* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download GAAP
Internal control wikipedia , lookup
Auditor's report wikipedia , lookup
Institute of Chartered Accountants of India wikipedia , lookup
Mergers and acquisitions wikipedia , lookup
Debits and credits wikipedia , lookup
Microsoft Dynamics GP wikipedia , lookup
James Bray Griffith wikipedia , lookup
Natural capital accounting wikipedia , lookup
Going concern wikipedia , lookup
Institute of Cost Accountants of India wikipedia , lookup
J. Lee Nicholson wikipedia , lookup
Lean accounting wikipedia , lookup
International Financial Reporting Standards wikipedia , lookup
South African Institute of Chartered Accountants wikipedia , lookup
Mark-to-market accounting wikipedia , lookup
Sustainability accounting wikipedia , lookup
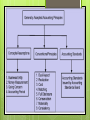
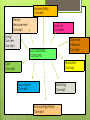
Accounting principles are guidelines to establish standards for sound accounting practices and procedures in reporting the financial status and periodic performance of a business. Accounting standards are written/policy documents issued by the govt. or professional institutes covering various aspects of recognition, measurement, treatment, presentation and disclosure of accounting transactions in the financial statements. Accounting principles are man made so they do not have the authoritativeness as universal principles like the principles of physics , chemistry and other natural sciences. The science of accounting is not in a finished form, it is in the process of evolution. The general acceptance of an accounting principle depends on how well it meets 3 criteria – relevance , objectivity and feasibility. Accounting concepts may be considered as postulates i.e., basic assumptions or conditions upon which the science of accounting is based. The term “conventions” denote circumstances or traditions which guide the accountants while preparing the accounting statements. This concept implies that business unit is separate and distinct from the person who supply capital to it. Irrespective of the firm of organisation , a business unit has got its own individuality as distinguished from the person who control and own it. The accounting equation is an expression of the entity concept because it shows that the business itself owns the assets and in turn owes to the various claimants. Assets = Liabilities + Capital Business is kept separate from the proprietor so that transactions of the business may also be recorded with him. In case this concept is not followed , affairs of the business will be mixed up with the private affairs of the proprietor and the true picture of the business will not be available. If the proprietor of the business invests 25000 to the business, it will be deemed that he has given that much of money to the business as a loan which will be shown as a liability in the books of a firm. On receipt of the amount, cash account will be debited and the proprietor ‘s capital account will be credited. Money is the only practical unit of measurement that can be employed to achieve homogeneity of financial data. Therefore accounting records only those transactions which can be expressed in terms of money though quantitative records are also kept. The advantages of expressing business transactions in terms of money is the money serves as a common denominator by means of which heterogeneous facts about a business can be expressed in terms of numbers which are capable of additions and subtractions. A business units has following assets: Cash in hand and cash at bank – Rs.25000 Sundry debtors- 48500 Bills receivable-6500 Motor cars -5 Stock – 6000 tons Furniture- 100 chairs and 20 tables Machines -7 They should be expressed as follows: Cash in hand and at bank – Rs.25000 Sundry debtors – Rs.48500 Bills receivable- Rs.6500 Motor cars –Rs.115000 Stock – Rs.400000 Furniture – Rs.5000 Total = Rs.600000 It is assumed that a business unit has a reasonable expectations of continuing business at a profit for an indefinite period of time. A business unit is deemed to be a going concern and not a gone concern. It will continue to operate in the future. Transactions are recorded in the books keeping in view the going concern aspect of the business unit. When an enterprise was set u for a particular purpose which has been achieved or to be achieved shortly. When a company is declared sick by BIFR . When an enterprise has been in the grip of severe financial crisis and is expected to wind up shortly. When a receiver or liquidator has been appointed in case of a company which is to be liquidated. The fundamental concept of accounting closely related to the going concern concept is that an asset is recorded in the books at the price paid to acquire it and that this concept is the basis foe all subsequent accounting for the assets. This concept does not mean that the assets will always be shown at cost but it means that cost becomes basis for all future accounting for the assets. The cost concept has the advantages of bringing objectivity in the accounts. Information given in the financial statements is not influenced by the personal bias or judgement of those who furnish such statement. This is the basic concept of accounting , according to this concept, every financial transaction involves a two fold aspect: Yielding of a benefit. Giving of that benefit. Every debit must have a corresponding credit and vice versa and upon this dual aspect has been raised the whole superstructure of DOUBLE ENTRY SYSTEM OF ACCOUNTING. If the business purchase machinery and furniture worth Rs. 25000 and Rs.5000 respectively out of Rs.40000 provided by the proprietor of the business, the situation will be as follows.. Assets = equities Machinery Rs.25000 + Furniture Rs.5000+ Cash Rs.10000.. = capital =Rs.40000 Subsequently if the business purchases stock worth Rs.8000 on credit the position will be as follows.. Machinery Rs.25000+ furniture Rs.5000+ cash Rs.10000+ stock Rs.8000= creditors Rs.8000+capital Rs.40000. Thus accounting equation demonstrates the fact that foe every debit there is an equivalent credit. A complete and accurate picture of the degree of success achieved by a business unit cannot be obtained until it is liquidated, converts its assets into cash and pays off its debts. The final accounts must be prepared on a periodic basis rather than waiting till the business is terminated. Normally accounting period adopted is one year as it helps to take any corrective action, to pay income tax, to absorb the seasonal fluctuations and for reporting to the outsiders. A period of more than one year reduces the utility of accounting data. The principle of segregating capital expenditure from revenue expenditure is based on the accounting period concept. This concept is based on the accounting period concept. It is widely accepted that desire of making profit is the most important motivation to keep the proprietors engaged in business activities. By `matching’ we mean appropriate association of related revenues and expenses pertaining to a particular accounting period. To put it in other words, profits made by a business in a particular accounting period can be ascertained only when the revenues earned during that period are compared with the expenses incurred for earning that revenue. In a business enterprise which adopts calendar year as accounting year, if rent for December 2013 was paid in January 2014, the rent so paid should be taken as the expenditure of the year 2013, revenues of that year should be matched with the costs incurred for earning that revenue including the rent for December 1989, though paid in January 2014. It is on account of this concept that adjustments are made for outstanding expenses, accrued incomes, prepaid expenses etc. while preparing financial statements at the end of the accounting period. The system of accounting which follows this concept is called as mercantile system. In contrast to this there is another system of accounting called as cash system of accounting where entries are made only when cash is received or paid, no entry being made when a payment or receipt is merely due. According to this concept revenue is considered as being earned on the date at which it is realised that is on the data when the property in goods passes to the buyer and he becomes legally liable to pay. This concept is criticised by economists on the ground that if an asset has increased in value then it is irrelevant because it has not yet been sold. As a result of this concept ,distinction is made between holding gains and operating gains . Holding gains arise as a result of increase in value from holding an asset and operating gains are realised as a result of selling assets. Holding gains are not recorded because property in goods has not yet transferred but operating gains are reported because they have resulted as a result of sale. As far as possible, every entry in accounting records should be supported by some objective evidence. Evidence should be such which will minimise the possibility of error and intentional bias or fraud. The provision for doubtful debts account is an estimate of the losses expected from failure to collect sales made on credit. Estimation of this account should be made on such objective factors as past experience in collecting debtors and reliable forecasts of future business activities. The essence of the accrual concept is that revenue is recognised when it is realised i.e., when sale is complete or services are given and it is immaterial whether cash is received or not. Similarly according to this concept, expenses are recognised in the accounting period in which they help in earning the revenue whether cash is paid or not. Thus to ascertain correct profit or loss for an accounting period and to show the true and fair financial position of the business at the end of the accounting period , we make record of all expenses and incomes relating to the accounting period whether actual cash has been paid or received or not. Accounting rules , practices and conventions should be continuously observed and applied i.e., these should not change from one year to another . The results of different years will be comparable only when accounting rules are continuously adhered to from year to year. Example… the principle of valuing stock at cost or net realisable value whichever is less should be followed year after year to get comparable results. Consistency serves to eliminate personal bias because the accountant will have to follow consistent rules , practices and conventions year after year. The rationale behind this concept is that frequent changes in accounting treatment would make the financial statements unreliable to the persons who use them. Consistency also implies external consistency i.e. financial statements of one enterprise should be comparable with another. Vertical consistency is achieved when the same accounting rules , policies , practices and conventions are adopted while preparing interrelated financial statements of the same date. Horizontal consistency is achieved when the same firm adopts the same accounting practices ,policies and methods from year to year.. According to this convention, all accounting statements should be honestly prepared and to that full disclosure of all significant information should be made. All information which is of material interest to proprietors, creditors and investors should be disclosed in accounting statements. The basis of valuation of fixed assets, investments and stock should be clearly stated in the balance sheet because it is of material interest to the proprietors, creditors and prospective investors . It is a policy of caution or playing safe and had its origin as a safeguard against possible losses in a world of uncertainity. It compels the businessman to wear a risk proof jacket for the working rule – anticipate no profits but provide for all possible losses. Example closing stock is valued at cost or net realisable value, whichever is less. But if the net realisable value is less than the cost, the higher amount of cost will be ignored and stock will be valued at net realisable value which is less than the cost. Contingent gains and benefits from contracts to the extent nit executed should not be accounted fir in financial statements. The materiality concept is the principle in accounting that states that all important matters are to be disclosed. Items that are large enough to matter are material items. Materiality refers especially to: • The level of detail appropriate for different financial reports. • The importance of errors such as: – Reporting expenses, revenues, liabilities, equities, or assets in inappropriate accounts, or reporting them for incorrect reporting periods. – Omitting or failing to report important financial data. • The materiality concept is an established, recognized accounting convention. Another such convention is the historical cost convention, by which transactions are recorded at the price prevailing when the transaction is made, and assets are valued at original cost. • Applying the materiality concept may call for more subjective judgment. Moreover, the subjective judgments of senior management, accountants, auditors, boards of directors, stockholders, and potential business partners, can differ, especially when competing interests are involved. Moreover, the subjective judgments of senior management, accountants, auditors, boards of directors, stockholders, and potential business partners, can differ, especially when competing interests are involved. Financial statement items are considered material (large enough to matter) if they could influence the economic decisions of users. The materiality concept is the universally accepted accounting principle that all material matters are to be disclosed. Some of the examples of material financial information to be disclosed are likely fall in the value of stocks, loss of markets due to competition or Government regulation, increase in wage bill under recently concluded agreement , etc. An item of small value may last for three years and technically its cost must be allocated to every one of the three years. Since its value is small, it can be treated as the expense in the year of purchase. As per A.S. – 1, materiality should govern the selection and application of accounting policies. According to the consideration of materiality financial statement should disclose all items which are material enough to affect evaluations or decisions. ILLUSTRATION : Company XYZ Ltd. bought 6 months supplies of stationary worth $600. QUESTION : Should the Company spread the cost of this stationary for 6 months by expensing off $100 per month to the income statement? ANSWER : Based on this concept, as the amount is so small or immaterial, it can be expensed off in the next month instead of tediously expensing it in the next 6 months. Accounting policies are the specific accounting principles and the methods of applying those principles that are considered by a business concern to be the most appropriate in the circumstances to present financial statements. Accounting policies represent choices among different accounting methods that can be used in recording financial transactions and preparing financial statements. Three consideration should govern the selection and application by management of the appropriate accounting policies and the preparation of financial statements. PRUDENCE – uncertainities inevitably surround many transactions .this should be recognised by exercising prudence in preparing financial statements. Prudence does not however just the creation of secret or hidden reserves. SUBSTANCE OVER FORM- transactions and other events should be accounted for and presented in accordance with their substance and financial reality and not merely with their legal form. MATERIALITY- financial statements should disclose all items which are material enough to affect evaluations or decisions. Hereby we conclude that both accounting principles and policies are an integral part of financial statements which need to be adhered to. Their presence makes accounting treatment easier and understandable. Short Answer Type Questions 1. Define accounting concepts and accounting conventions. Accounting concepts : Accounting concepts may be considered as postulates i.e., basic assumptions or conditions upon which the science of accounting is based. Accounting conventions : The term ‘conventions’ denote circumstances or traditions which guide the accountants while preparing the accounting statements. 2. Write the basic difference between concepts and conventions. Concepts and conventions are often used inter-changeable. The basic difference between them is that concepts are concerned with maintenance of accounts where as conventions are applicable while preparing financial statements i.e., Statement of Profit and Loss and Balance Sheet. 3. State the accounting concepts. Business Entity Concept Money Measurement Concept Going Concern Concept Cost Concept Dual Aspect Concept Accounting Period Concept Matching Concept Realisation Concept Objective Evidence Concept Accrual Concept 4. State the accounting conventions. Convention of Consistency Convention of Full Disclosure Convention of Conservatism Convention of Materiality 3. What is matching concept? Matching concept is based on the accounting period concept. The most important objective of running a business is to ascertain profit periodically. The determination of profit of a particular accounting period is essentially a process of matching the revenue recognised during the period and the cost to be allocated to the period to obtain the revenue. It is, thus, a problem of matching revenues and expired costs, the residual amount being the net profit or net loss for the period. 4. Write three fundamental accounting assumptions. Going concern : The enterprise is normally viewed as a going concern, that is, as continuing in operation for the foreseeable future. Consistency : It is assumed that the accounting policies are consistent from one period to another. Accrual: Revenues and costs are accrued, that is, recognised as they are earned or incurred and recorded in the financial statements of the periods to which they relate. 5. State the sources of Indian GAAP. Principle sources of Indian GAAP are: Company law. Accounting standards and related documents of the ICAI. SEBI requirements. Established Conventions. Long Answer Type Questions Q.1. What are the basic accounting concepts? Explain their implications. Ans: Accounting concepts may be considered as postulates i.e. basic assumptions or conditions upon which the science of accounting is based. There is no authoritative list of these concepts but most of the concepts have fairly general support. Business Entity Concept Money Measurement Concept Accrual Concept Going Concern Concept Objective Evidence Concept ACCOUNTING CONCEPTS Realisation Concept Cost Concept Dual Aspect Concept Matching Concept Accounting Period Concept IMPLICATIONS 1. Accounting concepts provide a standard to measure financial presentations. 2. Accounting concepts recognise the importance of reporting transactions and events in accordance with their substance. 3.Accounting concepts are common set of accounting principles that companies use while preparing their financial statements of the accounting period. 4. These are imposed on companies so that investors have a maximum level of consistency in the financial statements they use when analysing companies for investment purposes. 5. Accounting concepts are necessary so that accountant could follow these concepts about the measurement of revenue and expenses. Q.2. Why are accounting concepts and conventions necessary? How do you distinguish between accounting concepts and conventions? Ans: Accounting concepts and conventions are very necessary in ascertaining the profit of the financial companies. 1.These concepts and conventions have been made by accounting experts. They found that if any accountant will use these concepts and conventions in his professional work then he can save money, energy, time and provide effective services to organization. 2.Accounting concepts and conventions are necessary so that accountant could follow these concepts about the measurement of revenue and expenses. 3. Accounting concepts and conventions are a set of methodologies and guidelines when preparing financial statements, thereby ensure that accounting information is prepared in a manner which is consistent, true, fair and accurate. DIFFERENCE BETWEEN ACCOUNTING CONCEPTS AND ACCOUNTING CONVENTIONS ACCOUNTING CONCEPTS ACCOUNTING CONVENTIONS 1. Accounting concepts may be considered as postulates i.e. basic assumptions or conditions upon which the science of accounting is based. 1. Accounting conventions denote circumstances or traditions which guide the accountants while preparing the accounting statements. 2.Accounting concepts have been established by professional organizations and are standard principles that must be followed when preparing the financial accounts. 2. Conventions are generally accepted practices that can change and are updated over time, depending upon the changes in the financial reporting landscape. ACCOUNTING CONCEPTS ACCOUNTING CONVENTIONS 3. Accounting concepts are officially recorded. 3. Accounting conventions are not officially recorded and are followed as generally accepted guidelines. 4. Accounting concepts are concerned with maintenance of accounts. 4. Accounting conventions are applicable while preparing financial statements i.e. Statement of Profit and Loss and Balance Sheet. Q.3. What do you mean by basic accounting concepts and conventions? Discuss in brief some of the important concepts and conventions. Ans: Accounting concepts may be considered as postulates i.e. basic assumptions or conditions upon which the science of accounting is based. Accounting concepts have been established by professional organizations and are standard principles that must be followed when preparing the financial accounts. Accounting conventions denote circumstances or traditions which guide the accountants while preparing the accounting statements. Conventions are generally accepted practices that can change and are updated over time, depending upon the changes in the financial reporting landscape. Business Entity Concept: This concept implies that a business unit is separate and distinct from the person who supply capital to it. The transactions of the proprietor with the business are recorded so that true financial position and profitability of the business may be disclosed. 1. 2. Money Measurement Concept: Money is the only practical unit of measurement that can be employed to achieve homogeneity of financial data. Therefore, accounting records only those transactions which can be expressed in terms of money though quantitative records are also kept. The advantage of expressing business transactions in terms of money is that money serves as a common denominator. 3. Going Concern Concept: It is assumed that a business unit has a reasonable expectation of continuing business at a profit for an indefinite period of time. A business unit is deemed to be a going concern and not a gone concern. It will continue to operate in future. The transactions are recorded in the books keeping in view the going concern aspect of the business unit. 4. Cost concept: A fundamental concept of accounting closely related to the going concern concept is that an asset is recorded in the books at the price to acquire it and that this cost is the basis for all subsequent accounting for the asset. This concept does not mean that the asset will always be shown at cost but it means that cost becomes basis for all future accounting for the asset. 5. Dual aspect concept: This is the basic concept of accounting. According to this concept, every financial transaction involves a two fold aspect: (a) Yielding of a benefit (b) the giving of that benefit. ACCOUNTING CONVENTIONS: Convention of Consistency : Accounting rules, practices and conventions should be continuously observed and applied i.e. these should not change from one year to another. The results of different years will be comparable only when accounting rules are continuously adhered to from year to year. 1. 2. Convention of Full Disclosure: According to this convention, all accounting statements should be honestly prepared and to that end full disclosure of all significant information should be made. All information which is of material interest to proprietors, creditors and investors should be disclosed in accounting statements. 3. Convention of Conservatism or Prudence: Conservatism means taking the gloomy view of a situation. It is a policy of caution or playing safe and had its origin as a safeguard against possible losses in a world of uncertainty. It compels the businessman to wear a “risk proof” jacket for the working rule: anticipate no profits but provide for all possible losses. 4. Convention of Materiality: An accounting concept according to which all relatively important and relevant items ,(i.e. items, the knowledge of which might influence the decisions of the user of the financial statements) are disclosed in the financial statements. Q.4: Examine the accounting concepts of conservatism and materiality and their significance in the preparation of financial statements. Conservatism: Conservatism means taking a gloomy view of a situation. It is a policy of caution or playing safe. It compels the businessman to wear a risk-proof jacket, for the rule is anticipate no profits but provide for all possible losses. For example, closing stock is valued at cost or net realizable value whichever is less . If net realizable value us higher than cost, the higher amount of cost will be ignored and stock will be valued at net realizable value which less than cost. Other applications of the conservatism concept can be as follows: a) b) c) d) Research and development expenses are usually charged as expenses of the period in which they are incurred but benefits of research and development will be realized in future. Under the completed contract method revenue from long term construction contract is recognized only when the contract is completed substantially. In case of “cash or delivery sales” revenue is recognized when cash is received by the seller or his agent and not on delivery of goods to the buyer. As per AS4,”the amount of a contingent loss should be provided for by a charge in the statement of profit or loss if: i. ii. It is probable that at the date of the financial statements events subsequent thereto will confirm that an asset has been impaired or a liability has been incurred as at that date ,and A reasonable estimate of the amount of the resulting loss can be made. Contingent gains and benefits from contracts to the extent should not accounted for in financial statements .” Over optimism in reporting results is more undesirable results than over pessimism in reporting results because it shows position better than what actual financial position is. But the excessive application of the convention of conservatism could result in the creation of secret results, which is contrary to the convention of full disclosure. Conservatism carried beyond what is warranted by reasonable doubts distorts earnings in as much as net profit in one period may be understated than what actual profit is. • Materiality: Materiality depends on the amount involved in the transaction. The accountant should record an item as material even though it is of small amount if its knowledge seems to influence the decision of the proprietors or auditors or investors. Q.5:Explain the accounting concept of income. The essence of the accrual concept is that revenue is recognized when it is realized, that is when sale is complete or services are given and it is immaterial whether cash is received or not. Similarly, according to this concept, expenses are recognized in the accounting period in which they help in earning the revenue whether cash is paid or not. Q.6: Explain the meaning and significance of the following : a) b) c) d) e) f) g) The Going concern concept The Money Measurement concept The Cost concept The Business Entity concept The Matching concept The Accounting Period concept Dual Aspect concept a) Going Concern Concept: It is assumed that a business unit has a reasonable expectation of continuing business at a profit for an indefinite period of time. A business unit is deemed to be a Going Concern and not a Gone Concern. It will continue to operate in the future. Transactions are recorded in the books keeping in view the Going Concern aspect. b) Money Measurement Concept: Accounting records only those transactions which can be expressed in terms of money though quantitative records are also kept. Money provides a common denominator for measuring but it does not take care of inflation, which takes place with the passage of time. c) Cost Concept: A fundamental concept of accounting closely related to Going Concern concept is that an asset is recorded in the books at the price paid to acquire it and that this cost is the basis for all subsequent accounting for the asset. This concept does not mean that the asset will always be shown at cost, but it means that cost becomes basis for all future accounting for the asset. d) Business Entity Concept: This concept implies that a business unit is separate and distinct from the person who supplies capital to it. Irrespective of the form of organization, a business unit has got its own individuality as distinguished from the person who owns or controls it. The accounting equation i.e. assets = liabilities + capital is an expression of the entity concept because it shows that the business itself owns the assets and in turn owes to various claimants. e) Matching Concept: The determination of profit of a particular accounting period is essentially a process of matching the revenue recognized during the period and the cost to be allocated to the period to obtain the revenue. It is thus a problem of matching revenues and expired costs. The residual amount being the net profit or net loss for the period. f) Accounting Period Concept: Normally, accounting period adopted is one year as it helps to take any corrective action to pay income tax to absorb the seasonal fluctuations and for reporting to the outsiders. A period of more than one year reduces the utility of accounting data. The principle of segregating capital expenditure from revenue expenditure is based on the account period concept. g) Dual Aspect Concept: This is the basic concept of accounting. According to this concept, every financial transaction involves a two fold aspect, (a) yielding of a benefit and (b) the giving of that benefit. There must be a double entry to have a complete record of each business transaction, an entry being made in the receiving account and an entry of the same amount in the giving account. Q7. “Accrual concept is essentially the matching concept”. Explain the statement. In cash accounting, you record transactions in your books only when you receive cash or you pay out cash. Say you own a small business that produces crafts, and you sell 500 finished pieces to a retailer for $5 apiece. Under cash accounting, if you were paid in cash, you would immediately record $2,500 in revenue. But if you sold the items on credit, you wouldn't record the revenue until you actually got the cash. In accrual accounting, you recognize revenue whenever you earn it, regardless of when the money comes in. In the same scenario, you would record $2,500 in revenue immediately, whether you sold the items for cash or on credit. The matching concept exists only in accrual accounting. This principle requires that you match revenues with the expenses incurred to earn those revenues, and that you report them both at the same time. This means that if you owned a store and spent money to purchase items for your inventory, you wouldn't record that expense until you sold the items for revenue. Further, you would record only the portion of the expense attributable to each individual item as it got sold. Similarly, if you ran a crafts business, you wouldn't record the expenses involved in producing those crafts until you actually sold the items you had produced. GAAP serves as a common language among accounting and finance professionals, thereby allowing stakeholders to compare financial statements across corporations and vast time spans. An investor who wishes to invest in the automobile industry, for example, can meaningfully compare the profit figures of two automakers only if they were prepared using the same principles. Similarly, managers can only draw realistic conclusions about their divisions' performance if their accountants stick to a set of consistent principles over time. GAAP also minimizes the risk of unintentional errors through implementation of checks and safeguards, and provides confidence to the users of financial statements. The accounting entity concept recognizes a specific business enterprise as one accounting entity, separate and distinct from the owners, managers, and employees of that business. The going concern principle, also known as continuing concern concept or continuity assumption, means that a business entity will continue to operate indefinitely, or at least for another twelve months. Financial statements are prepared with the assumption that the entity will continue to exist in the future, unless otherwise stated. The going concern assumption is the reason assets are generally presented in the balance sheet at cost rather that at fair market value. Long-term assets are included in the books until they are fully utilized and retired. Q9. “Without accounting concepts and conventions objective, reliable, consistent and comparable accounts cannot be maintained.” comment. Separate entity concept: This concept assumes that, for accounting purposes, the business enterprise and its owners are two separate independent entities. Thus, the business and personal transactions of its owner are separate. For example, when the owner invests money in the business, it is recorded as liability of the business to the owner. Similarly, when the owner takes away from the business cash/goods for his/her personal use, it is not treated as business expense. Money Measurement concept: This concept assumes that all business transactions must be in terms of money. In our country such transactions are in terms of rupees. Thus, as per the money measurement concept, transactions which can be expressed in terms of money are recorded in the books of accounts Going concern concept: • This concept states that a business firm will continue to carry on its activities for an indefinite period of time. • Simply stated, it means that every business entity has continuity of life. Thus, it will not be dissolved in the near future. This is an important assumption of accounting, as it provides a basis for showing the value of assets in the balance sheet. Accounting period concept: The life of an entity is divided into short economic time periods on which reporting statements are fashioned. All the transactions are recorded in the books of accounts on the assumption that profits on these transactions are to be ascertained for a specified period. This is known as accounting period concept. Accounting cost concept: Accounting cost concept states that all assets are recorded in the books of accounts at their purchase price, which includes cost of acquisition, transportation and installation and not at its market price. It means that fixed assets like building, plant and machinery, furniture, etc are recorded in the books of accounts at a price paid for them. For example, a machine was purchased by XYZ Limited for Rs.500000, for manufacturing shoes. An amount of Rs.1,000 were spent on transporting the machine to the factory site. In addition, Rs.2000 were spent on its installation. The total amount at which the machine will be recorded in the books of accounts would be the sum of all these items i.e. Rs.503000. This cost is also known as historical cost. Matching Concept: The matching concept states that the revenue and the expenses incurred to earn the revenues must belong to the same accounting period. So once the revenue is realised, the next step is to allocate it to the relevant accounting period. The matching concept implies that all revenues earned during an accounting year, whether received/not received during that year and all cost incurred, whether paid/not paid during the year should be taken into account while ascertaining profit or loss for that year. Dual aspect concept Dual aspect is the foundation or basic principle of accounting. It provides the very basis of recording business transactions in the books of accounts. This concept assumes that every transaction has a dual effect, i.e. it affects two accounts in their respective opposite sides. Therefore, the transaction should be recorded at two places. It means, both the aspects of the transaction must be recorded in the books of accounts. For example, goods purchased for cash has two aspects which are (i) Giving of cash (ii) Receiving of goods. These two aspects are to be recorded. Thus, the duality concept is commonly expressed in terms of fundamental accounting equation : Assets = Liabilities + Capital Realisation concept This concept holds to the view that profit can only be taken into account when realisation has occurred. According to this concept revenue is recognised when a sale is made. Sale is considered to be made at the point when the property in goods passes to the buyer and he becomes legally liable to pay. Revenue is said to have been realised when cash has been received or right to receive cash on the sale of goods or services or both has been created ACCOUNTING CONVENTIONS The term ‘conventions’ includes those customs or traditions which guide the accountant while preparing the accounting statements. Accounting Conventions Conservatis m Full Disclosure Consistency Materiality Conservatism This convention is based on the principle that “Anticipate no profit, but provide for all possible losses”. It provides guidance for recording transactions in the books of accounts. It is based on the policy of playing safe in regard to showing profit. The main objective of this convention is to show minimum profit. Profit should not be overstated. If profit shows more than actual, it may lead to distribution of dividend out of capital. This is not a fair policy and it will lead to the reduction in the capital of the enterprise Full Disclosure Convention of full disclosure requires that all material and relevant facts concerning financial statements should be fully disclosed. Full disclosure means that there should be full, fair and adequate disclosure of accounting information. Consistency The convention of consistency means that same accounting principles should be used for preparing financial statements year after year. For example: if a stock is valued at “cost or market price whichever is less”, this principle should be followed year after year. Materiality The convention of materiality states that, to make financial statements meaningful, only material fact i.e. important and relevant information should be supplied to the users of accounting information. The question that arises here is what is a material fact. The materiality of a fact depends on its nature and the amount involved. Material fact means the information of which will influence the decision of its user. Q10. Explain the major conventions (or doctrine) followed in the preparation of financial statements . Ans. There are four major conventions which are followed in the preparation of financial statements. These conventions are as follows: 1. Convention of Consistency 2. Convention of full disclosure 3. Convention of conservatism 4. Convention of materiality 1. Convention of Consistency Accounting rules ,practices and conventions should be continuously observed and applied i.e. these should not change from one year to another . The results of different years will be comparable only when accounting rules are continuously adhered to from year to year. For example the principle of “valuing stock at cost or market price whichever is lower “ should be followed “year after year to get comparable results.” 2.Convention of Full Disclosure According to this convention , all accounting statements should be honestly prepared and to that end full disclosure of all significant information should be made. All information which is of material interest to proprietors , creditors and investors should be disclosed in accounting statements . 3. Convention Of Conservatism Literally speaking conservation means taking the gloomy view of a situation. It is policy of caution or playing had its origin as a safeguard against possible losses in world of uncertainty. It compels the businessman to were a “risk-proof” jacket for the working rule is: “ anticipate profit for all possible For example ,closing stock is valued at cost or losses.” market price .whichever is lower .if market price is higher than the cost ,the higher amount is ignored in the accounts and closing stock will be valued at cost which is lower than the market price. 4. Convention of Materiality An accounting concept according to which all relatively important and relevant items ,i.e., items, the knowledge of which might influence the decisions of the user of the financial statements are disclosed in the financial statements. Materiality depends on the amount involved in the transaction. For example ,minor expenditure of rupees 10 for the purchase of waste basket may be treated as an expense of the period than an asset . Q11. Discuss conventions regarding financial statements. Ans. There are four conventions regarding financial statements: - Convention of Consistency: Accounting rules ,practices and conventions should be continuously observed and applied i.e. these should not change from one year to another . The results of different years will be comparable only when accounting rules are continuously adhered to from year to year. Convention of Full Disclosure According to this convention , all accounting statements should be honestly prepared and to that end full disclosure of all significant information should be made. All information which is of material interest to proprietors , creditors and investors should be disclosed in accounting statements . Convention of Conservatism: Literally speaking conservation means taking the gloomy view of a situation. It is policy of caution or playing had its origin as a safeguard against possible losses in world of uncertainty. It compels the businessman to were a “risk-proof” jacket for the working rule is: “ anticipate profit for all possible losses.” Convention of Materiality: An accounting concept according to which all relatively important and relevant items ,i.e., items, the knowledge of which might influence the decisions of the user of the financial statements are disclosed in the financial statements. Materiality depends on the amount involved in the transaction. Q12. Describe in detail the accounting convention which states the rule “anticipate no profit but provide for all the possible losses.” Ans. Literally speaking conservation means taking the gloomy view of a situation. It is policy of caution or playing had its origin as a safeguard against possible losses in world of uncertainty. It compels the businessman to were a “risk-proof” jacket for the working rule is: “ anticipate profit for all possible losses.” For example , closing stock is valued at cost or market price ,whichever is lower .if market price is higher than the cost ,the higher amount of stock is ignored in the accounts and closing stock is valued at cost which is lower than market price. Q13. Explain the accounting concept of periodic matching of costs and revenue. Periodic Matching of Costs and Revenues: This concept is based on the accounting period concept. It is widely accepted that desire of making profit is the most important motivation to keep the proprietors engaged in business activities. Hence a major share of attention of the accountant is being devoted towards evolving appropriate techniques of measuring profits. One such technique is periodic matching of costs and revenues. In order to ascertain the profits made by the business during a period, the accountant should match the revenues of the period with the costs of that period. By `matching’ we mean appropriate association of related revenues and expenses pertaining to a particular accounting period. To put it in other words, profits made by a business in a particular accounting period can be ascertained only when the revenues earned during that period are compared with the expenses incurred for earning that revenue. The question as to when the payment was actually received or made is irrelevant. For e.g. in a business enterprise which adopts calendar year as accounting year, if rent for December 1989 was paid in January 1990, the rent so paid should be taken as the expenditure of the year 1989, revenues of that year should be matched with the costs incurred for earning that revenue including the rent for December 1989, though paid in January 1990. It is on account of this concept that adjustments are made for outstanding expenses, accrued incomes, prepaid expenses etc. while preparing financial statements at the end of the accounting period. The system of accounting which follows this concept is called as mercantile system. In contrast to this there is another system of accounting called as cash system of accounting where entries are made only when cash is received or paid, no entry being made when a payment or receipt is merely due. Q14. Briefly explain the convention of materiality. Give examples. Materiality Information is material if its omission or misstatement could influence the economic decisions of users taken on the basis of the financial statements (IASB Framework).Materiality therefore relates to the significance of transactions, balances and errors contained in the financial statements. Materiality defines the threshold or cutoff point after which financial information becomes relevant to the decision making needs of the users. Information contained in the financial statements must therefore be complete in all material respects in order for them to present a true and fair view of the affairs of the entity. Materiality is relative to the size and particular circumstances of individual companies. Example - Size A default by a customer who owes only $1000 to a company having net assets of worth $10 million is immaterial to the financial statements of the company. However, if the amount of default was, say, $2 million, the information would have been material to the financial statements omission of which could cause users to make incorrect business decisions. Example - Nature If a company is planning to curtail its operations in a geographic segment which has traditionally been a major source of revenue for the company in the past, then this information should be disclosed in the financial statements as it is by its nature material to understanding the entity's scope of operations in the future. Materiality is also linked closely to other accounting concepts and principles: Relevance: Material information influences the economic decisions of the users and is therefore relevant to their needs. Reliability: Omission or misstatement of an important piece of information impairs users' ability to make correct decisions taken on the basis of financial statements thereby affecting the reliability of information. Completeness: Information contained in the financial statements must be complete in all material respects in order to present a true and fair view of the affairs of the company. Q15. Briefly discuss the basic accounting concepts and fundamental accounting assumptions. Is there a conflict between the two? The Accounting Standard (AS-1) ‘Disclosure of Accounting Policies’ issued by Institute of Chartered Accountants of India, which states that there are three fundamental accounting assumptions: 1. 2. 3. Going Concern Consistency Accrual Going concern: The enterprise is normally viewed as a going concern, i.e. as continuing operations for the foreseeable future. It is assumed that the enterprise has neither the intention nor the necessity of liquidation. If an enterprise is not a going concern Valuation of its assets and liabilities on historical cost becomes irrelevant and as a consequence its profit/loss may not give reliable information. It is assumed that accounting policies are consistent from one period to another. This adds the virtue of comparability to accounting data. It comparability is lost, the relevance of accounting data for users’ judgment and decision making is gone. Consistency: Accrual : Revenues and costs are accrued, that is, recognized as they are earned or incurred (and not as money is received or paid) and recorded in the financial statements of the periods to which they relate. This assumption is the core of accrual accounting system. Disclosure requirements -If the fundamental accounting assumption, viz. going Concern, Consistency, and Accrual are followed in financial statements, specific disclosure is not required. If a fundamental accounting assumption is not followed, the fact should be disclosed. These are called fundamentals because these are to be followed and their disclosure in the financial statements is required if these are not followed. Otherwise there is no conflict between accounting concepts and fundamental accounting assumptions. In fact, fundamental accounting assumptions are part of the basic accounting concepts. Q19. What do you mean by fundamental accounting assumptions? Fundamental Accounting Assumptions: Following are recognized by the International Accounting Standards Committee and the Institute of Chartered Accountants of India as fundamental accounting assumptions as per International Accounting Standard 1 and Indian Accounting Standard 1. They are reproduced below: Going Concern. The enterprise is normally viewed as a going concern, that is , as continuing in operation for the foreseeable future. It is assumed that the enterprise has neither the intention nor the necessity of liquidation or of curtailing materially the scale of its operations. Consistency. It is assumed that the accounting policies are consistent from one period to another. Accrual. Revenues and costs are accrued , that is , recognised as they are earned or incurred (and not as money is received or paid) and recorded in the financial statements of the periods to which they relate. If fundamental accounting assumptions are not followed in the preparation and presentation of financial statements, the fact should be disclosed. If these are followed , no specific disclosure is necessary. These are called fundamental because these are to be followed and their disclosure in the financial statements is required if these are not followed. Otherwise there is no conflict between accounting concepts and fundamental accounting assumptions. In fact, fundamental accounting assumptions are part of the basic accounting concepts Q20. (a) Briefly state the three major characteristics which should be considered for the purpose of selection and application of accounting policies. Characteristics of Accounting Principles Following are the main characteristics of accounting principles: Accounting principles are man made so they do not have the authoritativeness as universal principle like the principle of physics, chemistry and other natural sciences. They represent the best possible guidelines based on reasons and observations and have been developed by accountants to enhance the usefulness of accounting data in an ever changing society. Accounting is a social science and is the natural result of economic phenomena. The science of accounting is not in a finished form, it is in the process of evolution. Consequently , accounting principles are fast developing. These are influenced by business practices and customs, government agencies and other business groups. The general acceptance of an accounting principle usually depends on how well it meets three criteria : relevance, objectivity and feasibility . A principle is relevant to the extent that it results in information that is useful to those who want to know something about certain business. A principle is objective to the extent that the accounting information is not influenced by the personal bias of those who furnish the information. The accounting information given in the financial statements should be free from the personal bias of the persons who have taken part in the preparation of such statements. A principle is feasible to the extent that it can be applied without undue complexity or cost. 20. (b) State the concept of materiality. An accounting concept according to which all relatively important and relevant items,(i.e., items, the knowledge of which might influence the decisions of the user of the financial statements) are disclosed in the financial statements. Whether something should be disclosed or not in the financial statements will depend on whether it is material or not. Materiality depends on the amount involved in the transaction . For example, minor expenditure of Rs10 for the purchase of waste basket may be treated as an expense of the period rather than an asset. The term “materiality ’’ is a subjective term . The accountant should record an item as material even though it is of small amount if its knowledge seems to influence the decision of the proprietors or auditors or investors. For example, commission paid to sole selling agents should be disclosed separately in the Statement of Profit and Loss. 20. (c) Transactions and events are guided by generally accepted accounting principles subject to laws of land. Comment. The Phrase ‘ Generally Accepted Accounting Principles’(GAAP) is a technical accounting term that encompasses the conventions , rules and procedures necessary to define accepted accounting practices at a particular time. It includes not only broad guidelines of general applications but also detailed practices and procedures . These rules and procedures provide a standard to measure financial presentations. GAAPs are only a set of standards. There is plenty of room within GAAPs for accountants to distort figures. So even when a company uses GAAP , still there is need to scrutinize its financial statements. Accounting statements are prepared in conformity with these principles in order to place more reliance on them. The need for the common accounting principles becomes more apparent when we contemplate the chaotic conditions that would prevail if every accountant could follow his own principles about the measurement of revenue and expenses. Q21. List out any four accounting concepts . (1) Business Entity Concept This concept implies that a business unit is separate and distinct from the person who supply capital to it. Irrespective of the form of organization , a business unit has got its own individually as distinguished from the person who own or control it. The accounting equation (i.e. Assets= Liabilities+Capital) is an expression of the entity concept because it shows that the business itself owns the assets and in turn owes to the various claimants. (2) Money Measurement Concept Money is the only practical unit of measurement that can be employed to achieve homogeneity of financial data. Therefore, accounting records only those transactions which can be expressed in terms of money though quantitative records are also kept. The advantages of expressing business transactions in terms of money is that money serves a common denominator by means of which heterogeneous facts about a business can be expressed in terms of numbers (i.e. money) which are capable of additions and subtractions. A business unit has the following assets on March, 31, 2014. Cash in hand and at bank Rs 25000, Sundry Debtors Rs 48500, Bills Receivable Rs 6500, Motor Cars 5, Stock 6000 tons, Furniture 100 chairs and 20 tables, Machines 7, Building space 5000 sq. meters, Land 10 acres The items given in different units of measurement cannot be added together to get an idea of the total value of the assets owned by the business. To get an idea of the total value of the assets, all items should be expressed in terms of money as given below: Cash in hand and at bank Rs 25000, Sundry Debtors Rs 48500, Bills receivable Rs 6500, Motor Cars Rs 115000, Stock Rs 400000, Furniture Rs 5000, Machines Rs 250000, Building Rs 440000, Land Rs 100000, Total= 1390000. (3) Going Concern Concept It is assumed that a business unit has a reasonable expectation of continuing business at a profit for an indefinite period of time. A business unit is deemed to be a going concern and not a gone concern. It will continue to operate in the future . Transactions are recorded in the books keeping in view the going concern aspect of the business unit. It is because of this concept that suppliers supply goods and services and other business firms enter into business transactions with the business unit. Suppliers will not supply goods and services and other person will not have business dealings with the business entity if they have the feelings that the concern will be liquidated. This assumption provides much of the justification for recording fixed assets at original cost (i.e. acquisition cost) and depreciating them in a systematic manner without reference to their current realisable value. (4) Accrual Concept The essence of the accrual concept is that revenue is recognized when it is realized, that is when sale is complete or services are given and it is immaterial whether cash is received or not. Similarly, according to this concept, expenses are recognized in the accounting period in which they help in earning the revenue whether cash is paid or not.