53.1 2