* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File - Earth Science With Mrs. Locke
Survey
Document related concepts
History of climate change science wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
History of paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Supercontinent wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
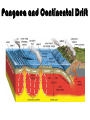
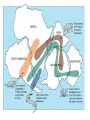
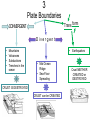
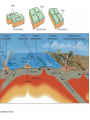
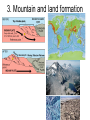
Pangaea and Continental Drift The Theory of Continental Drift • A hypothesis that the continents were once joined in a single, giant landmass called Pangaea- but they have since drifted apart and continue to drift (move). • First purposed by Alfred Wegner http://www.rocksinmyheadtoo.com/Pangea.jpg 3 PIECES OF EVIDENCE FOSSILS PUZZLE PIECES The SHAPE of the continents look like puzzle pieces that fit together The same or similar fossils are found on the edges of cont. that look like they fit together CLIMATE CHANGE • Warm climate plant fossils found in the Antarctic • large glacial scratches left in rocks Why do the continents move? The Theory of Plate Tectonics They move because the Earth’s lithosphere is broken into pieces called tectonic plates. • The plates move very slowly and don’t last forever How they moveHeat is transferred in the asthenosphere making Convection currents. magma closer to core is heated- becomes less dense- rises to crust- cools & gets more dense again- sinks back to lower mantle- creating giant looping patterns • Plates are dragged with the moving Asthenosphere. 3 Plate Boundaries Trans form CONVERGENT Divergent • • • • Mountains Volcanoes Subductions Trenches in the ocean • Earthquakes • Mid Ocean Ridge • Sea-Floor Spreading CRUST IS DESTROYED CRUST can be CREATED Crust NEITHER CREATED or DESTROYED Results of Plate Tectonics 1. Earthquakes 2. Volcanoes 3. Mountain and land formation 4. Sea-floor spreading • Oceans grow and sink 5. Continental Drift