* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Rome
Food and dining in the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Travel in Classical antiquity wikipedia , lookup
Roman economy wikipedia , lookup
Roman Senate wikipedia , lookup
Education in ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Senatus consultum ultimum wikipedia , lookup
Roman tribe wikipedia , lookup
Roman army of the late Republic wikipedia , lookup
Roman historiography wikipedia , lookup
Legislative assemblies of the Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Leges regiae wikipedia , lookup
Promagistrate wikipedia , lookup
Executive magistrates of the Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Constitutional reforms of Augustus wikipedia , lookup
Roman agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Culture of ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Rome (TV series) wikipedia , lookup
Constitutional reforms of Sulla wikipedia , lookup
Roman Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
History of the Constitution of the Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Conflict of the Orders wikipedia , lookup
Early Roman army wikipedia , lookup
Cursus honorum wikipedia , lookup
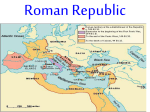
Rome The beginning and the republic… Rome--- Where is it? Rome, Italy Capital city Europe Peninsula Vatican & Pope Geography-Surrounded by water on three sides (Tyrrhenian Sea, Mediterranean Sea, Adriatic Sea), had rolling land with good soil for farming, was mountainous which provided protection from enemies, had few harbors making overseas travel and trade difficult, Alps lie to the north Rome: From the Beginning Romulus and Remus Twin sons of the God Mars Abandoned and raised by a she-wolf Decided to build a great city Argument Romulus kills Remus Names city after himself, Rome Invites all to live in city --- slaves, women, men, etc.. Romulus becomes the first King of Rome Monarchy Romulus & the war he caused Provides his men with wives by inviting neighboring tribe to festival and abducting young women Sabines go to war with Rome Following the war, Romulus shares kingship with Sabine king King Titus Tatius From Monarchy to Republic In about 600 BC neighboring people called the Etruscans took control of Rome The Etruscan King-King Tarquin the Proud was cruel and harsh. The Romans rebelled, ending the monarchy and starting a new government that they called a Republic Roman Republic Roman citizens do not make all of the decisions like in Athens. Instead, they elect representatives to make decisions. This council of representatives was called the Senate. The senate was made up of 300 Roman aristocrats (Rome’s elite) called the Patricians. From the senate two members, called Consuls were elected to run the daily affairs of Rome. To keep anyone from staying in power too long they elected new consuls every year. Patricians VS Plebeians Patrician-noblemen that held almost all of the power, they had the best education, and only they could become members of the Senate Plebeian-Common people that had few rights and almost no say in how they were governed. Patricians VS Plebeians Rome was divided into two unequal groups: Patricians and Plebeians A struggle was taking place between the two groups. Plebeians wanted rights and the patricians wanted to keep their power. The plebeians worked to obtain and secure their rights. They organized themselves and when they disagreed with the patricians, they would leave the city and refuse to listen. Eventually, the plebeians elected their own leaders, called Tribunes. Soon the plebeians were able to force the patricians to treat them better and allowing them a voice. The partricians realized that Rome’s economy would suffer without the plebians The patricians allowed the plebeian to elect 10 tribunes. These tribunes could attend senate meetings and could Veto (Refuse) laws that they did not agree with. Democracy v. Republic Democracy Republic Constraints on the government: No; the majority can impose its will on the minority Yes; the majority cannot take away certain inalienable rights Sovereignty is held by: the whole population (as a the people (individuals) group) Definition: is ruled by the omnipotent Representatives are majority. In a Democracy, selected to make decisions individuals have the power From a Republic to a Dictatorship Tax money made the patricians rich while slaves made the plebeians poor (slaves took their jobs). In 82 BC a civil war broke out. At the end, Lucius Sulla took power, turning Rome into a dictatorship. In BC Julius Ceaser became Rome’s dicatator. He envisioned many things for Rome