* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download powerpoint human disorders - Social Circle City Schools
Sexual dimorphism wikipedia , lookup
Segmental Duplication on the Human Y Chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Causes of transsexuality wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Biology and sexual orientation wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
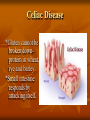
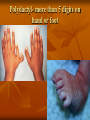
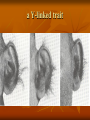
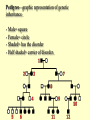
Human Heredity Do Now Read the statements below. Determine if they are true or false. Record answer. 1. The father determines the gender of the child. 2. Individuals may transmit characteristics to their offspring which they themselves do not show. 3. Identical twins always are of the same gender. Discuss 1. Which questions did we miss? Why? 2. Why is it helpful to understand human heredity? Vocab Carrier nondisjunction Pedigree telomere Incomplete dominance Codominance karyotype Multiple alleles polygenic trait Epistatis sex- linked trait Sex chromosome autosome Team 1 vs Team 2 Pictonary Each team will draw a word meaning on the board If your team gets the word in 45 seconds you win a point. Flip flop between teams. Human Chromosomes Humans have 46 chromosomes- 23 pairs Genotype of Female is XX Genotype of Male is XY karyotype: picture of chromosomes Most genetic disorders are caused by RECESSIVE alleles. Cystic fibrosis- large accumulation of muscus due to lack of protein. Phenylketonuria (PKU)- lack enzyme that converts phenylalanine to tyrosine. Tay-Sachs- lack of enzyme that breaks down fat in the CNS Albinism- lack of pigment in skin. Cystic Fibrosis *Caused by a defect in a protein that results in an overproduction of muscus. *Favors bacterial infections because mucos clogs the body like the pancreas, lungs and digestive system. *1 in 20 white Americans are carriers. Cystic Fibrosis cont… 1 in every 2000 children born to white Americans has this disorder. Without treatments, most children die before age 5. With treatments, can live into 20’s+ Treatment includes diet, meds, replacement enzymes and physical therapy Cystic Fibrosis Tay-Sachs- DON’T WRITE *Lack enzyme breaks down fat in the CNS- fat collects on the brain. *No treatment or cure. Most will die before the age of 6. • Found on chromosome #15 predominant in Eastern European Jewish decent. Tay- Sachs cont… Albinism *Absence of pigment melanin in hair, eyes and skin. *Affects eyesight Albinism Celiac Disease *Gluten cannot be broken downprotein in wheat, rye and barley. *Small intestine responds by attacking itself. Disorders caused by dominant alleles: Huntington’s *Disease- effects nervous system. 1/10,000 people in U.S between ages 30-50 yrs old. *Gradual loss of brain functions Dwarfism/ Achondroplasia *Genetic disorder due to lack of growth hormone • Little people is the PC term. • Many different forms not just height. • 75% are born to people of average height. Polydactyl- more than 5 digits on hand or foot Top 10 Genetic Disorders. top 10 Caused by changes in DNA (mutations): Sickle-cell Anemia: amino acid is changed in hemoglobin to give cells a sickle shape. Blocks the flow of red blood cells. Sex-Linked Disordersmost commonly found in males Mostly on X chromosome (recessive) and since males have only one X chromosome they will express the disorder more often. Examples: Colorblindness Hemophilia Muscular Dystrophy DON’T WRITE Some genes are located on the X chromosome. Females receive two alleles for these genes, but males only receive one. If the parent is a male, the genotype is automatically known. A colorblind male has to be b, since he only has one allele and colorblindness is recessive. A normal male must then be B Females can be heterozygous for the colorblindness trait - they are called carriers. A female can be BB normal, Bb - carrier, or bb - colorblind The following shows a cross between a normal man and a woman who is a carrier colorblindess test a Y-linked trait Chromosomal Disorders Nondisjunction: chromosomes fail to separate properly during meiosis (formation of gametes) Chromosomal Disorders Down Syndrome- extra chromosome on #21 (results in total of 47 chrom) Turner’s- only 1 sex chromosome and alters female development Klinefelter’s- males with an extra X chromosome. Alters testosterone development. May cause infertility Down Syndrome- Extra chromosome on #21. Total of 47 chromosomes Turner’s Only 1 X Klinefelter”s Extra X Karyotype A karyotype is an image of whole chromosomes stained during metaphase. Show identical genes on homologous chromosomes. Pairs are arranged by decreasing size. Down Syndrome Karyotype Klinefelter’s Karyotype Turner’s Karyotype Karyotype activity You and a partner will assemble the Karyotype of your human in the envelope. 1. match up chromosomes 2. arrange by size 3. label # 1-23 pairs and each individual chromosome 4. match up with known karyotypes and identify your human 5. If they have a disorder list symptoms. Pedigree A pedigree is a family history study. If a trait is expressed the shape is darkened If not shaded trait not expressed Half shaded carrier but not expressed Pedigree—graphic representation of genetic inheritance. - Male= square - Female= circle - Shaded= has the disorder - Half shaded= carrier of disorder. Activity Pick one of the case studies or page 300