* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download N1A 3 2012 - The Open University
Neo-Piagetian theories of cognitive development wikipedia , lookup
Transformational grammar wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Theory of mind in animals wikipedia , lookup
Empirical theory of perception wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Panpsychism wikipedia , lookup
Mental image wikipedia , lookup
Situated cognition wikipedia , lookup
MOGUL framework wikipedia , lookup
Michael Tomasello wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive development wikipedia , lookup
Personal knowledge base wikipedia , lookup
Junction Grammar wikipedia , lookup
Affective neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Formal concept analysis wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive semantics wikipedia , lookup
Conceptual combination wikipedia , lookup
Emotion perception wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive psychology wikipedia , lookup
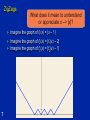
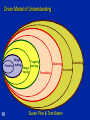
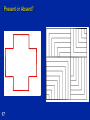
(Some) Promoting Mathematical Thinking Psychology of Learning & Doing Mathematics Oxford N1A §3 2012 1 The Open University Maths Dept University of Oxford Dept of Education Seeing & Believeing 2 Psychology: study of the psyche Cognition, intellect Enaction, behaviour Affect, emotion Attention & will How these are influenced by the social 3 What does it mean to ‘understand’ in mathematics? To carry out procedures unaided – By templating – By re-constructing To have come to mind appropriate procedures and concepts To explain adequately to someone – – – – Own narrative To a Novice To a Peer/Colleague To an Expert To modify to meet new circumstances To be familiar with a viable model (structural relationships treated as properties) Understand or Overview or Appreciate? 4 Concept Image “ … all the cognitive structure in the individual's mind that is associated with a given concept” (Tall & Vinner 1981) the total cognitive structure that is associated with the concept, which includes all the mental pictures and associated properties and processes. It is built up over the years through experiences of all kinds, changing as the individual meets new stimuli and matures. Concept Image ≠ Concept Definition 5 Concept Images: examples What – – – – 6 is A fraction Angle between two lines Differentiability Tangent to a curve ZigZags What does it mean to understand or appreciate x –> |x|? Imagine the graph of f1(x) = |x – 1| Imagine the graph of f2(x) = |f1(x) – 2| Imagine the graph of f3(x) = |f2(x) – 1| 7 Onion Model of Understanding Image Primitive making 10 Image having Property noticing Inventising Observing Formalising Structuring Susan Pirie & Tom Kieren Templating & Re-Constructing Instrumental & Relational Understanding (Skemp 1971) Following a Template & Reconstructing to Meet Circumstances Procedural & Conceptual Formal & Intuitive insight/comprehension Trained Behaviour & Educated Awareness 11 Templating & Reconstruction: examples Reverse Number Notation What can be said about f if 12 f (x) - 3 lim =5 x->2 x - 2 Development Manipulating familiar confidence inspiring objects (specialising, particularising) In order to get a sense of underlying structural relationships (modelling, axiomatising, justifying, proving …) Bringing this experience to articulation, which over time, becomes more succinct and useable (manipulable) 13 Structure of the Psyche Awareness (cognition) Imagery Will Emotions (affect) Body (enaction) Habits Practices 14 Structure of a Topic Language Patterns & prior Skills Imagery/Senseof/Awareness; Connections Root Questions predispositions Different Contexts in which likely to arise; dispositions Standard Confusions & Obstacles Techniques & Incantations Emotion Only Emotion is Harnessable 15 Only Awareness is Educable Only Behaviour is Trainable Coming to Know in Mathematics Observing What strikes us (disturbance revealing expectation ) Probing and elucidating underlying structure (Modelling, Axiomatising, Proving) 16 Present or Absent? 17 Attention (Will) in Mathematics Holding Wholes (gazing) Discerning Details Recognising Relationships (in the situation) Perceiving Properties Reasoning on the basis of agreed properties 18 Worlds of Experience Inner World of imagery World of Symbols Material World enactive 19 iconic symbolic Summary Concept Image & Concept Definition Templating & Reconstructing Awareness (ability to act) – Emotion – Behaviour – Only awareness is educable – Only behaviour is trainable – Only emotion is harnessable Structure of a Topic Onion model of coming to understand Manipulating – getting-a-sense-of – Articulating Enactive – Iconic – Symbolic modes or worlds Attention: 20 – Gazing (holding wholes) – Discerning Details – Recognising Relationships – Perceiving Properties – Reasoning on the basis of agreed properties