* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PerfectTenses - Ector County ISD.
Modern Hebrew grammar wikipedia , lookup
Modern Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Esperanto grammar wikipedia , lookup
Lexical semantics wikipedia , lookup
Sanskrit grammar wikipedia , lookup
French grammar wikipedia , lookup
Navajo grammar wikipedia , lookup
Georgian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Germanic weak verb wikipedia , lookup
Scottish Gaelic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Old Irish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Old English grammar wikipedia , lookup
Old Norse morphology wikipedia , lookup
Udmurt grammar wikipedia , lookup
Macedonian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ukrainian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Polish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Hungarian verbs wikipedia , lookup
Portuguese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Pipil grammar wikipedia , lookup
Italian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Sotho verbs wikipedia , lookup
Tense–aspect–mood wikipedia , lookup
Germanic strong verb wikipedia , lookup
Swedish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Lithuanian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Kannada grammar wikipedia , lookup
Chichewa tenses wikipedia , lookup
Yiddish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Latin conjugation wikipedia , lookup
Latin syntax wikipedia , lookup
Serbo-Croatian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Spanish grammar wikipedia , lookup
English clause syntax wikipedia , lookup
Danish grammar wikipedia , lookup
English verbs wikipedia , lookup
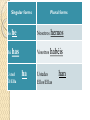
Perfect Tenses Present Perfect Pluperfect (Past Perfect) INTRODUCTION The perfect tenses [tiempos perfectos] are compound tenses [tiempos compuestos]; that is, they are made up of two parts, a helping verb [verbo auxiliar] and a past participle [participio pasado]. PRESENT PERFECT The present perfect tense in Spanish is formed with: • The present tense of the helping verb haber, plus • The past participle of the main verb. Example:Yo he terminado mi proyecto. Singular forms Plural forms Yo he Nosotros hemos Tú has Vosotros habéis Usted Él/Ella ha Ustedes Ellos/Ellas han The past participles are normally formed by dropping the verb ending and adding: -ado for –ar verb, hablar hablado -ido for –er and –ir verbs, comer comido and vivir vivido. Variations -er and –ir verbs whose stems end in a vowel need a written accent mark: leer leído ; oír oído. (copy the irregular past participles from p. 46 of your book.) Note: Compound words based on these roots typically show the same irregularities: • Componer Compuesto (repaired) • Follow the same pattern to fill in the rest of the past participles. Uses: The present perfect may be used to indicate an action or state that has been completed. It is used in almost the same way as we use it in English: I have seen that movie. He visto esa película. Exceptions: • To indicate an action that began in the past and is still going on, use the present tense: Hace 4 años que vivo en Texas. I have been living (and am still living) in Texas for 4 years. Exceptions: • To express the idea of “to have just done something,” use the present tense of acabar de plus the infinitive verb: Acabo de terminar mi proyecto. I have just finished my project. THE PAST PERFECT – el pluscuamperfecto The past perfect tense views an action or state as having occurred – and been completed – at a time before another past action, state, or time. It is used in almost exactly the same way as we use it in English. The wedding started at 3. By then, all the guests had arrived. La boda empezó a las 3. Para entonces, todos los invitados habían llegado. THE PAST PERFECT – el pluscuamperfecto To form the Past Perfect, use the imperfect of haber plus the past participle: Yo había hablado. Tú habías hablado. Ud./él/ella había hablado. Nosotros habíamos hablado. Vosotros habíais hablado. Uds./ellos/ellas habían hablado.