* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Mendelian Traits in YOU!
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Essential gene wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
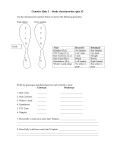
Mendelian Traits in YOU! • The presence of mid-digital hair is a dominant condition; therefore those lacking it are homozygous recessive. Freckles are controlled primarily by the MC1R gene. Freckles show a dominant inheritance pattern: parents who have freckles tend to have children with freckles. Variations, also called alleles, of MC1R control freckle number. Freckles are small, concentrated spots of a skin pigment called melanin. Most fair-skinned, redhaired people have them. Other genes and the environment influence freckle size, color, and pattern. For example, sun exposure can temporarily cause more freckles to appear. Some people can curl up the sides of their tongue to form a tube shape. In 1940, Alfred Sturtevant observed that about 70% of people of European ancestry could roll their tongues and the remaining 30% could not. Many sources state that tongue rolling is controlled by a single gene. However, as Sturtevant observed, people can learn to roll their tongue as they get older, suggesting that environmental factors—not just genes— influence the trait. Consistent with this view, just 70% of identical twins share the trait (if tongue rolling were influenced only by genes, then 100% of identical traits would share the trait). • A distinct downward peak of the frontal hairline • Having a widow’s peak is a dominant trait. • Homozygous recessive individuals possess a straight hairline. • Is your earlobe attached or unattached? • Free or unattached earlobe is dominant. • The homozygous recessive condition is expressed as a direct attachment of the earlobe to the head. Dimples are small, natural indentations on the cheeks. They can appear on one or both sides, and they often change with age. Some people are born with dimples that disappear when they’re adults; others develop dimples later in childhood. Dimples are highly heritable, meaning that people who have dimples tend to have children with dimples—but not always. Because their inheritance isn't completely predictable, dimples are considered an “irregular” dominant trait. Having dimples is probably controlled mainly by one gene but also influenced by other genes Round hair follicles make straight hair, flattened or cshaped hair follicles make curly hair, and oval hair follicles make wavy hair. Hair texture is a continuous trait, meaning that hair can be straight or curly or anywhere in between. Curly hair is influenced by genes much more than by the environment. While curly hair runs in families—people with curly hair tend to have children with curly hair—its inheritance patterns are often unpredictable. Multiple genes control hair texture, and different variations in these genes are found in different populations. For instance, curly hair is common in African populations, rare in Asian populations, and in-between in Europeans. Straight hair in Asians is mostly caused by variations in two genes—different genes from the ones that influence hair texture in Europeans. And different genetic variations make hair curly in African and European populations. • Hyperextensibility of the thumb is recessive. • Those who cannot bend at least one thumb backward about 45 degrees are probably carrying the dominant gene. Sorry… But no hitchhikers thumb… • Can you taste the bitterness of the PTC paper? • People who can taste the bitterness are either homozygous dominant (TT) or heterozygous dominant (Tt). • People who cannot taste the bitterness are homozygous recessive.