* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File rome creates a republic
History of science in classical antiquity wikipedia , lookup
Roman economy wikipedia , lookup
Conflict of the Orders wikipedia , lookup
Leges regiae wikipedia , lookup
Roman agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Roman historiography wikipedia , lookup
Roman army of the late Republic wikipedia , lookup
Roman Republican governors of Gaul wikipedia , lookup
Roman Senate wikipedia , lookup
Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Centuriate Assembly wikipedia , lookup
Senatus consultum ultimum wikipedia , lookup
Culture of ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Education in ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Travel in Classical antiquity wikipedia , lookup
Promagistrate wikipedia , lookup
Constitutional reforms of Augustus wikipedia , lookup
Legislative assemblies of the Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Constitutional reforms of Sulla wikipedia , lookup
Roman Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Elections in the Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Early Roman army wikipedia , lookup
Executive magistrates of the Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
History of the Roman Constitution wikipedia , lookup
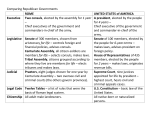
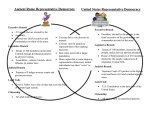
Pgs 141-143 Earliest settlers of the Italian peninsula arrived between 1000 BC and 500 BC. -Latins, Greeks, and Etruscans They were farmers, shephards, metalworkers, and engineers Greek culture heavily influenced Roman culture -growing grapes and olives -gods and religion Greek god Zeus became Roman god Jupiter. Greek god Hera became Roman god Juno In 600 BC, Etruscan kings began ruling over Rome. -Romans did not like being ruled by a monarch and overthrew the king, leading to the development of republic. Consuls were officials who ruled Rome in place of a king. They (1)commanded the army and (2)directed the government. In Rome, there were two who ruled together. However, the consuls powers were limited. 1.A consul only served a one year term, and they could not be elected again for ten years. 2.One consul could always overrule, or veto, the other’s decisions. •The Senate was the aristocratic branch of government. • By tradition, there were 300 members chosen from the upper class of Roman society. •Membership was for life. •The Senate heavily influenced domestic policy, (how government treated its own country), and foreign policy, (how government deals with other nations). The Centuriate Assembly •Made up of citizen-soldiers •Appointed consuls and made laws for the Republic •Had less power than the Senate The Tribal Assembly •Elected the Tribunes and made laws for the common people •Rome would appoint a dictator in times of crisis. •He would have absolute power to make laws and command the army. •Power would last about six months •Dictators were chosen by the consuls and elected by the Senate. Define the following terms: 1. Plebeian 2. Patrician 3. Tribune 4. Republic 5. Legion How did the geography of Greece affect the people that settled there? Which Greek city-state valued military training, strength and discipline? Which Greek city-state valued education, philosophy and beauty? Who fought in the Peloponnesian War? What was Alexander the Great’s biggest weakness?