* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plate Tectonics Class Notes
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Oceanic trench wikipedia , lookup
Abyssal plain wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Geological history of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Supercontinent wikipedia , lookup
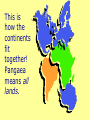
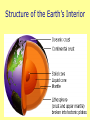
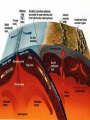
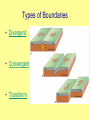
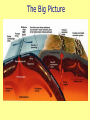
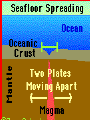
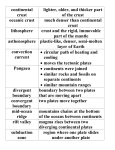
Plate Tectonics The Earth’s Crust in Motion… Essential Question: • What is the theory of continental drift? Continental Drift… Most scientists believe that millions of years ago, Earth was very different from the way it is today. There was only one super continent. Over time, the continent broke apart, becoming today’s seven continents. The Continental Drift Theory In 1910 Alfred Wegener begins to wonder… What’s the relationship Between the continents? Perhaps all these pieces used to be connected. Continental drift=slow movement over Earth’s surface 300 million years ago… What is the theory of Continental Drift? Alfred Wegener first proposed the theory of continental drift. Continental Drift is a theory that states that the continents were once a single landmass that broke apart and moved into the positions they are today. Wegener named this supercontinent Pangaea. Supercontinent Pangaea – all lands •Reptiles and insects •Tropical forests -coal deposits Tens of Millions of years! Pangaea Puzzle… • Can you and your team mate create the super-continent Pangaea? This is how the continents fit together! Pangaea means all lands. Evidence to Support the Theory • Fossils of tropical plants found on an island in the Arctic Ocean are evidence for the theory of continental drift. • Pieces of the continents fit together like pieces of a puzzle. Evidence to Support the Theory • Wegner studied fossils of the Lystrosaurus an animal that lived in fresh water. • He found fossils of this animal on both the continents of South America and Africa. • Mountain Ranges of different continents seem to match. A mountain range on the Eastern United States and Canada match mountain ranges in Greenland and Europe. Evidence to Support the Theory • Diamonds found in African & South American coal mines Are the same size and clarity. Theory Rejected!! Wegener’s theory was rejected by scientists during his day, because he could not explain what force pushes or pulls continents apart. • 1. The idea that continents move slowly on Earth’s surface is known as ____________ _____________. • 2. _______ _______ was the scientist who put forth the idea of continental drift. • 3. Wegener’s evidence for continental drift included all of the following EXCEPT: • a. matching fossils. • b. matching mountain ranges. • c. matching river beds. • d. matching coal beds. QOTD 1-19-12 Fossils of Lystrosaurus, an early landdwelling reptile, have been found in Antarctica, India, and South Africa. The distribution of these fossils suggests that these areas were once • • • • a. b. c. d. made of the same chemical elements. covered by oceanic crust. home to a wide variety of organisms. connected to one another. • WAC ATTACK… Explain how Pangaea supports the theory of continental drift. Question of the Day 3-25-14 • 1. The crust and solid upper mantle is called the _____________. • 2. It moves on top of a thick syrupy layer called the ______________. • 3. Why did the lithospheric plates break apart and move? • 4. If a fossil of a tropical plant was found on an island in the Arctic, what would this reveal about its past? Essential Question: • What is plate tectonic theory? Structure of the Earth’s Interior Now, scientists believe that… The upper mantle and crust make up the lithosphere. The asthenosphere is a soft layer that can bend like plastic. The lithospheric Plates float and move On top of the asthenosphere. How does it work? Plates – pieces of the lithosphere Plates fit closely together along cracks called Plate Boundaries Convection Currents movement How does it work? How is heat is transferred in the mantle? Is it by radiation, conduction, or convection. Convection is heat transfer by the movement of heated liquid. Lithospheric Plates The lithosphere is broken into separate sections called plates. The geological theory that states that pieces of Earth’s lithosphere are in constant, slow motion, driven by convection currents in the mantle is plate tectonics. Earth’s Puzzle • What plate do we live on? • What plates do we border? • USGS Earth’s Plates • How far do we move every year? Review Time!! 1. Earth’s crust is divided into sections called ____________. Review Time!! 2. How many major sections is Earth’s crust divided into? Review Time!! 3. The place where plates meet is called a… Review Time!! 4. Most volcanoes and earthquakes are located at the ………..…between two tectonic plates Essential Question: • How do lithospheric plates move? • How do the different types of movement create different landforms? Types of Boundaries • Divergent • Convergent • Transform Divergent Boundaries The place where two plates move apart or diverge is called a divergent boundary. When a divergent boundary develops on land, two of Earth’s plates slide apart. A deep valley called a rift valley forms along the divergent boundary. Convergent Boundaries A convergent boundary is where two plates come together, or converge. The result of the plates hitting together is called a collision. Transform Boundaries A transform boundary is a place where two plates slip past each other, moving in opposite directions. These transform boundaries cause EARTHQUAKES! Plate Movements-Icing on the Cake Activity A Divergent B Convergent C Transform •plates are moving apart •plates are coming together •plates are slipping past each other •crust is returning to the mantle •crust is not created or destroyed •new crust is created •Magma is coming to the surface A Divergent Continental crust rift valley B Convergent 2 continental plates mountain range C Transform Plates move against each other Stress builds up Oceanic crust midocean ridge 2 oceanic plates or oceanic + continental subduction Stress is released earthquake The Big Picture Let’s Play Mountains Plates move apart Volcanoes Changes the shape of the ocean floor Causes Earthquakes Plates collide Two plates slide past one another One plate slides under another When two plates converge ________ magma may work its way through the crust. A ____________ is volcano formed when magma breaks through to the surface. New _______ land is formed when the lava cools and hardens. An _______________ earthquake occurs when plates move and the crust slips or breaks past one another. Essential Question: • What is sea floor spreading? Sea-Floor Spreading The mid-ocean ridge is the longest chain of mountains on the ocean floor. Most of the mountains in the midocean ridge lie hidden under hundreds of meters of water. Hess proposed that the ocean floors move, carrying the continents along with them. The movement begins at the midocean ridge. At the mid-ocean ridge, molten material rises from the mantle and erupts. This is called Sea Floor Spreading. Sea Floor Spreading The process that continually adds new material to the ocean floor is called sea-floor spreading. The ocean floor plunges into deep underwater canyons called deepocean trenches. Subduction is the process by which the ocean floor sinks beneath a deepocean trench and back into the mantle. Ticket Out: • 1. Most volcanoes and earthquakes are located where two ___________ ________ meet. • 2. The upper mantle and crust make up the _______________. 3. The ____________is a soft layer that allows the lithosphere to float on top of it. Key Terms for Map convergent boundary divergent boundary transform boundary subduction rift valley mid-ocean ridge continental crust oceanic crust mountain range earthquake