* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 2 Section 2
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Geomorphology wikipedia , lookup
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Plate tectonics wikipedia , lookup
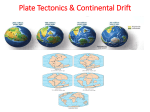
Forces of Change Earth is composed of three layers- the core, the mantle, and the crust. Very center is the core. - super hot but solid inner core. - 4000 miles under the surface. -Surrounding the inner core is a Liquid OUTER CORE. 85,000F -Next to outer core is a thick Layer of hot dense rock called the MANTLE. -Crust = rocky shell from 2miles through 75 miles thick. Continental Drift- Theory that the continents were once joined and then slowly drifted apart. Magma- Molten rock Subduction- Process by which mountains can form as sea plates dive beneath continental plates. Accretion- Slow process in which a sea plate slides under a continental plate, creating debris that can cause continents to grow outward. Spreading- Process by which new land is created when sea plates pull apart and magma wells up between the plates. Fault- A crack or break in the earth’s crust. Weathering- process that breaks down rocks on the earth’s surface into smaller pieces. Erosion- wearing away of the earth’s surface by wind, glaciers, and moving water. Loess- Fertile, yellow-grey soil deposited by wind. Glaciers- large bodies of ice that slowly move across the earth’s surface. Moraines- Piles of rocky debris left by melting glaciers.