* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Practice test answers
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
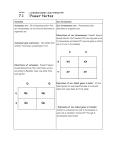
Genes and Chromsomes 1 of 8 http://www.cwcboe.org/cms/lib04/NJ01001185/Centricity/Domain/143/... Name: practice test Score: 0 / 19 (0%) [13 subjective questions not graded] Genes and Chromsomes Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Linked genes a. are never separated. b. assort independently. c. are on the same chromosome. d. are always recessive. ANSWER: C 2. What is the probability that a human sperm cell will carry an X chromosome? a. 0 percent c. 50 percent b. 25 percent d. 100 percent ANSWER: C 3. Colorblindness is more common in males than in females because a. fathers pass the allele for colorblindness to their sons only. b. the allele for colorblindness is located on the Y chromosome. c. the allele for colorblindness is recessive and located on the X chromosome. d. males who are colorblind have two copies of the allele for colorblindness. ANSWER: C 4. Because the X chromosome contains genes that are vital for normal development, no baby has been born a. with one X chromosome. c. without an X chromosome. b. with three X chromosomes. d. with four X chromosomes. ANSWER: C 5. Which of the following combinations of sex chromosomes represents a female? a. XY c. XXXY b. XXY d. XX ANSWER: D 6. In humans, a male has a. one X chromosome only. b. two X chromosomes. 3/26/2015 2:55 PM Genes and Chromsomes 2 of 8 http://www.cwcboe.org/cms/lib04/NJ01001185/Centricity/Domain/143/... c. one X chromosome and one Y chromosome. d. two Y chromosomes. ANSWER: C 7. Human females produce egg cells that have a. one X chromosome. c. one X or one Y chromosome. b. two X chromosomes. d. one X and one Y chromosome. ANSWER: A 8. Sex-linked genes are located on a. the autosomes. b. the X chromosome only. c. the Y chromosome only. d. both the X chromosome and Y chromosome. ANSWER: D 9. Each gene occupies a specific place on a chromosome. This is referred to as the genes a. genetic map c. linkage b. locus d. neighborhood. ANSWER: B 10. When genes are located on the same chromosome and when they tend to be inherited together they are considered ___________. a. a couple c. independent b. loci d. linked ANSWER: D 11. Morgan found that even when genes are linked there is a certain amount of recombination. This is due to ______________ a. the law of independent assortment c. synapsis b. the law of segregation d. crossing over ANSWER: D 12. A human sperm cell containing 24 chromosomes fertilizes a normal egg cell. There is now an extra copy of chromosome number 21. The resulting zygote is now ______ for chromosome number 21. a. trisomic c. polyploid b. monosomic d. diploid ANSWER: A 3/26/2015 2:55 PM Genes and Chromsomes 3 of 8 http://www.cwcboe.org/cms/lib04/NJ01001185/Centricity/Domain/143/... 13. The genotype of a white-eyed male fruit fly is written. (Red eyes are dominant) a. XYr c. XrY b. XRYr d. YrYr ANSWER: C 14. For most organisms the sex of their offspring is determined by the a. male c. neither b. female ANSWER: A Matching a. Duplication of part of a chromsome d. Base pair deletion b. Nondisjunction e. Inversion of part of a chromsome c. Deletion of a part of a chromosomes 15. Addition or loss of a nucleotide pair ANSWER: D 16. Homologous chromsomes are not seperated during meiosis ANSWER: B 17. loss of a piece of a chromsome ANSWER: C 18. A piece of a chromsome reattaches to a sister chromotid or a homologous chromosome ANSWER: A 19. A piece of a chromsome reattaches to the original chromosome but in the reverse orientation ANSWER: E 20. Part II 1. (Complete dominance) Cross a Heterozygous Tall, heterozygous wrinkled-seed pea plant with a heterozygous tall, heterozygous wrinkled-seed pea plant. Tall is dominant to short and wrinkled is dominant to smooth. a. Parental Genotypes _____________________ 3/26/2015 2:55 PM Genes and Chromsomes 4 of 8 http://www.cwcboe.org/cms/lib04/NJ01001185/Centricity/Domain/143/... b. Punnett Square c. Phenotypic ratio _______________________ 2. (Complete dominance) Cross a person who is heterozygous for Huntington’s disease with a person who is normal. Huntington’s disease is dominant, normal is recessive. a. parental genotypes ______________________ b. punnett square c. Genotypic ratio ______________________ d. Phenotypic ratio _____________________ 3. (Incomplete dominance) Cross a pink snapdragon with a pink snapdragon. Red is incompletely dominant to white. a. parental genotypes ____________________ b. punnett square c. Phenotypic ratio ________________________ d. Genotypic ratio ________________________ 4. (Codominance) Cross a person who has sickle cell anemia with a person who is heterozygous for sickle cell anemia. Sickle cell hemoglobin and normal hemoglobin are both dominant. a. Parental Genotypes __________________________ b. Punnett Square c. Genotypic Ratio ____________________________ d. Phenotypic ratio ____________________________ 5. (Sex-linked) Cross a Color blind male with a heterozygous normal female. Normal vision is dominant. Color blind vision is recessive. a. Parental Genotypes _____________________________ b. Punnett square d. Phenotypic Ratio for the males _____________________________ 3/26/2015 2:55 PM Genes and Chromsomes 5 of 8 http://www.cwcboe.org/cms/lib04/NJ01001185/Centricity/Domain/143/... e. Phenotypic ratio for the females _____________________________ 6. (Complete dominance / Codominance) Cross a person who is heterozygous for type A blood with a person who has type O blood. Type A blood and Type B blood are both dominant. Type O blood is recessive. a. Parental Genotypes _____________________ b. Punnett Square c. Genotypic Ratio _____________________ d. Phenotypic Ratio _____________________ RESPONSE: ANSWER: This is the same worksheet we completed in class. Refer to the worksheet for the answers Short Answer 21. Color blindness is a recessive sex-linked genetic disorder. Cross a colorblind male with a heterozygous (carrier) female. a. parental genotypes b. What is the phenotypic ratio for all of the offspring? c. What percentage of the male offspring will be color blind? d. What percentage of the female offspring will be colorblind? e. punnett square RESPONSE: ANSWER: a. XbY, XBXb b. 2:2 normal:colorblind c. 50% d. 50% 22. People who have the genetic disorder hemophilia are missing a protein for normal blood clotting. This is a recessive sex-linked genetic disorder. A normal male is crossed with a normal female. 50% of the male offspring have hemophilia. a. What are the parental genotypes? 3/26/2015 2:55 PM Genes and Chromsomes 6 of 8 http://www.cwcboe.org/cms/lib04/NJ01001185/Centricity/Domain/143/... b. What is the phenotypic ratio for all of the offspring? c. What percentage of the females has hemophilia? d. Punnett square RESPONSE: ANSWER: a. XHXh, XHY b. 3:1, normal:hemophilia c. 0% Other USING SCIENCE SKILLS Figure 14–2 23. Applying Concepts In the human karyotype in Figure 14-2, what are the chromosomes in each numbered group called? RESPONSE: ANSWER: The chromosomes in each group are called homologous chromosomes. 24. Classifying Which chromosomes in Figure 14-2 are autosomes? RESPONSE: ANSWER: The chromosomes in groups 1 through 22 are autosomes. 25. Interpreting Graphics In the human karyotype in Figure 14-2, how many chromosomes are shown? RESPONSE: ANSWER: Forty-seven chromosomes are shown. 26. Drawing Conclusions Identify the sex chromosomes in Figure 14-2. Does the karyotype show the normal number of sex chromosomes? Explain. 3/26/2015 2:55 PM Genes and Chromsomes 7 of 8 http://www.cwcboe.org/cms/lib04/NJ01001185/Centricity/Domain/143/... RESPONSE: ANSWER: The karyotype shows two X chromosomes and one Y chromosome, which is not normal. The normal number of sex chromosomes is two. 27. Inferring Is the individual represented by the karyotype in Figure 14-2 male or female? Explain. RESPONSE: ANSWER: The individual is male. In the presence of the Y chromosome, the human embryo will also develop as a male, no matter how many X chromosomes are present. USING SCIENCE SKILLS To determine a person’s blood type, a drop of anti-A serum and a drop of anti-B serum are placed at either end of a microscope slide. Then, a drop of the person’s blood is added to each drop of serum. Clumping in anti-A serum or anti-B serum indicates the presence of antigen A or antigen B in the blood, respectively. Figure 14–3 28. Interpreting Graphics Which numbered slide in Figure 14–3 shows type B blood? RESPONSE: ANSWER: Slide 2 shows type B blood. 29. Inferring In Figure 14–3, which slide shows the blood of a person who can safely receive any type of blood in a transfusion? Identify the person’s blood type. RESPONSE: ANSWER: Slide 3 shows the blood of a person who can safely receive any type of blood. The person’s blood type is AB. 3/26/2015 2:55 PM Genes and Chromsomes 8 of 8 http://www.cwcboe.org/cms/lib04/NJ01001185/Centricity/Domain/143/... 30. Interpreting Graphics Which slide in Figure 14–3 shows blood that contains no antigens? How do you know? RESPONSE: ANSWER: The blood on slide 4 contains no antigens. There is no clumping in either drop of blood. 31. Inferring In Figure 14–3, what is the genotype or genotypes of the person whose blood is shown in slide 1? RESPONSE: ANSWER: The person’s genotype is IAIA or IAi. 32. Inferring Anti-sera are extracted from blood. Based on what is shown in Figure 14–3, what type of blood does not contain anti-A or anti-B serum? Explain why. RESPONSE: ANSWER: Type AB blood does not contain anti-A or anti-B serum because it contains both antigen A and antigen B. If it did contain either serum, the serum would cause the blood to clump in the person’s body. 3/26/2015 2:55 PM