* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 1.1 Cell Theory and the Microscope - Hutchison
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
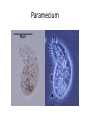
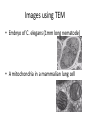
1.1 Cell Theory Pages 7-10 Characteristics of Living Things • • • • • • • Try to maintain a constant internal environment Reproduce Made up of cells Moves They make their own food or feed on another living thing Consumes gas and releases gas Senses/responds to changes in their environment Cell Theory • All living things are composed of one or more cells • Cells are the basic structural and functional units of life • All cells arise from the division of other cells Observing Cells • The simple light microscope Observing Cells • Compound Light Microscope Brightfield • The image is viewed against a bright background Darkfield Bright image against a dark background. Compound Light Microscope Magnification • Multiply ocular lens magnification by objective lens magnification • 10X x 40X = 400X magnification Resolution Good resolution produces a clean, sharp image Phase Contrast Microscope • Takes advantage of the slight differences in a specimen’s capacity to bend light rays, enhancing light and dark regions • You can observe living specimens • Magnification up to 1500X. Resolution • Images must be photographed or displayed on a monitor. Phase Contrast Specimen • Comparing brightfield with Phase Contrast Paramecium Observing Cells The Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM) Aims a beam of electrons through a thin slice of specimen. Cell must be dead, coated in plastic and shaved 1 000 000X magnification. 0.2nm resolution Greater resolution and magnification. Image must be photographed or showed on a monitor Images using TEM • Embryo of C. elegans (1mm long nematode) • A mitochondria in a mammalian lung cell Observing Cells • • • • • • • The Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) Reflects electrons from the surface of the specimen Thicker samples can be used Use magnets to focus the beam of electrons 3-D image, 300 000X magnification, resolution 10nm Greater contrast and depth SEM must be photographed or viewed on a monitor SEM images • Spider • pollen